无机材料学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (1): 65-72.DOI: 10.15541/jim20190073 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20190073
所属专题: MAX相和MXene材料; 优秀作者论文集锦; 2019~2020年度优秀作者作品欣赏:环境材料; MXene材料专辑(2020~2021)
收稿日期:2019-02-15
修回日期:2019-03-20
出版日期:2020-01-20
网络出版日期:2019-05-29
作者简介:宋 环(1994-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail:songhuan@ihep.ac.cn
基金资助:
SONG Huan1,WANG Lin2,WANG Hong-Qing1( ),SHI Wei-Qun2(
),SHI Wei-Qun2( )
)
Received:2019-02-15
Revised:2019-03-20
Published:2020-01-20
Online:2019-05-29
About author:SONG Huan(1994-), male, Master candidate. E-mail:songhuan@ihep.ac.cn
Supported by:摘要:
对无机二维过渡金属碳化物(MXene)进行碱化处理, 成功制备了碱化碳化钛(Na-Ti3C2Tx), 用于对Eu(III)的快速去除。采用固液比、溶液pH和离子强度、动力学、等温线、热力学等批次实验方法对Na-Ti3C2Tx去除Eu(III)的行为进行了系统研究。实验结果表明: 整个吸附过程受溶液pH和离子强度影响较大, 吸附过程在很短的时间(5 min)就达到了吸附平衡, 该过程更符合Langmuir吸附模型, 在298 K时最大吸附容量可达54.05 mg/g。热力学结果表明Na-Ti3C2Tx对Eu(III)的吸附为自发吸热反应过程。使用能量色散X射线光谱(EDS)、粉末XRD和扩展X射线吸收精细结构光谱学(EXAFS)对其吸附机理进行了分析, 结果表明酸性条件下主要的吸附机理是Eu 3+离子与MXene层间的Na +离子发生了离子交换, 吸附后的Eu(III)主要以外层配位络合物的形式存在, 而近中性条件下则出现了内配位络合作用。鉴于Na-Ti3C2Tx具有较低的合成成本与优异的吸附性能, 该材料有望应用于放射性废水中三价次锕系核素与镧系核素的快速高效清除。
中图分类号:
宋环, 王琳, 王宏青, 石伟群. 碱化Ti3C2Tx MXene对Eu(III)高效去除与机理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(1): 65-72.
SONG Huan, WANG Lin, WANG Hong-Qing, SHI Wei-Qun. Adsorption of Eu(III) on Alkalized Ti3C2Tx MXene Studied by Batch Experiment and Its Mechanism Investigation[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(1): 65-72.
