
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2020, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (4): 461-468.DOI: 10.15541/jim20190176
Special Issue: 生物材料论文精选(2020)
• RESEARCH PAPER • Previous Articles Next Articles
TANG Shuai,ZHANG Wentai,QIAN Junyu,XIAN Peng,MO Xiaoshan,HUANG Nan,WAN Guojiang( )
)
Received:2019-04-25
Revised:2019-06-07
Published:2020-04-20
Online:2020-04-10
Supported by:CLC Number:
TANG Shuai,ZHANG Wentai,QIAN Junyu,XIAN Peng,MO Xiaoshan,HUANG Nan,WAN Guojiang. Long-term in Vitro Corrosion Behavior of Zinc in Ringer’s Solution[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(4): 461-468.
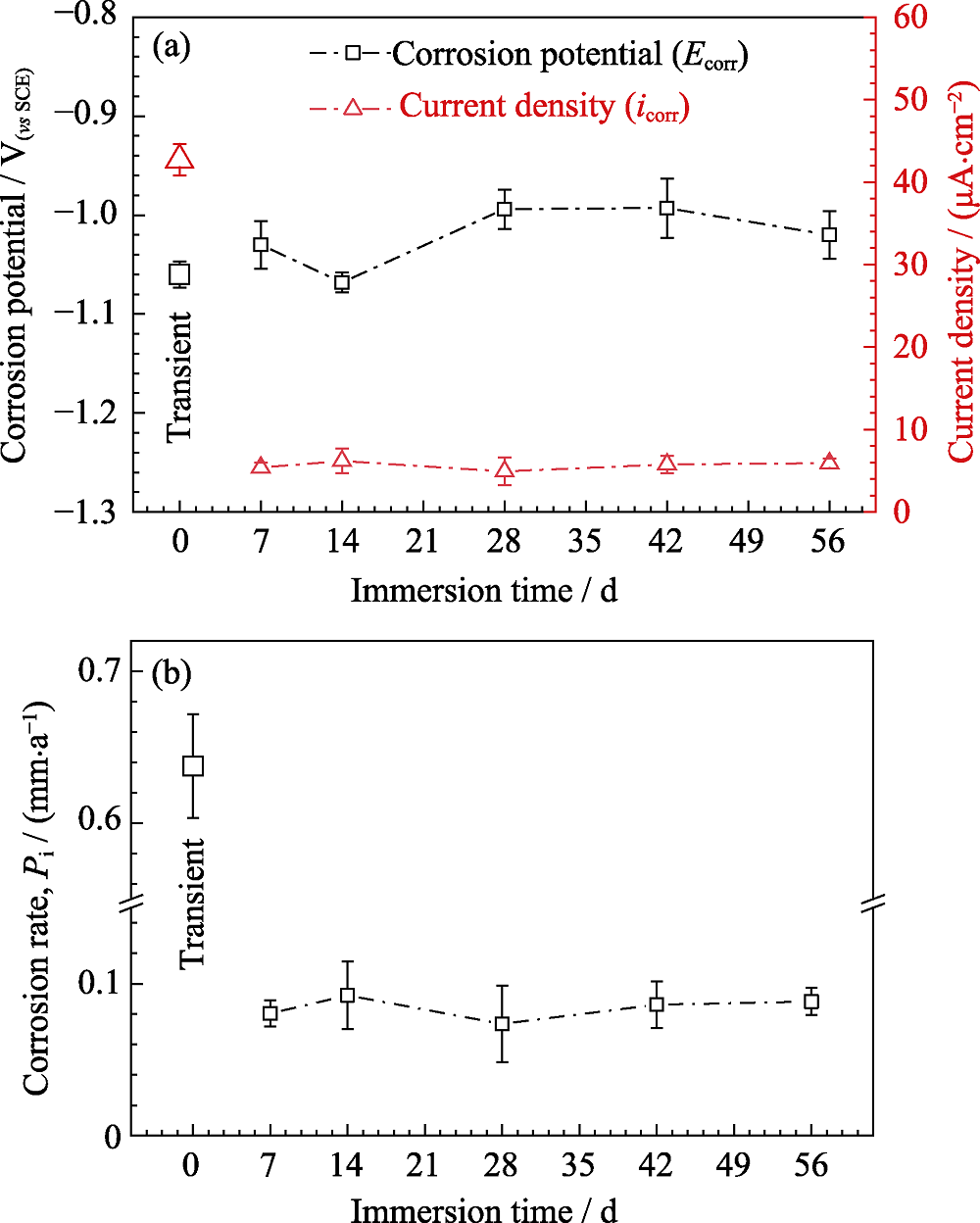
Fig. 2 Parameters of corrosion potential and corrosion current density obtained from PDP curves (a), and corrosion rate Pi obtained from current density (b)
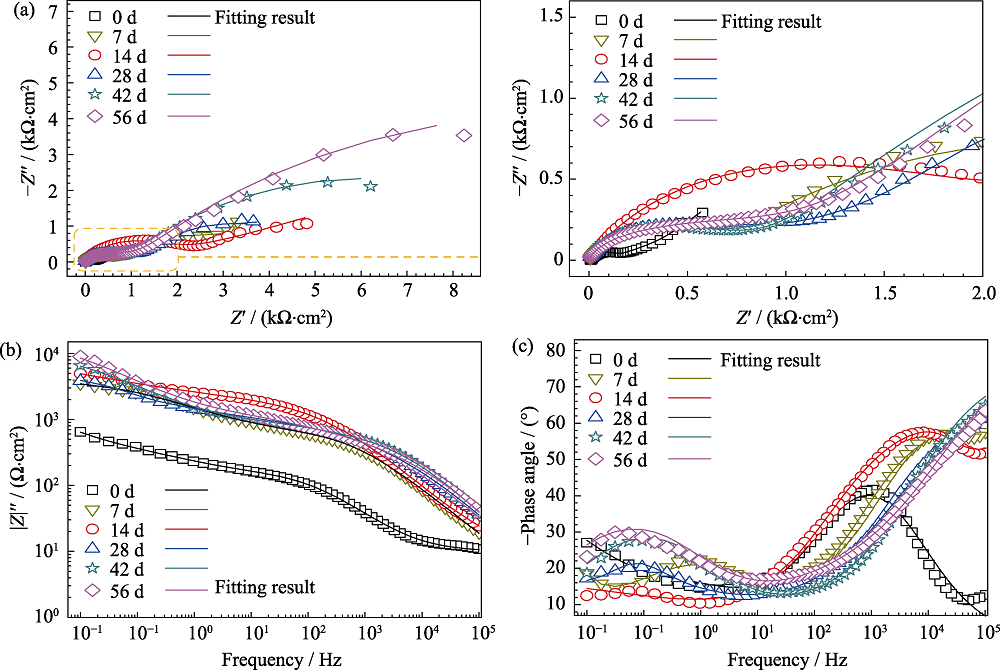
Fig. 3 Nyquist plots measured by Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) (a), bode plots of |Z| vs. frequency (b) and bode plots of phase angle vs. frequency (c) of Zn immersed in Ringer’s solution at (37±0.5) ℃ for 7, 14, 28, 42 and 56 d
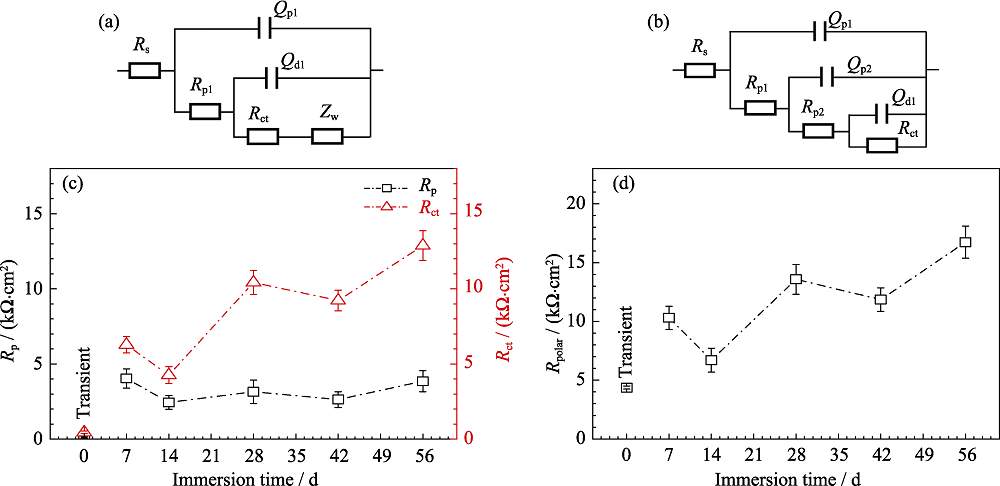
Fig. 4 EIS data fitted with Equivalent electrical circuit (EEC) for 0 d (a) and EEC for 7 to 56 d (b), interfacial charge transfer resistance Rct and the corrosion products resistance Rp obtained from fitted results of the EIS spectra (c), and polarization resistance Rpolar calculated from EIS components as a function of time (d)
