无机材料学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (7): 731-749.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220677 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20220677
所属专题: 【信息功能】发光材料与器件(202506)
李乾利1( ), 黎乃鑫1, 李育成1, 刘慎业2, 程帅3, 杨光1, 任宽2(
), 黎乃鑫1, 李育成1, 刘慎业2, 程帅3, 杨光1, 任宽2( ), 王峰2, 赵景泰1,3(
), 王峰2, 赵景泰1,3( )
)
收稿日期:2022-11-14
修回日期:2022-12-27
出版日期:2023-02-21
网络出版日期:2023-02-21
通讯作者:
任 宽, 副研究员. E-mail: yunlongrk1990@sina.com;作者简介:李乾利(1989-), 男, 博士, 副教授. E-mail: liqianli@shu.edu.cn
基金资助:
LI Qianli1( ), LI Naixin1, LI Yucheng1, LIU Shenye2, CHENG Shuai3, YANG Guang1, REN Kuan2(
), LI Naixin1, LI Yucheng1, LIU Shenye2, CHENG Shuai3, YANG Guang1, REN Kuan2( ), WANG Feng2, ZHAO Jingtai1,3(
), WANG Feng2, ZHAO Jingtai1,3( )
)
Received:2022-11-14
Revised:2022-12-27
Published:2023-02-21
Online:2023-02-21
Contact:
REN Kuan, associate professor. E-mail: yunlongrk1990@sina.com;About author:LI Qianli (1989-), male, PhD, associate professor. E-mail: liqianli@shu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
随着我国核辐射技术的进步, 辐射探测在近些年也得到了高速发展, 并被广泛应用于辐射安全监测、放射性医学诊疗、X射线安监系统、工业无损探伤以及微观粒子轨迹探测等诸多领域。辐射光致发光(Radio- photoluminescence, RPL)是一种在电离辐射作用下, 材料内部产生新的发光中心, 并被紫外光激发进而发光的现象, 可作为一种新型辐射探测手段。RPL材料通常具有存储辐射信息、信息几乎不衰减、剂量线性响应好、均匀稳定的高辐射灵敏度、能量依赖性小和可重复读数等特点, 弥补了光释光(Optically stimulated luminescence, OSL)和热释光(Thermally stimulated luminescence, TSL)材料在存储稳定性和重复使用性等方面的不足。自RPL现象被报道以来, RPL材料层出不穷, 如传统的Ag掺杂磷酸盐玻璃、Al2O3:C,Mg和LiF, 再到新型的Cu离子掺杂体系、Sm离子掺杂体系以及无掺杂体系材料等。同时, RPL应用也被不断发掘, 目前它已成为辐射探测领域不可或缺的材料之一。基于此, 本文概述了RPL材料的最新进展, 重点梳理了传统和新型RPL材料的发光原理、性能特点及其应用, 特别对比了不同RPL材料在辐射探测性能方面的差异。最后, 本文对RPL材料的优势及其不足之处进行了归纳分析, 并对其发展趋势进行了展望。
中图分类号:
李乾利, 黎乃鑫, 李育成, 刘慎业, 程帅, 杨光, 任宽, 王峰, 赵景泰. 辐射光致发光材料及其应用研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(7): 731-749.
LI Qianli, LI Naixin, LI Yucheng, LIU Shenye, CHENG Shuai, YANG Guang, REN Kuan, WANG Feng, ZHAO Jingtai. Research Progress of Radio-photoluminescence Materials and Their Applications[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(7): 731-749.
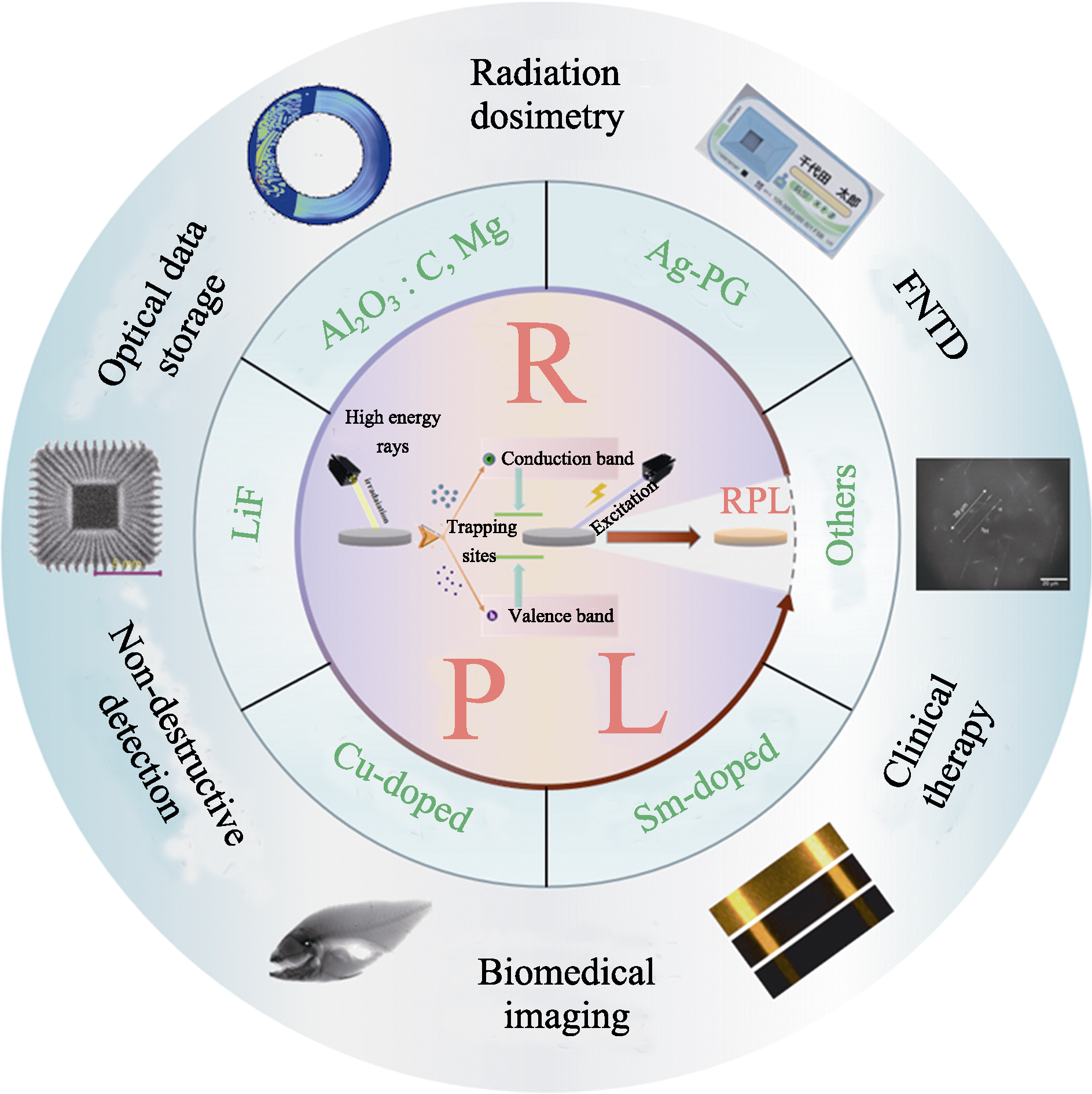
图1 RPL材料及其应用
Fig. 1 RPL materials and their applications The central area is a general luminescence diagram of RPL materials, the central ring area introduces common and new RPL materials, and the outer ring area lists some potential applications of RPL materials. FNTD: fluorescent nuclear track detector

图2 三种通用发光机制的示意图以及Ag离子掺杂材料、Al2O3:C,Mg和LiF的RPL响应及其RPL中心
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of three general luminescence mechanism, and RPL responses and RPL centers of Ag-doped materials, Al2O3:C,Mg and LiF (a) Schematic diagram of RPL/OSL/TSL general luminescence mechanisms[13]; (b) Excitation and emission spectra of Ag-PG[7]; (c) Emission spectra of Ag-PG under different doses of X-ray irradiation[51]; (d) Excitation spectrum (pink dotted line) and emission spectrum of Ag-Rb glass before and after X-ray (10 Gy) irradiation[53]; (e) Emission spectra of Ag-Nd co-doped phosphate glass at different radiation doses (310 nm excitation)[54]; (f) Excitation spectrum (dashed line) and emission spectrum (solid line) of Ag-doped CsCl before and after X-ray irradiation[58]; (g) Excitation and emission contour spectra of Al2O3:C,Mg irradiated by β-rays (90Sr/90Y)[61]; (h) Excitation spectrum and emission spectrum of LiF after X-ray irradiation (126 Gy)[62]; (i) RPL defect center in LiF, where F3+ is formed by three anionic vacancies capturing two electrons and F2 is formed by two anionic vacancies capturing two electrons[7]; Colorful figures are available on website