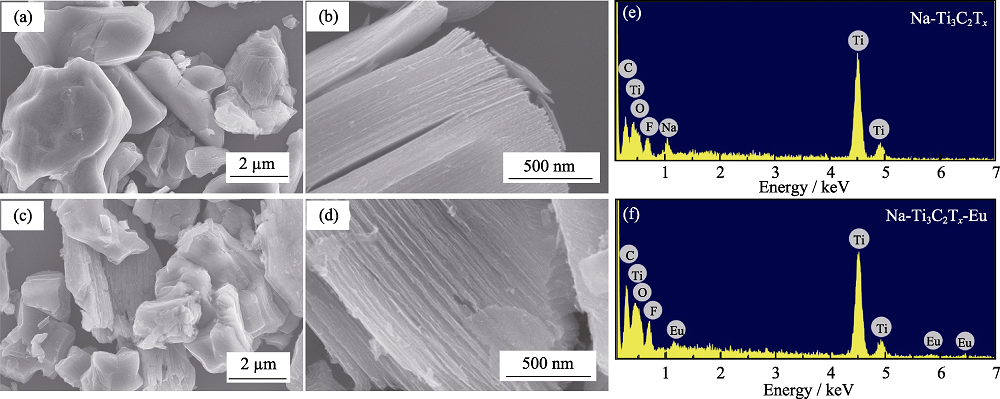
图2 Na-Ti3C2Tx吸附Eu(III)前的SEM照片(a~b); Na-Ti3C2Tx吸附Eu(III)后的SEM照片(c~d); Na-Ti3C2Tx吸附Eu(III)前的EDS图谱(e); Na-Ti3C2Tx吸附Eu(III)后的EDS图谱(f)
Fig. 2 SEM images of Na-Ti3C2Tx before (a-b), and after (c-d) adsorption of Eu(III), with EDS analysis resulted of Na-Ti3C2Tx before (e) and after (f) adsorption of Eu(III)
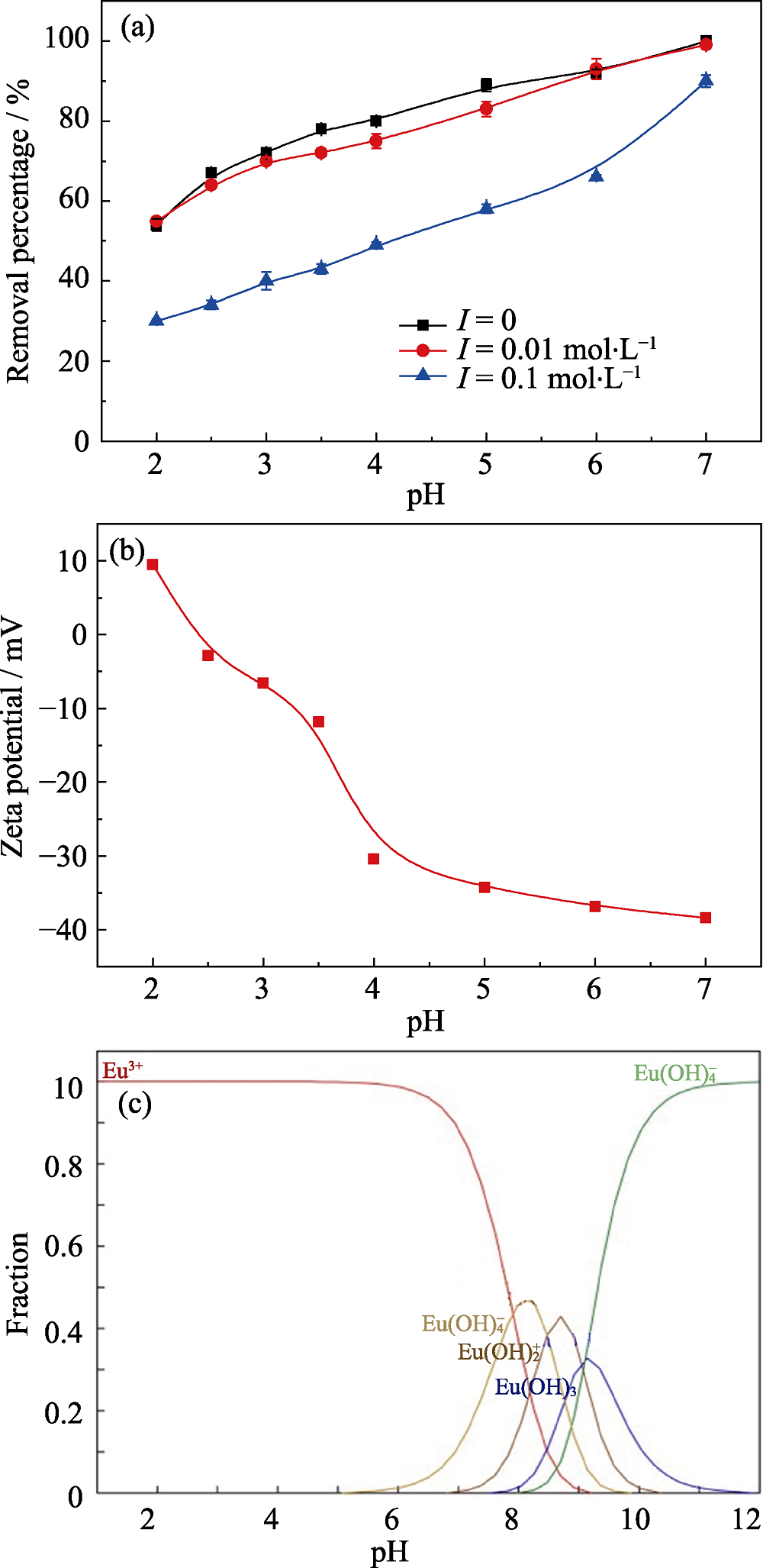
图4 溶液pH和离子强度对Na-Ti3C2Tx去除Eu(III)的影响(a); Na-Ti3C2Tx的Zeta电位图(b); 使用MEDUSA程序计算得到的Eu(III)在不同pH下的形态分布图(c)
Fig. 4 Effect of solution pH and ionic strength on removal of Eu(III) by Na-Ti3C2Tx (a), Zeta potential of Na-Ti3C2Tx (b), and distribution of Eu(III) species in aqueous solution as a function of pH calculated using the MEDUSA program (c)
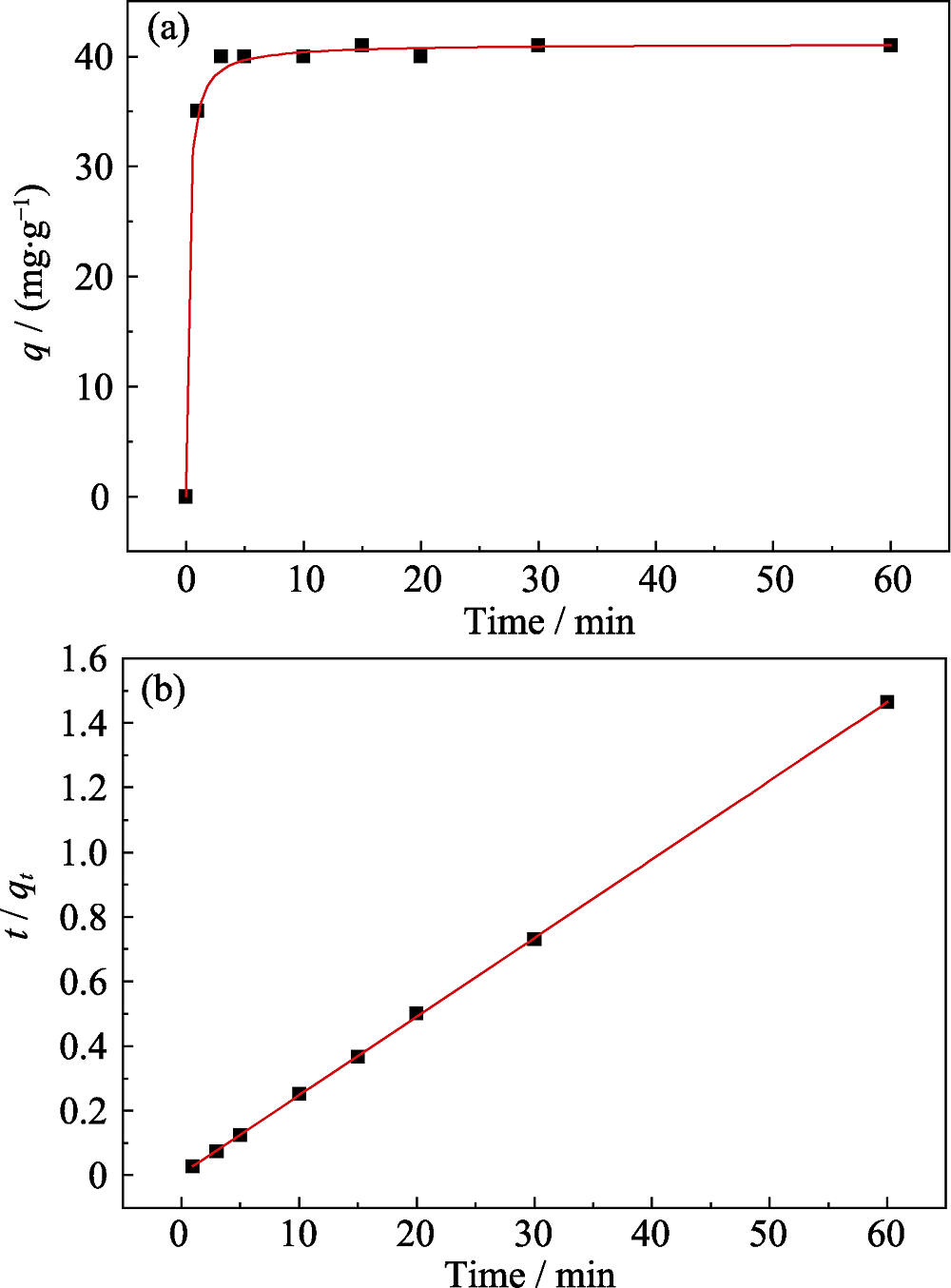
图5 Na-Ti3C2Tx吸附Eu(III)的动力学曲线(pH=(4.0±0.1), T= 293 K, m/V = 0.4 g/L) (a); Eu(III)在Na-Ti3C2Tx上的准二级动力学拟合曲线(b)
Fig. 5 Time-dependent adsorption of Eu(III) on Na-Ti3C2Tx (pH= (4.0±0.1), T = 293 K, m/V = 0.4 g/L) (a), and pseudo-second- order kinetic plots of Eu(III) on Na-Ti3C2Tx (b)
| Sample | Pseudo-first-order model | Pseudo-second-order model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na-Ti3C2Tx | k1/min-1 | R2 | k2/(g·mg-1·min-1) | R2 |
| 0.0212 | 0.4111 | 0.1312 | 0.9999 | |
表1 准一级和准二级动力学模型拟合参数
Table 1 Optimized parameters of pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order kinetic models