| Samples | Rs/ (Ω∙cm2) | Qp1/(×10-6, sn*∙Ω-1∙cm-2) | n1 | Rp1/ (Ω∙cm2) | Qp2/(×10-6, sn*∙Ω-1∙cm-2) | n2 | Rp2/ (Ω∙cm2) | Qdl/(×10-6, sn*∙Ω-1∙cm-2) | n3 | Rct/(×103, Ω∙cm2) | Zw/(×10-3, s1/2∙Ω-1∙cm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 d | 21.09 | 35.00 | 0.76 | 105 | — | — | — | 2376 | 0.80 | 0.45 | 3.81 |
| 7 d | 22.48 | 5.05 | 0.71 | 576 | 315.0 | 0.49 | 3458 | 155 | 0.61 | 6.28 | — |
| 14 d | 16.21 | 1.24 | 0.65 | 175 | 13.7 | 0.74 | 2266 | 798 | 0.56 | 4.26 | — |
| 28 d | 21.28 | 16.80 | 0.72 | 260 | 344.0 | 0.22 | 2893 | 322 | 0.81 | 10.42 | — |
| 42 d | 22.91 | 0.95 | 0.74 | 430 | 232.0 | 0.49 | 2200 | 243 | 0.82 | 9.22 | — |
| 56 d | 23.56 | 2.71 | 0.70 | 511 | 121.0 | 0.50 | 3342 | 290 | 0.57 | 12.88 | — |
Table 1 The evolution of fitted results of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy of Zn in Ringer’s solution at (37±0.5) ℃
| Samples | Rs/ (Ω∙cm2) | Qp1/(×10-6, sn*∙Ω-1∙cm-2) | n1 | Rp1/ (Ω∙cm2) | Qp2/(×10-6, sn*∙Ω-1∙cm-2) | n2 | Rp2/ (Ω∙cm2) | Qdl/(×10-6, sn*∙Ω-1∙cm-2) | n3 | Rct/(×103, Ω∙cm2) | Zw/(×10-3, s1/2∙Ω-1∙cm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 d | 21.09 | 35.00 | 0.76 | 105 | — | — | — | 2376 | 0.80 | 0.45 | 3.81 |
| 7 d | 22.48 | 5.05 | 0.71 | 576 | 315.0 | 0.49 | 3458 | 155 | 0.61 | 6.28 | — |
| 14 d | 16.21 | 1.24 | 0.65 | 175 | 13.7 | 0.74 | 2266 | 798 | 0.56 | 4.26 | — |
| 28 d | 21.28 | 16.80 | 0.72 | 260 | 344.0 | 0.22 | 2893 | 322 | 0.81 | 10.42 | — |
| 42 d | 22.91 | 0.95 | 0.74 | 430 | 232.0 | 0.49 | 2200 | 243 | 0.82 | 9.22 | — |
| 56 d | 23.56 | 2.71 | 0.70 | 511 | 121.0 | 0.50 | 3342 | 290 | 0.57 | 12.88 | — |
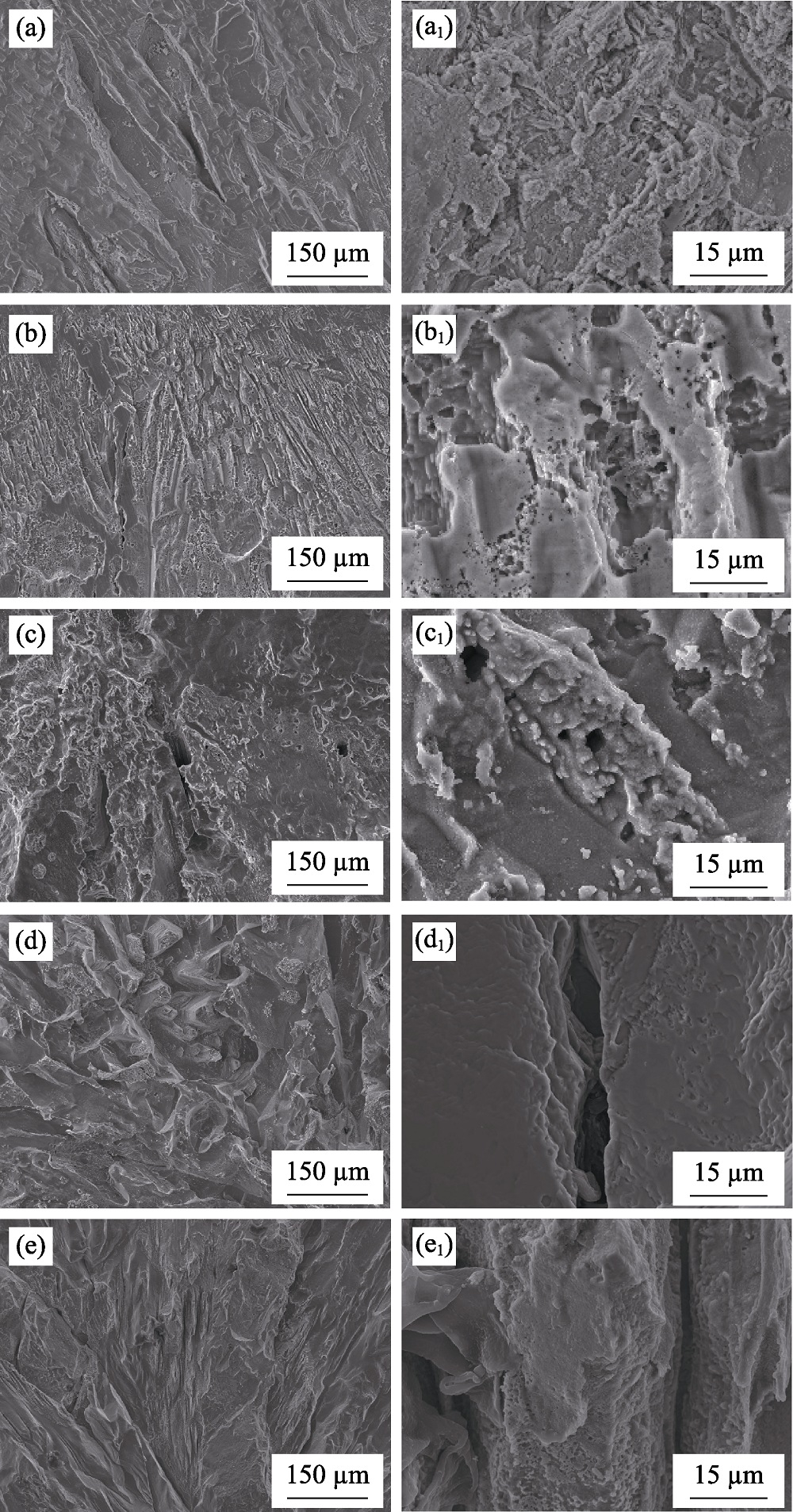
Fig. 9 Surface morphology of Zn immersed in Ringer’s solution at (37±0.5) ℃ for 7 (a), 14 (b), 28, (c) 42 (d), and 56 d (e) after removal of corrosion products