| No. | Material | Material forma | RPL center | λem/mm | λex/mm | Sensitivity/Gy | Build-up | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | NaPO3-Al(PO3)3:Ag | Glass | Ag0, | 400-500 | 325/339 | 1×10-6-10 | Yesb | [22-24] |
| Ag2+, Ag2+ | 600-700 | |||||||
| 2 | LiPO4-Al(PO3)3:Ag | Glass | Ag2+ | 630 | 340 | [25] | ||
| 3 | KPO3-Al(PO3)3:Ag | Glass | Ag2+ | 550-700 | 300-350 | 0.1-10 | [26] | |
| 4 | P2O5-Al2O3-Na2O-SiO2:Ag | Glass | Ag0 | 460 | 310 | 0.1×10-3-10 | Yes | [27] |
| Ag2+, Ag2+ | 630 | |||||||
| 5 | NaCl:Ag | S.C | Ag0 | 550-650 | 289 | [28] | ||
| 500-600 | 339 | |||||||
| 6 | KCl:Ag | S.C | Ag0 | 400-550 | 289 | [28] | ||
| 500-700 | 339 | |||||||
| 7 | Al2O3:C,Mg | S.C. | F+(Mg) | 325 | 255 | 2×10-3-200 | Yes | [11,19, 29] |
| F2 | 500 | 300 | ||||||
| F2+(2Mg) | 750 | 355 | ||||||
| F22+(2Mg) | 510 | 435 | ||||||
| 8 | LiF:Mg | S.C. | F3+, F2 | 530 | 450 | 0.1-1.4×104 | Yes | [30] |
| 9 | MgF2:Sm | P.C. | Sm2+ | 700-800 | 340 | 1-1×103 | No | [31] |
| 10 | SrB4O7:Sm | P.C. | Sm2+ | 670-830 | 408 | 0.2-5×103 | [32] | |
| 11 | BaAlBO3F2:Sm | G.C. | Sm2+ | 670-850 | 300-500 | 0.01-10 | No | [33] |
| 12 | CaSO4:Sm | P.C. | Sm2+ | 600-900 | 300 | 0.015-5 | No | [34] |
| 13 | Ca2SiO4:Eu | P.C. | Eu2+ | 500-800 | 250-500 | 0.01-10 | [35] | |
| 14 | BaAlBO3F2:Eu | G.C. | Eu2+ | 510 | 300-450 | 0.02-10 | Yes | [36] |
| 15 | KCaPO4:Eu | P.C. | Eu2+ | 610 | 200-500 | 0.01-10 | [37] | |
| 490 | 350 | |||||||
| 16 | 90KPO3-10Al2O3:Ce | S.C. | Ce3+ | 300-400 | 310 | 1×10-5-1 | [38] | |
| 17 | NaCl:Yb | S.C. | Yb2+ | 425-430 | 200-400 | 0.1-100 | [39] | |
| 18 | C:N | S.C. film | NV | 689 | 546 | Yes | [40] | |
| 19 | SiO2-B2O3-Al2O3-Na2O:Cu | Glass | Cu+ | 500-800 | 240 | ~500 | Yes | [41] |
| 20 | MgF2 | P.C. | 415 | 340 | 100-1000 | Yes | [42] | |
| 700 | ||||||||
| 21 | CaF2 | S.C. | F2+ | 660 | 370/560 | [43] | ||
| (F2+)A | 760 | 390/610 | ||||||
| 22 | CaF2:Na | S.C. | (F2+)A | 750 | 390/610 | 1×10-5-10 | [44] | |
| F3 | 950 | 450/610 | ||||||
| 23 | Li2CO3 | P.C. | 470 | 340 | 1×10-5-0.1 | [45] | ||
| 24 | K2CO3 | P.C. | 440 | 340 | 1×10-3-10 | [46] | ||
| 25 | CaSO4 | P.C. | 690 | 590 | 4×10-4-5 | No | [47] |
表1 不同种类的RPL材料
Table 1 Different kinds of RPL materials
| No. | Material | Material forma | RPL center | λem/mm | λex/mm | Sensitivity/Gy | Build-up | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | NaPO3-Al(PO3)3:Ag | Glass | Ag0, | 400-500 | 325/339 | 1×10-6-10 | Yesb | [22-24] |
| Ag2+, Ag2+ | 600-700 | |||||||
| 2 | LiPO4-Al(PO3)3:Ag | Glass | Ag2+ | 630 | 340 | [25] | ||
| 3 | KPO3-Al(PO3)3:Ag | Glass | Ag2+ | 550-700 | 300-350 | 0.1-10 | [26] | |
| 4 | P2O5-Al2O3-Na2O-SiO2:Ag | Glass | Ag0 | 460 | 310 | 0.1×10-3-10 | Yes | [27] |
| Ag2+, Ag2+ | 630 | |||||||
| 5 | NaCl:Ag | S.C | Ag0 | 550-650 | 289 | [28] | ||
| 500-600 | 339 | |||||||
| 6 | KCl:Ag | S.C | Ag0 | 400-550 | 289 | [28] | ||
| 500-700 | 339 | |||||||
| 7 | Al2O3:C,Mg | S.C. | F+(Mg) | 325 | 255 | 2×10-3-200 | Yes | [11,19, 29] |
| F2 | 500 | 300 | ||||||
| F2+(2Mg) | 750 | 355 | ||||||
| F22+(2Mg) | 510 | 435 | ||||||
| 8 | LiF:Mg | S.C. | F3+, F2 | 530 | 450 | 0.1-1.4×104 | Yes | [30] |
| 9 | MgF2:Sm | P.C. | Sm2+ | 700-800 | 340 | 1-1×103 | No | [31] |