| Sample | Pseudo-first-order model | Pseudo-second-order model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na-Ti3C2Tx | k1/min-1 | R2 | k2/(g·mg-1·min-1) | R2 |
| 0.0212 | 0.4111 | 0.1312 | 0.9999 | |
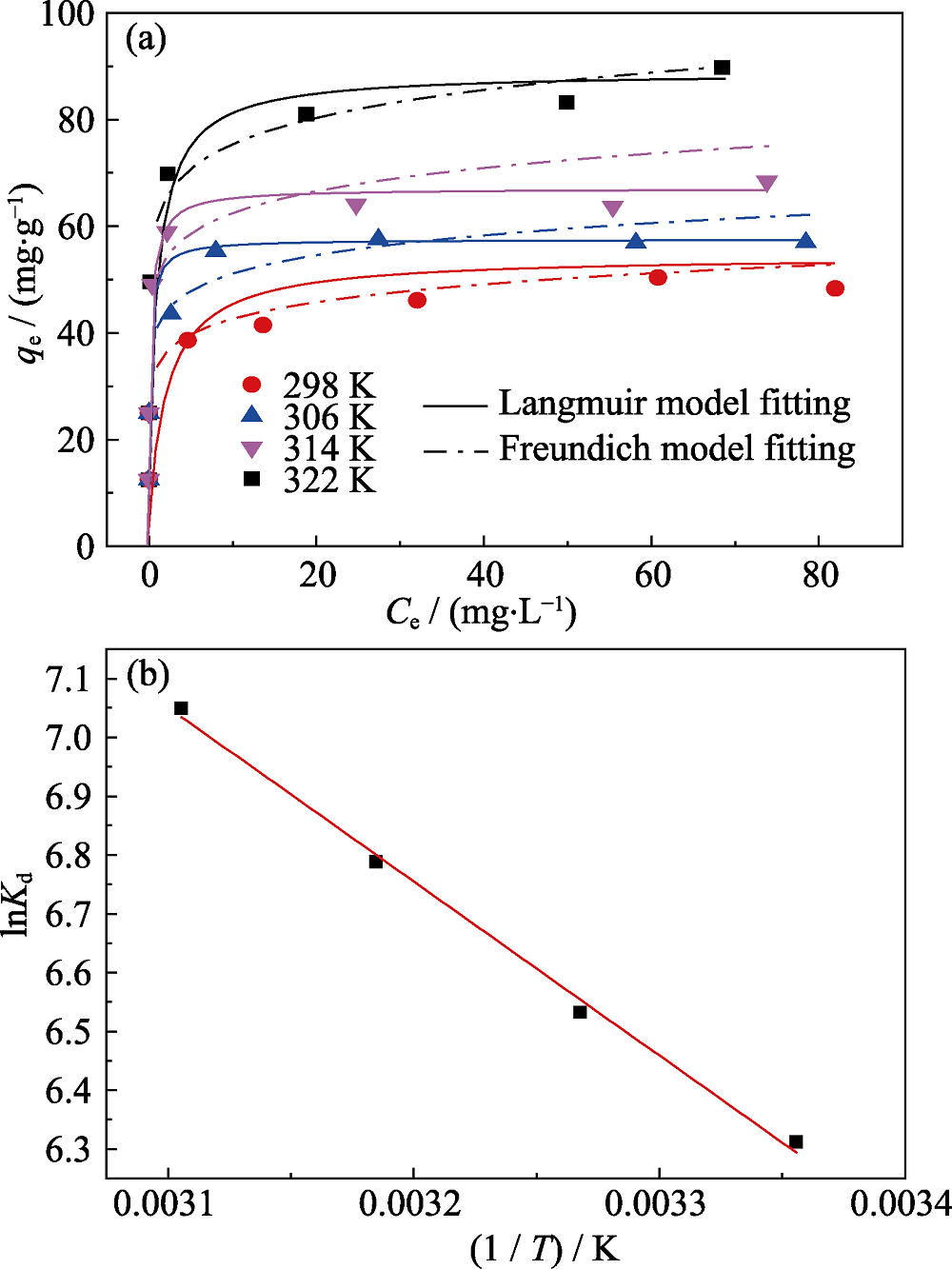
图6 pH=4.0时Na-Ti3C2Tx对Eu(III)的吸附等温线(a)和lnKd对1/T的线形图(b)
Fig. 6 (a) Isotherms of Na-Ti3C2Tx towards Eu(III) under the conditions of pH (4.0±0.1) and m/V=0.40 g/L, and (b) plot of lnKd vs 1/T
| Models | Parameters | Temperature/K | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 298 | 306 | 314 | 322 | ||
| Langmuir | qm/(mg·g-1) | 54.05 | 57.14 | 66.67 | 88.50 |
| KL/(L·mg-1) | 0.49 | 5.00 | 3.49 | 1.04 | |
| R2 | 0.9931 | 0.9999 | 0.9981 | 0.9973 | |
| Freundlich | KF/(mg1-n·Ln·g-1) | 33.52 | 40.87 | 50.37 | 60.87 |
| 1/n | 9.78 | 10.50 | 10.88 | 10.92 | |
| R2 | 0.9436 | 0.9487 | 0.9212 | 0.9645 | |
表2 Langmuir和Freundlich等温吸附模型的拟合参数
Table 2 Fitting parameters of Langmuir and Freundlich models
| Models | Parameters | Temperature/K | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 298 | 306 | 314 | 322 | ||
| Langmuir | qm/(mg·g-1) | 54.05 | 57.14 | 66.67 | 88.50 |
| KL/(L·mg-1) | 0.49 | 5.00 | 3.49 | 1.04 | |
| R2 | 0.9931 | 0.9999 | 0.9981 | 0.9973 | |
| Freundlich | KF/(mg1-n·Ln·g-1) | 33.52 | 40.87 | 50.37 | 60.87 |
| 1/n | 9.78 | 10.50 | 10.88 | 10.92 | |
| R2 | 0.9436 | 0.9487 | 0.9212 | 0.9645 | |