| [1] | BOWEN PATRICK K, DRELICH JAROSLAW, GOLDMAN JEREMY . Zinc exhibits ideal physiological corrosion behavior for bioabsorbable stents. Advanced Materials, 2013,25(18):2577-2582. |
| [2] | BOWEN PATRICK K, SHEARIER EMILY R, ZHAO SHAN , et al. Biodegradable metals for cardiovascular stents: from clinical concerns to recent Zn-Alloys. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2016,5(10):1121-1140. |
| [3] | MOSTAED EHSAN, SIKORA-JASINSKA MALGORZATA, DRELICH JAROSLAW W , et al. Zinc-based alloys for degradable vascular stent applications. Acta Biomaterialia, 2018,71:1-23. |
| [4] | BIN BUM-HO, BHIN JINHYUK, TAKAISHI MIKIRO , et al. Requirement of zinc transporter ZIP10 for epidermal development: implication of the ZIP10-p63 axis in epithelial homeostasis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2017,114(46):12243-12248. |
| [5] | ZHU DONG-HUI, SU YING-CHAO, YOUNG MARCUS L , et al. Biological responses and mechanisms of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to Zn and Mg biomaterials. ACS Applied materials & Interfaces, 2017,9(33):27453-27461. |
| [6] | HAASE HAJO, RINK LOTHAR . Multiple impacts of zinc on immune function. Metallomics, 2014,6(7):1175-1180. |
| [7] | LIN SONG, WANG QI-LONG, YAN XIN-HAO , et al. Mechanical properties, degradation behaviors and biocompatibility evaluation of a biodegradable Zn-Mg-Cu alloy for cardiovascular implants. Materials Letters, 2019,234:294-297. |
| [8] | KAFRI ALON, OVADIA SHIRA, GOLDMAN JEREMY , et al. The suitability of Zn-1.3% Fe alloy as a biodegradable implant material. Metals, 2018,8(3):153. |