| 10 | SrB4O7:Sm | P.C. | Sm2+ | 670-830 | 408 | 0.2-5×103 | [32] | |
| 11 | BaAlBO3F2:Sm | G.C. | Sm2+ | 670-850 | 300-500 | 0.01-10 | No | [33] |
| 12 | CaSO4:Sm | P.C. | Sm2+ | 600-900 | 300 | 0.015-5 | No | [34] |
| 13 | Ca2SiO4:Eu | P.C. | Eu2+ | 500-800 | 250-500 | 0.01-10 | [35] | |
| 14 | BaAlBO3F2:Eu | G.C. | Eu2+ | 510 | 300-450 | 0.02-10 | Yes | [36] |
| 15 | KCaPO4:Eu | P.C. | Eu2+ | 610 | 200-500 | 0.01-10 | [37] | |
| 490 | 350 | |||||||
| 16 | 90KPO3-10Al2O3:Ce | S.C. | Ce3+ | 300-400 | 310 | 1×10-5-1 | [38] | |
| 17 | NaCl:Yb | S.C. | Yb2+ | 425-430 | 200-400 | 0.1-100 | [39] | |
| 18 | C:N | S.C. film | NV | 689 | 546 | Yes | [40] | |
| 19 | SiO2-B2O3-Al2O3-Na2O:Cu | Glass | Cu+ | 500-800 | 240 | ~500 | Yes | [41] |
| 20 | MgF2 | P.C. | 415 | 340 | 100-1000 | Yes | [42] | |
| 700 | ||||||||
| 21 | CaF2 | S.C. | F2+ | 660 | 370/560 | [43] | ||
| (F2+)A | 760 | 390/610 | ||||||
| 22 | CaF2:Na | S.C. | (F2+)A | 750 | 390/610 | 1×10-5-10 | [44] | |
| F3 | 950 | 450/610 | ||||||
| 23 | Li2CO3 | P.C. | 470 | 340 | 1×10-5-0.1 | [45] | ||
| 24 | K2CO3 | P.C. | 440 | 340 | 1×10-3-10 | [46] | ||
| 25 | CaSO4 | P.C. | 690 | 590 | 4×10-4-5 | No | [47] |

图3 Cu离子掺杂材料的RPL现象及其响应
Fig. 3 RPL and its responses of Cu-doped materials (a) Photos of undoped, 0.005% and 0.01% Cu-doped (in mole fraction) aluminoborosilicate glass under natural and ultraviolet light (254 nm) with brown part of the glass being exposed to X-ray[41]; (b) Emission spectra of undoped and doped aluminoborosilicate glass at 240 nm excitation before and after X-ray irradiation[41]; (c) Relationship between PL intensity and irradiation (or absorption) dose of 0.005% Cu-doped aluminumborosilicate glass irradiated by γ-ray (60Co)[41]; (d) Effect of heat treatment on X-ray irradiated 0.005% Cu-doped aluminoborosilicate glass[41]; (e) Emission spectra of Cu-doped silica glass before and after γ-ray irradiation at 240 nm excitation[64]; (f) Emission spectra of Cu-doped silica glass before and after irradiation with γ-rays (1519 Gy) with emission band after irradiation containing two bands of 2.5 and 2.1 eV (blue line)[64]; (g) Fitting curve of the relationship between PL intensity and radiation dose of Cu-doped silica glass[64]; (h) Emission spectra of Cu-doped aluminoborosilicate glasses before and after X-ray irradiation at 240 nm with inset showing ABS25 (top) and ABS30 (bottom) before (left) and after (right) X-ray irradiation, respectively[65]
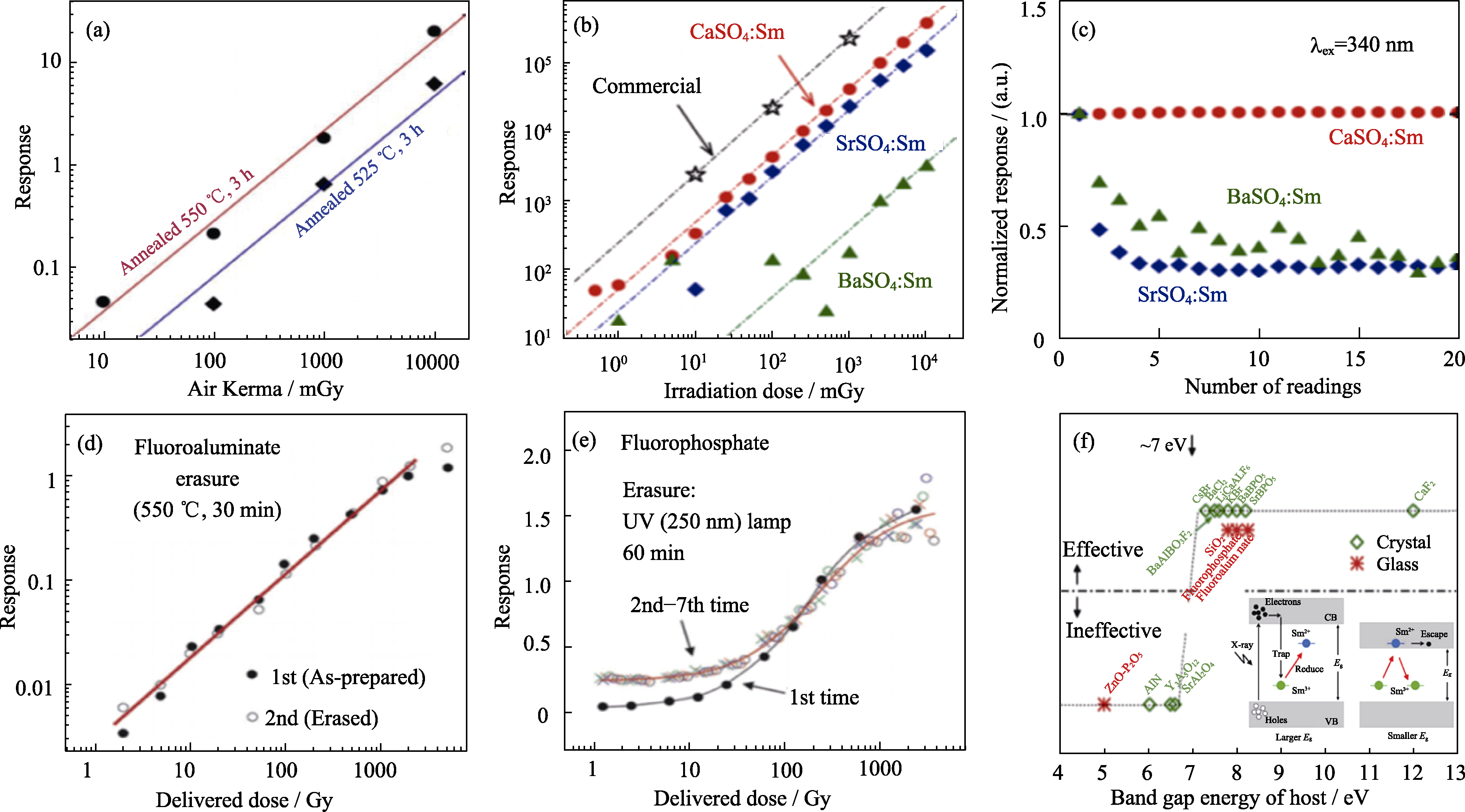
图4 Sm离子掺杂材料的RPL响应、重复使用性以及RPL有效性与主体材料带隙能量的关系
Fig. 4 RPL responses, reusability and effectiveness of RPL in relation to band gap energy of host in Sm-doped materials (a) Linear response lines of RPL intensity and radiation dose of Sm-doped BaF2-Al2O3-B2O3[33]; (b) Dose response curves of Sm-doped CaSO4, SrSO4, BaSO4 and commercial RPL glass dosimeter (Ag-PG)[34]; (c) Stability curves of RPL signals doped with CaSO4, SrSO4 and BaSO4 during UV excitation. The measured irradiation dose of each group was fixed at 5.0 Gy, and PL spectra were measured every minute after irradiation (20 times in total) to obtain its response value[34]; Reusability of Sm-doped RPL detectors after (d) heat treatment and (e) UV irradiation erasure[7]; (f) Effectiveness of RPL in Sm-doped RPL materials as a function of band gap energy of host[71]
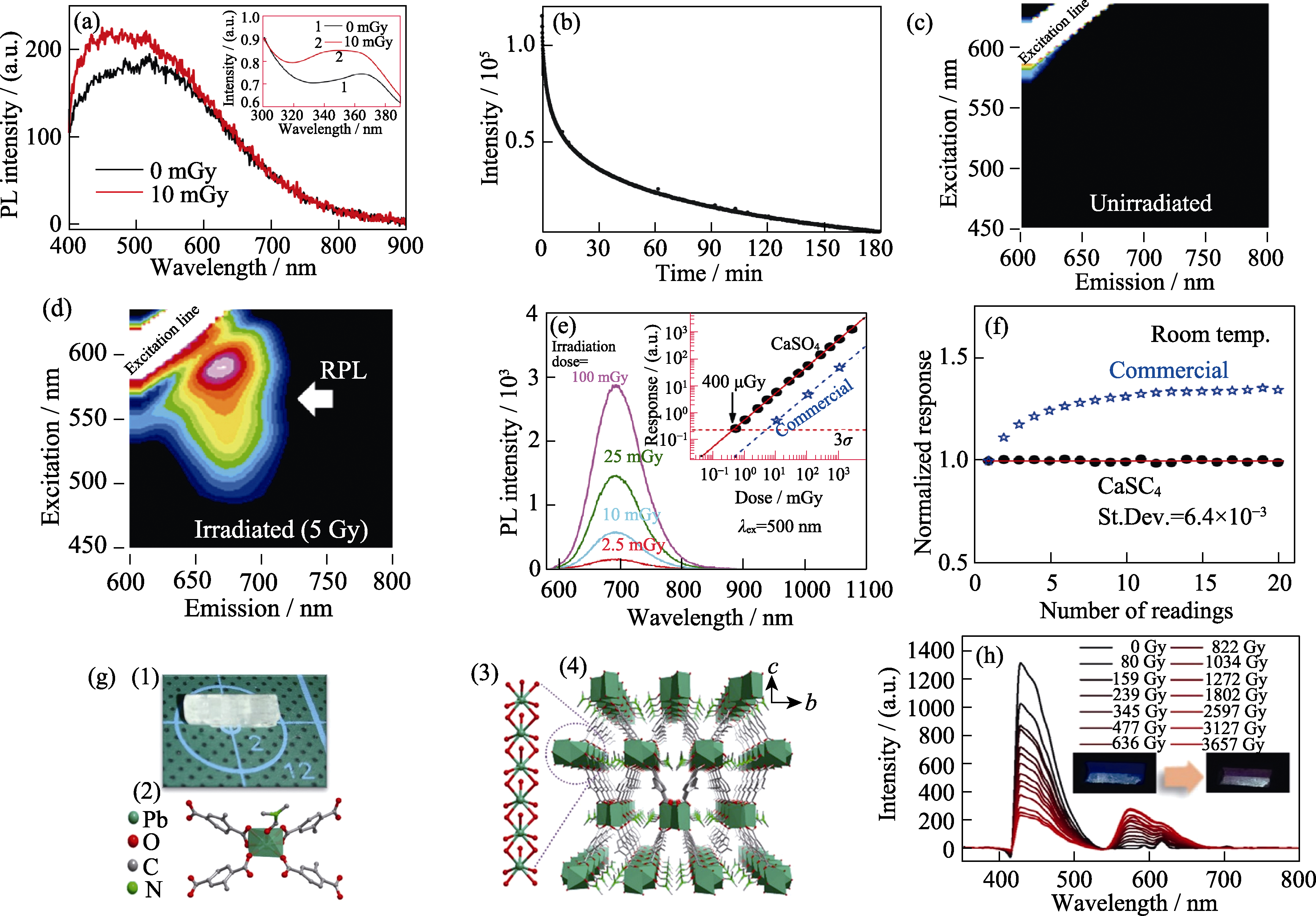