| Temperature/K | ΔH/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔS/(J·mol-1·K-1) | ΔG/(kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 298 | 24.539 | 134.81 | -15.57 |
| 306 | -16.65 | ||
| 314 | -17.73 | ||
| 322 | -18.80 |
表3 Na-Ti3C2Tx去除Eu(III)的热力学参数
Table 3 Thermodynamic parameters for removal of Eu(III) by Na-Ti3C2Tx
| Temperature/K | ΔH/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔS/(J·mol-1·K-1) | ΔG/(kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 298 | 24.539 | 134.81 | -15.57 |
| 306 | -16.65 | ||
| 314 | -17.73 | ||
| 322 | -18.80 |
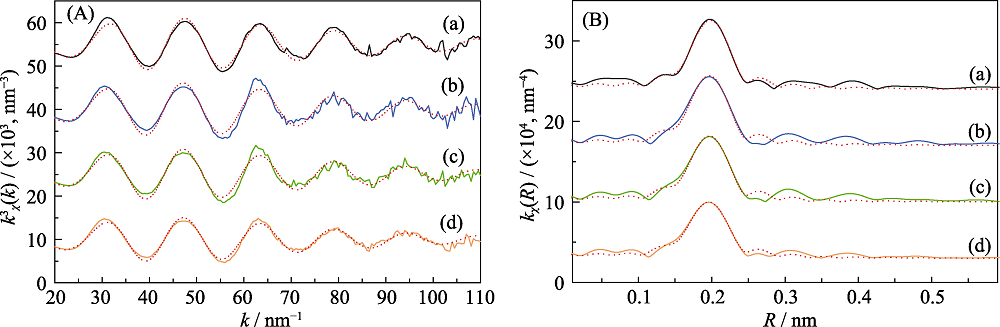
图7 (A)不同溶液pH条件样品的Eu L3边k3加权EXAFS谱(实线)与最佳理论拟合结果(点线), (B)对应的非相移校正傅里叶变换 (a) Reference of Eu3+ aqueous solution; (b) pH=4.0; (c) pH=5.0; (d) pH=6.0
Fig. 7 (A) Eu L 3 edge k3-weighted EXAFS spectra (solid lines) and the best theoretical fits (dots lines) of Eu-loaded Na-Ti3C2Tx samples under different solution pH, and (B) corresponding non-phase shift corrected Fourier transforms
| Sample | Path | CNa | Rb/nm | σ2c/(×10-4, nm2) | ΔEd/eV | R-factore |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eu3+(aq) | Eu-O | (9.0±0.6) | (0.243±0.001) | 0.8 | (3.9±0.6) | 0.006 |
| pH=4.0 | Eu-O | (9.1±1.6) | (0.243±0.002) | 0.9 | (2.4±1.6) | 0.019 |
| pH=5.0 | Eu-O | (8.7±1.4) | (0.243±0.001) | 0.9 | (2.6±1.5) | 0.016 |
| pH=6.0 | Eu-O | (7.8±0.9) | (0.242±0.001) | 1.0 | (2.2±1.1) | 0.008 |
表4 从EXAFS谱的最小二乘拟合分析中提取拟合参数
Table 4 Fitting parameters extracted from least-squares fitting analysis of EXAFS spectra