| [9] | SHI ZHANG-ZHI, YU JING, LIU XUE-FENG , et al. Effects of Ag, Cu or Ca addition on microstructure and comprehensive properties of biodegradable Zn-0.8 Mn alloy. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 2019,99:969-978. |
| [10] | ZHENG YU-FENG, WU YUAN-HAO . Revolutionizing metallic biomaterials. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2017,53(3):257-297. |
| [11] | CHEN YING-QI, ZHANG WEN-TAI, MAITZ MANFRED F , et al. Comparative corrosion behavior of Zn with Fe and Mg in the course of immersion degradation in phosphate buffered saline. Corrosion Science, 2016,111:541-555. |
| [12] | TÖRNE KARIN, LARSSON MARIANN, NORLIN ANNA , et al. Degradation of zinc in saline solutions, plasma, and whole blood. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials, 2016,104(6):1141-1151. |
| [13] | ZHAO LI-CHEN, ZHANG ZHE, SONG YU-TING , et al. Mechanical properties and in vitro biodegradation of newly developed porous Zn scaffolds for biomedical applications. Materials & Design, 2016,108:136-144. |
| [14] | LIU LI-JUN, MENG YAO, DONG CHAO-FANG , et al. Initial formation of corrosion products on pure zinc in simulated body fluid. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2018,34(12):2271-2282. |
| [15] | LIU XIAO, YANG HONG-TAO, LIU YANG , et al. Comparative studies on degradation behavior of pure zinc in various simulated body fluids. JOM, 2019,71(4):1414-1425. |
| [16] | STANDARD ASTM . G102-89, Standard Practice for Calculation of Corrosion Rates and Related Information from Electrochemical Measurements. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, 2015. |