图5 其他新型材料(Li2CO3、CaSO4和MOF结构)的RPL响应以及MOF的晶体结构
Fig. 5 RPL responses of other novel materials and their crystal structure of MOF (a) Emission spectra of Li2CO3 before and after X-ray (10 mGy) irradiation, with the excitation wavelength of (340±40) nm with inset showing the excitation spectrum before and after X-ray (1 Gy) irradiation at the monitoring wavelength 470 nm[45]; (b) Curve of RPL response strength of Li2CO3 ceramics with time at the excitation of (340±40) nm[45]; Excitation emission contour maps of undoped CaSO4 before (c) and after (d) X-ray irradiation (5 Gy)[47]; (e) Relationship between PL spectrum and irradiation dose of undoped CaSO4 with inset showing the dose-response function compared with commercial RPL glass detector[47]; (f) Relationship between the RPL response stability and the number of readings of CaSO4 and commercial RPL glass detectors[47]; (g) Crystal structure of SCU-200 with schematic diagrams (1)-(4) indicating crystal habit and size of a crystal (1), coordination mode of the Pb2+ ion (2), one-dimensional chain constructed from PbO7 polyhedra (3), and three-dimensional arrangement of the one-dimensional chain (4), respectively[74]; (h) Emission spectra of SCU-200 after irradiation with different doses of X-ray[74]; Colorful figures are available on website

图6 RPL材料用于辐射剂量计
Fig. 6 RPL materials for radiation dosimetry (a) Fluorescence attenuation curve (top) and novel readout technique using pulsed ultraviolet laser (bottom)[7]; (b) Internal images of RPLGD[7]; (c) Comparison of RPL response signals irradiated by different metal filters and different types of radiation (X, γ and β-rays)[7]; (d) Spherical RPLGD prepared by melting method[79]; (e) Spherical RPLGD used to monitor radioactive contaminants in harsh environments[80]; (f) 2D dose distribution of each layer at different depths of the hand model soaked in polyester resin block (left) and 3D dose distribution of the complete structure of the hand model after X-ray irradiation[83]; (g) Contrast enhanced image of RPL photograph after digital image processing with inset showing RPL glass particles covered with polystyrene plate placed in a petri dish. When the dose is higher than 5 Gy, RPL can be observed with a digital camera at a dose higher than 0.5 Gy, and when RPL glass particles were exposed to gamma rays (60Co) they can emit orange light under UV light[84]; Colorful figures are available on website

图7 RPL材料用于FNTD以及MRT
Fig. 7 RPL materials for FNTD and MRT (a) Nuclear track detection of fast neutrons demonstrated by using Al2O3:C,Mg[85]; (b) Nuclear track image obtained by using LiF as FNTD[7]; (c) Histogram of nuclear tracks detected by Al2O3:C,Mg[86]; (d) Dose response function of Sm-doped RPL materials for dose monitoring in MRT[71]

图8 RPL材料用于辐射成像
Fig. 8 RPL materials for radiation imaging (a) Microscale patterns of (1) two-dimensional code, (2) lines, circles and dots written on Ag-PG using a focused proton beam with an energy of 1.7 MeV and a current of 4 pA, (3) 3D images of dots- and lines-patterns written on Ag-PG using a focused proton beam with an energy of 1.7 MeV and a current of 20 pA[93]; (b) X-ray imaging of Ag-PG used in (1) medical imaging and (2) industrial nondestructive testing[95]; (c) X-ray imaging of LiCaAlF6:Sm with the micron level spatial resolution[69]; (d) X-ray imaging of