| Sample | Path | CNa | Rb/nm | σ2c/(×10-4, nm2) | ΔEd/eV | R-factore |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eu3+(aq) | Eu-O | (9.0±0.6) | (0.243±0.001) | 0.8 | (3.9±0.6) | 0.006 |
| pH=4.0 | Eu-O | (9.1±1.6) | (0.243±0.002) | 0.9 | (2.4±1.6) | 0.019 |
| pH=5.0 | Eu-O | (8.7±1.4) | (0.243±0.001) | 0.9 | (2.6±1.5) | 0.016 |
| pH=6.0 | Eu-O | (7.8±0.9) | (0.242±0.001) | 1.0 | (2.2±1.1) | 0.008 |
| [1] |
JOHNSTONE E V, HOFMSNN S, CHERKOUK A , et al. Study of the interaction of Eu3+ with microbiologically induced calcium carbonate precipitates using TRLFS. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016,50(22):12411-12420.
DOI URL PMID |
| [2] |
ZHANG W, HE X, YE G , et al. Americium(III) capture using phosphonic acid-functionalized silicas with different mesoporous morphologies: adsorption behavior study and mechanism investigation by EXAFS/XPS. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014,48(12):6874-6881.
DOI URL PMID |
| [3] |
XU L, ZHENG T, YANG S , et al. Uptake mechanisms of Eu(III) on hydroxyapatite: a potential permeable reactive barrier backfill material for trapping trivalent minor actinides. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016,50(7):3852-3859.
DOI URL PMID |
| [4] |
WANG X, YU S, WANG X K . Removal of radionuclides by metal-organic framework-based materials. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019,34(1):17-26.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