| [17] | STANDARD ASTM . G31-72. Standard practice for laboratory immersion corrosion testing of metals. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, 2004. |
| [18] | SHI ZHI-MING, LIU MING, ATRENS ANDREJ . Measurement of the corrosion rate of magnesium alloys using Tafel extrapolation. Corrosion Science, 2010,52(2):579-588. |
| [19] | HUANG JUN . Diffusion impedance of electroactive materials, electrolytic solutions and porous electrodes: Warburg impedance and beyond. Electrochimica Acta, 2018,281:170-188. |
| [20] | WU J, ZHANG SD, SUN WH , et al. Influence of oxidation related structural defects on localized corrosion in HVAF-sprayed Fe-based metallic coatings. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2018,335:205-218. |
| [21] | SHI ZHI-MING, CAO FU-YONG, SONG GUANG-LING , et al. Low apparent valence of Mg during corrosion. Corrosion Science, 2014,88:434-443. |
| [22] | SIMõES AM, BASTOS AC, FERREIRA MG , et al. Use of SVET and SECM to study the galvanic corrosion of an iron-zinc cell. Corrosion Science, 2007,49(2):726-739. |
| [23] | BLANDA GIUSEPPE, BRUCATO VALERIO, PAVIA FRANCESCO CARFì , et al. Galvanic deposition and characterization of brushite/ hydroxyapatite coatings on 316L stainless steel. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 2016,64:93-101. |
| [1] | LI Ziyi, ZHANG Jiajia, ZOU Xiaoqin, ZUO Jiayu, LI Jun, LIU Yingshu, PUI David Youhong. Synthesis and Gas Separation of Chabazite Zeolite Membranes [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(6): 579-591. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||