BaF2-Al2O3-B2O3:Sm with a spatial resolution of 5l lp/mm (100 μm)[33]; (e) X-ray images (1) using a disk-type imaging detector with LiF film[62] with two reconstructed dose distribution images using a disk-type Ag-PG detector in (2) orange and (3) blue RPL[98]; (f) Photograph of (1) a flexible imaging plate made by using (Ba1-xSrx)2SiO4:Eu before X-ray irradiation, (2) image of the X-ray irradiated imaging plate under UV excitation with the luminous color changing from red to green, X-ray images obtained after (3) 10 and (4) 28 d at room temperature in the dark[99]
| [1] | OU X Y, CHEN X, XU X N, et al. Recent development in X-ray imaging technology: future and challenges. Research, 2021, 2021: 9892152. |
| [2] | ZHANG H J. Development trend of nuclear radiation detection equipment and technology. Chemical Engineering and Equipment, 2016, 8: 277. |
| [3] | WU R, FAN D H, KANG Y, et al. Research progress on semiconductor materials and devices for radiation detection. Journal of Synthetic Crystals, 2021, 50(10): 1813. |
| [4] |
TAKAYUKI Y, OKADA G, TAKUMI K, et al. A review and future of RPL dosimetry. Radiation Measurements, 2022, 158: 106847.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
DURAGKAR A, MULEY A, PAWAR N R, et al. Versatility of thermoluminescence materials and radiation dosimetry-a review. Luminescence, 2019, 34(7): 656.
DOI URL |
| [6] | YUAN L, JIN Y, SU Y, et al. Optically stimulated luminescence phosphors: principles, applications, and prospects. Laser & Photonics Reiews, 2020, 14(12): 2000123. |
| [7] | OKADA G, YANAGIDA T, NANTO H, et al. Radiophotoluminescence(RPL)//TAKAYUKI Y, MASANORI K. Phosphors for Radiation Detectors. Hoboken: Wiley, 2022: 247-281. |
| [8] |
SCHULMAN J H, GINTHER R J, KLICK C C, et al. Dosimetry of X-rays and gamma-rays by radiophotoluminescence. Journal of Applied Physics, 1951, 22(12): 1479.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
YOKOTA R, IMAGAWA H. Radiophotoluminescent centers in silver-activated phosphate glass. Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 1966, 23(5): 1038.
DOI URL |
| [10] | PIESCH E, BURGKHARDT B, FISCHER M. Properties of radioluminescent glass dosimeter systems using pulsed laser UV excitation. Radiaion Protection Dosimetry, 1986, 17: 273. |
| [11] |
DE SAINT-HUBERT M, CASTELLANO F, LEBLANS P, et al. Characterization of 2D Al2O3:C, Mg radiophotoluminescence films in charged particle beams. Radiation Measurements, 2021, 141: 106518.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
MUNEEM A, YOSHIDA J, EKAWA H, et al. Study on the reusability of fluorescent nuclear track detectors using optical bleaching. Radiation Measurements, 2022, 158: 106863.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
YANAGIDA T, OKADA G, KAWAGUCHI N. Ionizing-radiation- induced storage-luminescence for dosimetric applications. Journal of Luminescence, 2019, 207: 14.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
ASSENMACHER F, BOSCHUNG M, HOHMANN E, et al. Dosimetric properties of a personal dosimetry system based on radio- photoluminescence of silver doped phosphate glass. Radiation Measurements, 2017, 106: 235.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
CHAND S, MEHRA R, CHOPRA V. Recent developments in phosphate materials for their thermoluminescence dosimeter (TLD) applications. Luminescence, 2021, 36(8): 1808.