WANG X, PANG H, WU Y , et al. >Removal of radionuclides by layered double hydroxides materials. Sci. Sin. Chim., 2019,49(1):2-11.
DOI URL PMID |
| [6] | WANG S, YU S, WU Y ,et al. Highly efficient removal of radioactive uranium on polyaniline modified carbon nanofiber composites. Sci. Sin. Chim., 2019,49(1):71-79. |
| [7] | YAO W, WU Y, PANG H , et al. In-situ reduction synthesis of manganese dioxide@polypyrrole core/shell nanomaterial for highly efficient enrichment of U(VI) and Eu(III). Sci. China Chem., 2018,61(7):812-823. |
| [8] |
KUMAR S, GODBOLE S V, TOMAR B S . Speciation of Am(III)/Eu (III) sorbed on gammaalumina: effect of metal ion concentration. Radiochimica Acta, 2013,101(2):73-80.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
TAN X L, WANG X K, GECKEIS H , et al. Sorption of Eu(III) on humic acid or fulvic acid bound to hydrous alumina studied by SEM-E DS, XPS, TRLFS, and batch techniques. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008,42(17):6532-6537.
DOI URL PMID |
| [10] |
NOEMIE J, BENEDETTI M F, REILLER P E . Colloidal α-Al2O3 europium (III) and humic substances interactions: a macroscopic and spectroscopic study. Environmental Science & Technology, 2011,45(8):3224-3230.
DOI URL PMID |
| [11] |
TAN X, FAN Q, WANG X , et al. Eu(III) sorption to TiO2(anatase and rutile): batch, XPS, and EXAFS studies. Environmental Science & Technology, 2009,43(9):3115-3121.
