无机材料学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (3): 377-384.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250210 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20250210
李泽熙( ), 卢文杰, 王朝, 张璐, 李述体, 高芳亮(
), 卢文杰, 王朝, 张璐, 李述体, 高芳亮( )
)
收稿日期:2025-05-15
修回日期:2025-07-03
出版日期:2025-09-11
网络出版日期:2025-09-11
通讯作者:
高芳亮, 研究员. E-mail: gaofl@m.scnu.edu.cn作者简介:李泽熙(2000-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: 2022023502@m.scnu.edu.cn
基金资助:
LI Zexi( ), LU Wenjie, WANG Chao, ZHANG Lu, LI Shuti, GAO Fangliang(
), LU Wenjie, WANG Chao, ZHANG Lu, LI Shuti, GAO Fangliang( )
)
Received:2025-05-15
Revised:2025-07-03
Published:2025-09-11
Online:2025-09-11
Contact:
GAO Fangliang, professor. E-mail: gaofl@m.scnu.edu.cnAbout author:LI Zexi (2000-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: 2022023502@m.scnu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
二维氮化镓(GaN)因既具有宽禁带半导体特性, 又具有量子限域效应双重特征, 在紫外光电子领域具有广阔的应用前景。然而, 金属有机化学气相沉积和分子束外延等常用方法制备二维GaN通常需要较高的生长温度、较长的制备时间和相对较高的成本。针对上述关键挑战, 本研究利用液态金属镓具有低温下熔化和易氧化的特点, 研发了一种高效、相对低温的二维GaN制备策略。首先, 利用简单易行的旋涂剥离法, 直接从液态镓表面提取获得非晶态氧化镓(Ga2O3); 随后, 通过氮化处理工艺, 在相对较低的温度(850 ℃)下, 对非晶Ga2O3进行处理, 成功实现了高晶体质量GaN的制备。研究结果表明, 制备的二维GaN厚度约为2.2 nm, 横向尺寸为厘米量级, 晶体结构为六方纤锌矿结构。基于制备的二维GaN构建了光电导型紫外光电探测器, 性能测试表明在5 V偏置电压和325 nm波长紫外光照射下, 器件展示出良好的响应度(4.14 A/W)和较高的探测率(1.02×1013 Jones)。本研究基于液态金属镓制备了大面积二维GaN材料, 为开发低维高性能紫外光电探测器提供了参考借鉴。
中图分类号:
李泽熙, 卢文杰, 王朝, 张璐, 李述体, 高芳亮. 基于液态金属镓制备二维氮化镓及其光电性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(3): 377-384.
LI Zexi, LU Wenjie, WANG Chao, ZHANG Lu, LI Shuti, GAO Fangliang. Two-dimensional GaN: Preparation Based on Liquid Metal Gallium and Photoelectric Properties[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2026, 41(3): 377-384.
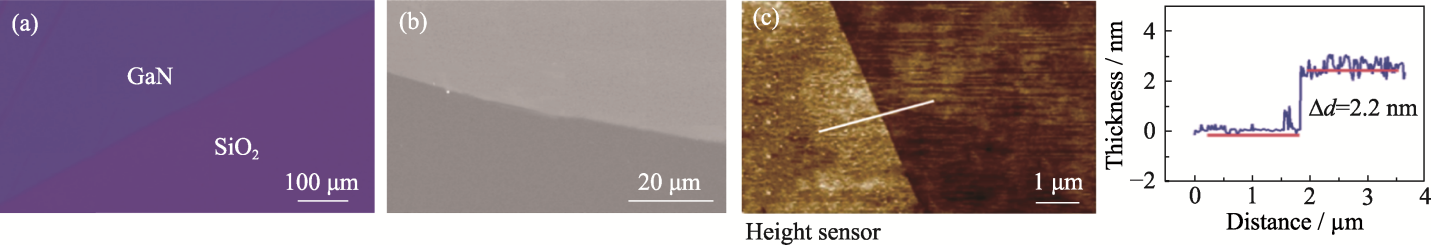
图2 二维GaN的形貌表征
Fig. 2 Morphological characterization of two-dimensional GaN (a) Optical microscope image; (b) SEM image; (c) AFM image with the right figure showing height profile
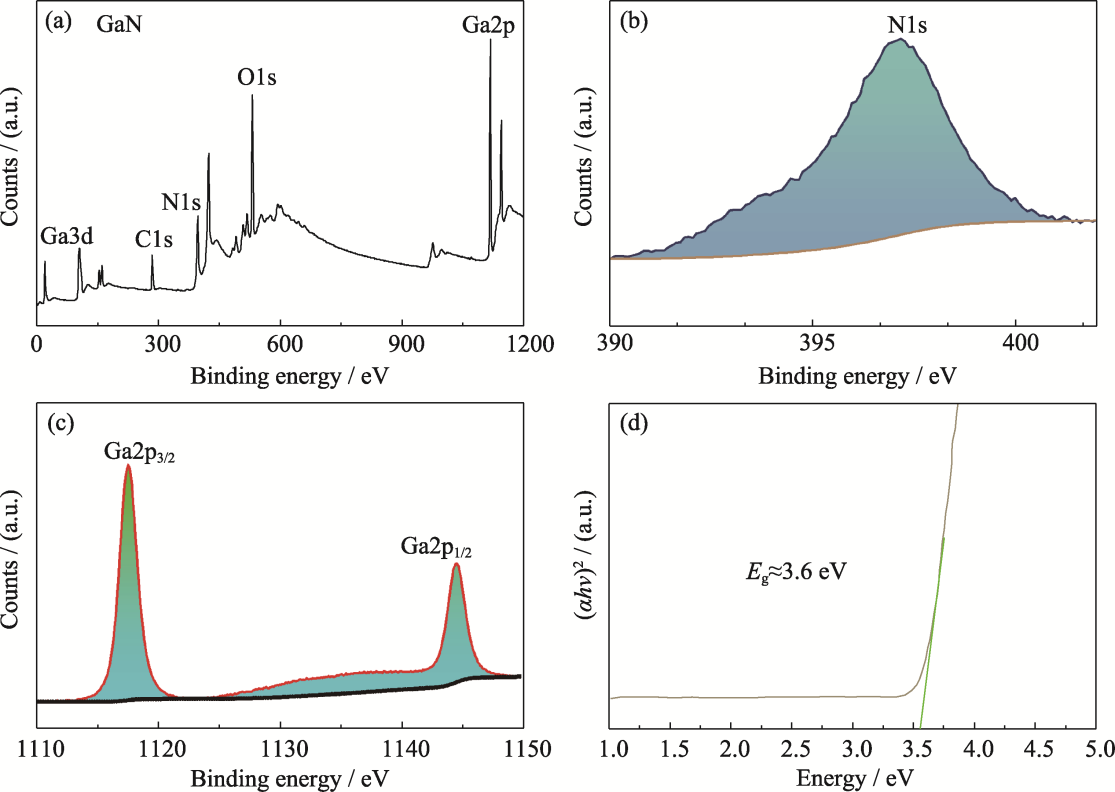
图4 二维GaN的表面化学分析与光学性质表征
Fig. 4 Surface chemical analysis and optical property characterization of two-dimensional GaN (a) High-resolution XPS total spectrum; (b) High-resolution N1s XPS spectrum; (c) High-resolution Ga2p XPS spectrum; (d) Tauc plot corresponding to the absorption spectrum
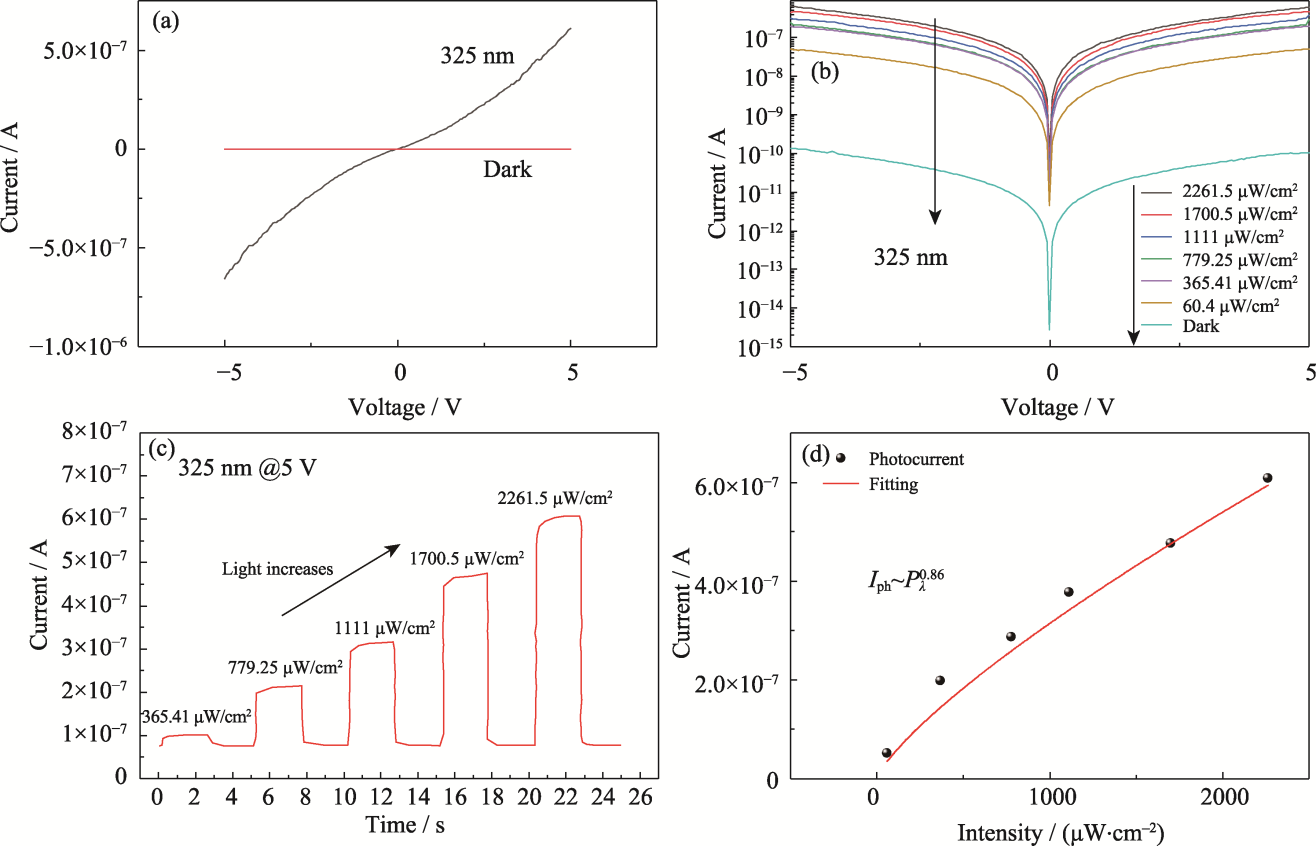
图5 二维GaN光电探测器的探测性能
Fig. 5 Detection performance of two-dimensional GaN photodetector (a) I-V curves in dark and 325 nm light (2.26 mW·cm2); (b) I-V curves of the ultraviolet light with different light intensities in the logarithmic coordinates; (c) I-T curve measured by the ultraviolet light with different light intensities; (d) Light intensity-light current power function diagram
| Material | R/(A·W-1) | EQE/% | D*/Jones | Test voltage/V | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2D | 2.01 | 683 | 5.34×1010 | 10 | [ |