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
JAIN M, KUMAR R, KOOK M. A novel coupled RPL/OSL system to understand the dynamics of the metastable states. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 15565.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
OKADA G, HIRASAWA K, YANAGIDA T, et al. TSL/OSL/RPL automated and integrated measurement system (TORAIMS). Sensors and Materials, 2021, 33(6): 2117.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
KUROBORI T, ZHENG W, MIYAMOTO Y, et al. The role of silver in the radiophotoluminescent properties in silver-activated phosphate glass and sodium chloride crystal. Optical Materials, 2010, 32(9): 1231.
DOI URL |
| [19] | AKSELROD G M, AKSELROD M S, BENTON E R, et al. A novel Al2O3 fluorescent nuclear track detector for heavy charged particles and neutrons. Nuclear Instruments & Methods in Physics Research Section B-Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 2006, 247(2): 295. |
| [20] |
LEVITA M, SCHLESINGER T, FRIEDLAND S S. LiF dosimetry based on radiophotoluminescence (RPL). IEEE Transaction Nuclear Science, 1976, 23: 667.
DOI URL |
| [21] | REGULLA D F. Lithium fluoride dosimetry based on radiophotoluminescence. Health Physcis, 1972, 22(5): 491. |
| [22] |
MCKEEVER S W S, SHOLOM S, SHRESTHA N. Observations regarding the build-up effect in radiophotoluminescence of silver- doped phosphate glasses. Radiation Measurements, 2019, 123: 13.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
KAWAMOTO H, FUJIMOTO Y, KOSHIMIZU M, et al. Temperature dependence of radiophotoluminescence in Ag-doped phosphate glasses containing different alkali metals. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2019, 58(6): 062003.
DOI URL |
| [24] | HUANG D Y C, HSU S M. Radio-photoluminescence Glass Dosimeter (RPLGD). Advances in Cancer Therapy, INTECH, 2011: 553-568. |
| [25] |
TATSUMI H, OKADA G, MASAI H, et al. Radiophotoluminescence and thermally-stimulated luminescence of Ag-doped Li3PO4- Al(PO3)3 glass. Journal of Luminescence, 2016, 179: 545.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
SHIRATORI D, ISOKAWA Y, SAMIZO H, et al. Evaluation of optical and radio-photoluminescence properties in Ag-doped 30KPO3- 70Al(PO3)3 glasses. Journal of the Ceramic Society of Japan, 2019, 127(7): 455.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
KATO T, SHIRATORI D, IWAO M, et al. Ag concentration dependence of build-up effect of radio-photoluminescence in Ag-doped P2O5-Al2O3-Na2O-SiO2 glasses. Sensors and Materials, 2021, 33(6): 2163.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
KAWAMOTO H, KOSHIMIZU M, FUJIMOTO Y, et al. Formation of radiophotoluminescence centers at room temperature in Ag-doped alkali halides. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2019, 58(6): 062004.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
SYKORA G J, AKSELROD M S. Photoluminescence study of photochromically and radiochromically transformed Al2O3:C,Mg crystals used for fluorescent nuclear track detectors. Radiation Measurements, 2010, 45: 631.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
GOPAL J N, SANYAL B, LAKSHMANAN A. Radiophotoluminescence and thermoluminescence characteristics of undoped and Mg doped LiF phosphor in the high dose region. Radiation Measurements, 2018, 109: 24.
DOI URL |
| [31] | OKADA G, NAKAMURA F, KAWANO N, et al. Radiation- induced luminescence centres in Sm:MgF2 ceramics. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B, 2018, 435: 268. |
| [32] | BELEV G, OKADA G, TONCHEV D, et al. Valency conversion of samarium ions under high dose synchrotron generated X-ray radiation. Physica Status Solidi C-Current Topics in Solid State Physics, 2010, 8(9): 2822. |
| [33] |
OKADA G, SHINOZAKI K, KOMATSU T, et al. Radio- photoluminescence in Sm-doped BaF2-Al2O3-B2O3 glass- ceramics. Radiation Measurements, 2017, 106: 73.
DOI URL |
| [34] | OKADA G, HIRASAWA K, KUSANO E, et al. Radio- photoluminescence properties of samarium-doped alkaline earth sulfates. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B, 2020, 466: 56. |
| [35] |
ASADA S, OKADA G, KATO T, et al. Eu-doped Ca2SiO4 as a new radio-photoluminescence phosphor. Chemistry Letters, 2018, 47(1): 59.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
OKADA G, SHINOZAKI K, SHIRATORI D, et al. Radio- photoluminescence observed in Eu-doped BABF glass-ceramics. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(7): 9376.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
SHIRATORI D, KATO T, NAKAUCHI D, et al. Luminescence properties of Eu:KCaPO4 ceramics that generate new luminescent centers upon X-ray irradiation. Sensors and Materials, 2021, 33(6): 2171.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
SHIRATORI D, ISOKAWA Y, SAMIZO H, et al. Dosimetric, optical and radio-luminescence properties of Ce-doped 90KPO3- 10Al2O3 glasses. Journal of Materials Science-Materials in Electronics, 2019, 30(3): 2464.
DOI |
| [39] |
FUJIMOTO Y, OKADA G, SEKINE D, et al. Radiation induced change in the optical properties of NaCl:Yb crystal. Radiation Measurements, 2020, 133: 106274.