DOI URL PMID |
| [12] |
BOUBY M, LUTZENKIRCHEN J, DARDENNE K , et al. Sorption of Eu(III) onto titanium dioxide: measurements and modeling. J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2010,350(2):551-561.
DOI URL PMID |
| [13] |
RABUNG T, PIERRET MC, BAUER A , et al. Sorption of Eu(III)/Cm(III) on Ca-montmorillonite and Na-illite. Part 1: batch sorption and time-resolved laser fluorescence spectroscopy experiments. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 2005,69(23):5393-5402.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
FAN Q H, TAN X L, LI J X , et al. Sorption of Eu(III) on attapulgite studied by batch, XPS, and EXAFS techniques. Environmental Science & Technology, 2009,43(15):5776-5782.
DOI URL PMID |
| [15] |
GALUNIN E, ALBA M D, SANTOS M J , et al. Lanthanide sorption on smectitic clays in presence of cement leachates. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 2010,74(3):862-875.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
GAD H M H, AWWAD N S . Factors affecting on the sorption/ desorption of Eu (III) using activated carbon. Separation Science & Technology, 2007,42(16):3657-3680.
DOI URL PMID |
| [17] |
ACCORSI G, ARMAROLI N, PARISINI A , et al. Wet adsorption of a luminescent Eu(III) complex on carbon nanotubes sidewalls. Advanced Functional Materials, 2010,17(15):2975-2982.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
CHEN C L, WANG X K, NAGATSU M . Europium adsorption on multiwall carbon nanotube/iron oxide magnetic composite in the presence of polyacrylicacid. Environmental Science & Technology, 2009,43(7):2362-2367.
DOI URL PMID |
| [19] |
SUN Y, WANG Q, CHEN C , et al. Interaction between Eu(III) and graphene oxide nanosheets investigated by batch and extended X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy and by modeling techniques. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012,46(11):6020-6027.
DOI URL PMID |
| [20] |
XIE Y, NAGUIB M, MOCHALIN V N , et al. Role of surface structure on Li-ion energy storage capacity of two-dimensional transition-metal carbides. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2014,136(17):6385-6394.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
ZHAO S, WEI K, XUE J . Role of strain and concentration on the Li adsorption and diffusion properties on Ti2C layer. Journal of Physical Chemistry Cv, 2014,118(27):14983-14990.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
EAMES C, ISLAM M S . Ion intercalation into two-dimensional transition-metal carbides: global screening for new high-capacity battery materials. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2015,46(14):16270-16276.
DOI URL PMID |
| [23] |
HU M, LI Z, ZHANG H , et al. Self-assembled Ti3C2Tx MXene film with high gravimetric capacitance. Chem. Commun., 2015,51(70):13531-13533.
DOI URL PMID |
| [24] |
ZHU M, HUANG Y, DENG Q , et al. Highly flexible, freestanding supercapacitor electrode with enhanced performance obtained by hybridizing polypyrrole chains with MXene. Advanced Energy Materials, 2016,6(21):1600969.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
ZHI W S, FREDRICKSON K D, ANASORI B , et al. Two- dimensional molybdenum carbide (MXene) as an efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution. ACS Energy Letters, 2016,1(3):589-594.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
LING C, SHI L, OUYANG Y , et al. Transition metal-promoted V2CO2(MXenes): a new and highly active catalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. Advanced Science, 2016,3(11):1600180.
DOI URL PMID |
| [27] |
MA T Y, CAO J L, JARONIEC M , et al. Interacting carbon nitride and titanium carbide nanosheets for high-performance oxygen evolution. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2016,128(3):1150-1154.
DOI URL PMID |
| [28] |
SHAHZAD F, ALHABEB M, HATTER C B , et al. Electromagnetic interference shielding with 2D transition metal carbides (MXenes). Science, 2016,353(6304):1137-1140.
DOI URL PMID |
| [29] |
HAN M, YIN X, WU H , et al. Ti3C2 MXenes with modified surface for high-performance electromagnetic absorption and shielding in the X-band. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016,8(32):21011-21019.
DOI URL PMID |
| [30] |
QING Y, ZHOU W, LUO F , et al. Titanium carbide (MXene) nanosheets as promising microwave absorbers. Ceramics International, 2016,42(14):16412-16416.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
YU X F, LI Y, CHENG J B , et al. Monolayer Ti2CO2: a promising candidate for NH3 sensor or capturer with high sensitivity and selectivity. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015,7(24):13707-13713.