DOI URL |
| [40] | ONODA S, HARUYAMA M, TERAJI T, et al. New application of NV centers in CVD diamonds as a fluorescent nuclear track detector. Physica Status Solidi A-Applications and Materials Science, 2015, 212(11): 2641. |
| [41] |
HASHIKAWA R, FUJII Y, KINOMURA A, et al. Radiophotoluminescence phenomenon in copper-doped aluminoborosilicate glass. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2019, 102(4): 1642.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
NAKAMURA F, KATO T, OKADA G, et al. Scintillation, TSL and RPL properties of MgF2 transparent ceramic and single crystal. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(9): 7211.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
KATO T, NAKAUCHI D, KAWAGUCHI N, et al. Radio- photoluminescence phenomenon in non-doped CaF2 ceramic. Materials Letters, 2020, 270: 127688.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
KATO T, OKADA G, NAKAUCHI D, et al. Na-concentration dependence on radiophotoluminescence properties of CaF2. Solid State Sciences, 2022, 128: 106892.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
NAKAMURA F, KATO T, OKADA G, et al. Non-doped Li2CO3 ceramics as a new radio-photoluminescence material. Materials Letters, 2018, 221: 51.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
NAKAMURA F, KATO T, OKADA G, et al. Radio- photoluminescence in non-doped K2CO3 ceramics. Materials Letters, 2018, 211: 100.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
OKADA G, KOGUCHI Y, YANAGIDA T, et al. Undoped CaSO4 showing highly enhanced radio-photoluminescence properties. Materials Today Communications, 2020, 24: 101013.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
YAMAMOTO T, MAKI D, SATO F, et al. The recent investigations of radiophotoluminescence and its application. Radiation Measurements, 2011, 46(12): 1554.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
MCKEEVER S W S, SHOLOM S, SHRESTHA N, et al. Build-up of radiophotoluminescence (RPL) in Ag-doped phosphate glass in real-time both during and after exposure to ionizing radiation: a proposed model. Radiation Measurements, 2020, 132: 106246.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
MIYAMOTO Y, KINOSHITA K, KOYAMA S, et al. Emission and excitation mechanism of radiophotoluminescence in Ag+-activated phosphate glass. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2010, 619(1/2/3): 71.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
SHOLOM S, MCKEEVER S W S. High-dose dosimetry with Ag-doped phosphate glass: applicability test with different techniques. Radiation Measurements, 2020, 132: 106263.
DOI URL |
| [52] | KAWAMOTO H, KAWAMURA I, KOMIYA H, et al. Elucidation of electron and hole transfer at high temperature in Ag-doped Na and Al phosphate glasses. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2022, 61(SB): SB1026. |
| [53] |
SHIRATORI D, TAKEBUCHI Y, KATO T, et al. Radio-photoluminescence properties of heavy-element-based alkaline phosphate glasses and their application to X-ray imaging. Sensors and Materials, 2022, 34(2): 745.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
MA X B, CHENG J M, FAN S J, et al. Silver-neodymium codoped lithium aluminum metaphosphate glasses for radio-photoluminescence dosimeter. Materials, 2022, 15(16): 5527.
DOI URL |
| [55] | FAN S J, YU C L, HE D B, et al. Preparation and property of radio-photoluminescence dosimeter glass. Atomic Energy Science and Technology, 2013, 47(03): 502. |
| [56] |
TANAKA H, FUJIMOTO Y, SAEKI K, et al. Radiophotoluminescence properties of Ag-doped mixed phosphate glasses. Radiation Measurements, 2017, 106: 180.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
ARYAL P, KIM H, SAHA S, et al. Radio-photoluminescence of silver- doped phosphate glass. New Physics: Sae Mulli, 2019, 69(7): 714.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
KIMURA H, OKADA G, KATO T, et al. Radio-photoluminescence properties of silver-doped cesium chloride transparent ceramics. Journal of Luminescence, 2021, 236: 118099.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
AKSELROD M S, AKSELROD A E, ORLOV S S, et al. Fluorescent aluminum oxide crystals for volumetric optical data storage and imaging applications. Journal of Fluorescence, 2003, 13(6): 503.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
AKSELROD M S, AKSELROD A E. New Al2O3:C, Mg crystals for radiophotoluminescent dosimetry and optical imaging. Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 2006, 119: 218.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
AKSELROD M S, SYKORA G J. Fluorescent nuclear track detector technology-a new way to do passive solid state dosimetry. Radiation Measurements, 2011, 46(12): 1671.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
KUROBORI T, MIYAMOTO Y, MARUYAMA Y, et al. A comparative study of optical and radiative characteristics of X-ray- induced luminescent defects in Ag-doped glass and LiF thin films and their applications in 2-D imaging. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 2014, 326: 76.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
MROZIK A, BILSKI P, MARCZEWSKA B, et al. Radio- photoluminescence of highly irradiated LiF:Mg,Ti and LiF:Mg,Cu,P detectors. Radiation Measurements, 2014, 71: 31.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
HASHIKAWA R, TAKADA Y, NISHI Y, et al. Electron and hole capture processes in Cu-doped glass exhibiting radiophotoluminescence. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 2022, 34(2): 025701.
DOI |
| [65] |
NISHI Y, OKADA A, KINOMURA A, et al. Radiation-induced valence conversion and photoluminescence of copper ions in aluminoborosilicate glasses. Journal of Materials Research, 2022, 37(9): 1626.
DOI |
| [66] |
SCHUYT J J, WILLIAMS G V M. Oxygen-impurity charge transfer in NaMgF3:Ln (Ln = Yb, Sm, or Eu): establishing the lanthanide energy levels in NaMgF3. Journal of Luminescence, 2019, 211: 413.
DOI URL |
| [67] |
OKADA G, MORRELL B, KOUGHIA C, et al. Spatially resolved measurement of high doses in microbeam radiation therapy using samarium doped fluorophosphate glasses. Applied Physics Letters, 2011, 99(12): 121105.
DOI URL |
| [68] |
OKADA G, UEDA J, TANABE S, et al. Samarium-doped oxyfluoride glass-ceramic as a new fast erasable dosimetric detector material for microbeam radiation cancer therapy applications at the Canadian synchrotron. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2014, 97(7): 2147.
DOI URL |
| [69] |
OKADA G, KAWAGUCHI N, KASAP S, et al. Radio-photoluminescence properties of LiCaAlF6:Sm. Radiation Measurements, 2020, 132: 106251.
DOI URL |
| [70] |
SCHUYT J J, WILLIAMS G V M. Quenching of the Sm2+ luminescence in NaMgF3:Sm via photothermal ionization: alternative method to determine divalent lanthanide trap depths. Applied Physics Letters, 2019, 115(18): 181104.
DOI URL |
| [71] |
OKADA G. Novel radio-photoluminescence materials and applications. Journal of the Ceramic Society of Japan, 2021, 129(7): 419.
DOI URL |
| [72] |
TAKUMI K, DAISUKE N, NORIAKI K, et al. Radio- photoluminescence properties of CaF2 transparent and opaque ceramics. Current Applied Physics, 2020, 20(11): 1195.
DOI URL |
| [73] |
OKADA G, KOJIMA T, USHIZAWA J, et al. Radio- photoluminescence observed in non-doped Mg2SiO4 single crystal. Current Applied Physics, 2017, 17(3): 422.