DOI URL PMID |
| [32] |
LIU H, DUAN C, YANG C , et al. A novel nitrite biosensor based on the direct electrochemistry of hemoglobin immobilized on MXene- Ti3C2. Sensors & Actuators B Chemical, 2015,218:60-66.
DOI URL PMID |
| [33] |
FAN M, WANG L, PEI C , et al. Alkalization intercalation of MXene for electrochemical detection of uranyl ion. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019,34(1):85-90.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
MICHAEL N, MURAT K, VOLKER P , et al. Two-dimensional nanocrystals produced by exfoliation of Ti3AlC2. Advanced Materials, 2011,23(37):4248-4253.
DOI URL PMID |
| [35] |
MINOLI G . Cation intercalation and high volumetric capacitance of two-dimensional titanium carbide. Science, 2013,341(6153):1502-1505.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
MASHTALIR O, NAGUIB M, MOCHALIN V N , et al. Intercalation and delamination of layered carbides and carbonitrides. Nature Communications, 2013,4(2):1716.
DOI URL PMID |
| [37] |
PENG Q, GUO J, ZHANG Q , et al. Unique lead adsorption behavior of activated hydroxyl group in two-dimensional titanium carbide. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2014,136(11):4113-4116.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
SHAHZAD A, RASOOL K, MIRAN W , et al. Mercuric ion capturing by recoverable titanium carbide magnetic nanocomposite. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017,344:811-818.
DOI URL PMID |
| [39] |
WANG L, SONG H, YUAN L , et al. Efficient U(VI) reduction and sequestration by Ti2CTx MXene. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018,52(18):10748-10756.
DOI URL PMID |
| [40] |
WANG L, TAO W, YUAN L , et al. Rational control of the interlayer space inside two-dimensional titanium carbides for highly efficient uranium removal and imprisonment. Chem. Commun., 2017,53(89):12084-12087.
DOI URL PMID |
| [41] |
MU W, DU S, YU Q , et al. Improving barium ions adsorption on two-dimensional titanium carbide by surface modification. Dalton Transactions, 2018,47(25):8375-8381.
DOI URL PMID |
| [42] |
WANG L, YUAN L, CHEN K , et al. Loading actinides in multiayered structures for nuclear waste treatment: the first case study of uranium capture with vanadium carbide MXene. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2016,8(25):16396-16403.
DOI URL PMID |
| [43] | FAN M, WANG L, ZHANG Y , et al. Research progress of MXene materials in radioactive element and heavy metal ion sequestration. Sci. Sin. Chim., 2019,49(1):27-38. |
| [44] |
SCHLEGEL M L, INGMAR P, NATHALIE C , et al. Mechanism of europium retention by calcium silicate hydrates: an EXAFS study. Environmental Science & Technology, 2004,38(16):4423-4431.
DOI URL PMID |
| [45] |
MONTAVON G, MARKAI S, ANDRES Y , et al. Complexation studies of Eu(III) with alumina-bound polymaleic acid: effect of organic polymer loading and metal ion concentration. Environmental Science & Technology, 2002,36(15):3303-3309.
DOI URL PMID |
| [46] |
SHENG G D, YANG S T, ZHAO D L , et al. Adsorption of Eu (III) on titanate nanotubes studied by a combination of batch and EXAFS techique. Science China Chemistry, 2012,55(1):182-194.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 马磊, 黄毅, 邓浩, 银航, 田强, 晏敏皓. 氟磷灰石对酸性水溶液中铀(VI)的去除研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(4): 395-403. |
| [2] | 王婷婷, 史书梅, 柳晨媛, 朱万诚, 张恒. 多级多孔硅酸镍微球的合成及其对碱性品红的高效吸附[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(12): 1330-1336. |
| [3] | 董丽佳, 吴思颖, 李生波, 魏作富, 杨国, 胡保卫. 稻草生物炭对铕的吸附行为及机理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(3): 390-398. |
| [4] | 耿瑞文, 杨晓京, 谢启明, 李芮, 罗良. 基于划刻实验的单晶锗材料去除机理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(8): 867-872. |
| [5] | 徐从斌, 杨文杰, 孙宏亮, 刘伟江, 杨苑钰, 林爱军. 膨胀石墨负载零价铁的合成及其对水中Pb(II)去除效果与机制[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(1): 41-47. |
| [6] | 刘守新,刘正锋. TiO2/ACF复合材料的Sol-Gel法制备及其对苯的去除性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2009, 24(2): 209-214. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||