DOI URL |
| [74] |
LIU H Z, QIN H M, SHEN N N, et al. Emergence of a radical- stabilizing metal-organic framework as a radio-photoluminescence dosimeter. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(35): 15209.
DOI URL |
| [75] |
DOTY F P, BAUER C A, SKULAN A J, et al. Scintillating metal- organic frameworks: a new class of radiation detection materials. Advanced Materials, 2009, 21(1): 95.
DOI URL |
| [76] | SATO F, ZUSHI N, NAGAI T, et al. Development of radiophotoluminescence glass dosimeter usable in high temperature environment. Radiation Measurements, 2013, 53-54: 8. |
| [77] |
IWAO M, TAKASE H, SHIRATORI D, et al. Ag-doped phosphate glass with high weathering resistance for RPL dosimeter. Radiation Measurements, 2021, 140: 106492.
DOI URL |
| [78] |
SATO F, TOYOTA Y, MAKI D, et al. Development of bead-type radiophotoluminescence glass dosimeter applicable to various purposes. Radiation Measurements, 2013, 55: 68.
DOI URL |
| [79] |
SATO F, TOYOTA Y, ZUSHI N, et al. Synthesis and characterization of spherical radiophotoluminescence glass detectors by melting method. Radiation Measurements, 2018, 113: 1.
DOI URL |
| [80] |
YAMAMOTO T, YANAGIDA-MIYAMOTO Y, IIDA T, et al. Current status and future prospect of RPL glass dosimeter. Radiation Measurements, 2020, 136: 106363.
DOI URL |
| [81] | NAGAMOTO K, MORITAKE T, NAKAGAMI K, et al. A multicenter study of radiation doses to the eye lenses of clinical physicians performing radiology procedures in Japan. Journal of Occupational Health, 2021, 63(1): e12305. |
| [82] |
SATO F, HASHIMOTO T, TAMAKI S, et al. Development of string-shaped radiophotoluminescence dosimeter for high-radiation field. Radiation Measurements, 2018, 111: 1.
DOI URL |
| [83] |
SATO F, MAEKAWA T, SAKIYAMA T, et al. Development of human hand phantom containing radiophotoluminescence material. Radiation Measurements, 2016, 85: 18.
DOI URL |
| [84] |
SATO F, ZUSHI N, MAEKAWA T, et al. Visualization of high radiation field by radiophotoluminescence photography. Radiation Measurements, 2014, 68: 23.
DOI URL |
| [85] |
SYKORA G J, SALASKY M, AKSELROD M S. Properties of novel fluorescent nuclear track detectors for use in passive neutron dosimetry. Radiation Measurements, 2008, 43: 1017.
DOI URL |
| [86] |
SYKORA G J, AKSELROD M S, BENTON E R, et al. Spectroscopic properties of novel fluorescent nuclear track detectors for high and low LET charged particles. Radiation Measurements, 2008, 43: 422.
DOI URL |
| [87] |
BILSKI P, MARCZEWSKA B, KLOSOWSKI M, et al. Detection of neutrons with LiF fluorescent nuclear track detectors. Radiation Measurements, 2018, 116: 35.
DOI URL |
| [88] |
KODAIRA S, KUSUMOTO T, KITAMURA H, et al. Characteristics of fluorescent nuclear track detection with Ag+-activated phosphate glass. Radiation Measurements, 2020, 132: 106252.
DOI URL |
| [89] |
NIKLAS M, ABDOLLAHI A, AKSELROD M S, et al. Subcellular spatial correlation of particle traversal and biological response in clinical ion beams. International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics, 2013, 87(5): 1141.
DOI PMID |
| [90] |
VAHEDI S, OKADA G, MORRELL B, et al. X-ray induced Sm3+ to Sm2+ conversion in fluorophosphate and fluoroaluminate glasses for the monitoring of high-doses in microbeam radiation therapy. Journal of Applied Physics, 2012, 112(7): 073108.
DOI URL |
| [91] |
CHICILO F, OKADA G, BELEV G, et al. Instrumentation for high-dose, high-resolution dosimetry for microbeam radiation therapy using samarium-doped fluoroaluminate and fluorophosphate glass plates. Measurement Science and Technology, 2020, 31(1): 015201.
DOI URL |
| [92] |
OKADA G, VAHEDI S, MORRELL B, et al. Examination of the dynamic range of Sm-doped glasses for high-dose and high- resolution dosimetric applications in microbeam radiation therapy at the Canadian synchrotron. Optical Materials, 2013, 35(11): 1976.
DOI URL |
| [93] | KUROBORI T, KADA W, SHIRAO T, et al. Two-photon excited microscale colour centre patterns in Ag-activated phosphate glass written using a focused proton beam. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2018, 57(2S2): 02CC01. |
| [94] |
HARB J, GUERINEAU T, MORANA A, et al. Femtosecond direct laser writing of silver clusters in phosphate glasses for X-ray spatially-resolved dosimetry. Chemosensors, 2022, 10(3): 110.
DOI URL |
| [95] |
NANTO H, OKADA G, HIRASAWA K, et al. Radiophotoluminescence imaging reader for passive dosimetry. Sensors and Materials, 2022, 34(2): 757.
DOI URL |
| [96] |
KUROBORI T, NAKAMURA S. A novel disk-type X-ray area imaging detector using radiophotoluminescence in silver-activated phosphate glass. Radiation Measurements, 2012, 47(10): 1009.
DOI URL |
| [97] | KUROBORI T, MATOBA A. Development of accurate two- dimensional dose-imaging detectors using atomic-scale color centers in Ag-activated phosphate glass and LiF thin films. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2014, 53(2S): 02BD14. |
| [98] |
KUROBORI T, TAKEMURA A, MIYAMOTO Y, et al. A disk- type dose imaging detector based on blue and orange RPL in Ag-activated phosphate glass for 2D and 3D dose imaging applications. Radiation Measurements, 2015, 83: 51.
DOI URL |
| [99] |
YANG Z T, HU J Q, VAN DER HEGGEN D, et al. Realizing simultaneous X-ray imaging and dosimetry using phosphor-based detectors with high memory stability and convenient readout process. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(31): 2201684.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 胡 辰, 刘书萍, 冯召东, 秦秀波, 石 云, 潘裕柏. LuAG:Ce, Mg闪烁陶瓷的X射线平板探测器成像研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(8): 814-818. |
| [2] | 沈沪江,王林军,黄 健,徐 闰,史伟民,夏义本. 基于(100)定向金刚石薄膜的辐射探测器研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2009, 24(6): 1254-1258. |
| [3] | 李玉红,张弘,李振生,李丹民,贺德衍. 真空蒸发法制备PbI2多晶薄膜研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2005, 20(5): 1239-1242. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||