| Thin film | 0.13 | 49.76 | 9.79×108 | 5 | [ |
| Porous | 0.187 | 62.8 | 4.34×1012 | -3 | [ |
| Nanowires | 0.023 | − | 4.40×1011 | 0 | [ |
| Bulk | 0.34 | − | 1.24×109 | 5 | [ |
| 2D | 4.14 | 1400 | 1.02×1013 | 5 | This work |
表1 不同类型GaN紫外光电探测器的性能对比
Table 1 Performance comparison of GaN-based ultraviolet photodetectors
| Material | R/(A·W-1) | EQE/% | D*/Jones | Test voltage/V | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2D | 2.01 | 683 | 5.34×1010 | 10 | [ |
| Thin film | 0.13 | 49.76 | 9.79×108 | 5 | [ |
| Porous | 0.187 | 62.8 | 4.34×1012 | -3 | [ |
| Nanowires | 0.023 | − | 4.40×1011 | 0 | [ |
| Bulk | 0.34 | − | 1.24×109 | 5 | [ |
| 2D | 4.14 | 1400 | 1.02×1013 | 5 | This work |
| [1] | DONG M, ZHENG X, LI Q, et al. Multi-effect coupling enhanced self-powered heterojunction ultraviolet photodetector with ultra-low detection limit. Materials Today, 2024, 74: 85. |
| [2] | CHEN K, DENG C, ZOU C, et al. Plasmonic hot-hole injection combined with patterned substrate for performance improvement in trapezoidal PIN GaN microwire self-powered ultraviolet photodetector. Nano Energy, 2022, 104: 107926. |
| [3] | UM D Y, CHANDRAN B, KIM J Y, et al. New charge carrier transport-assisting paths in ultra-long GaN microwire UV photodetector. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(40): 2306143. |
| [4] | CHAUDHURI R, BADER S J, CHEN Z, et al. A polarization-induced 2D hole gas in undoped gallium nitride quantum wells. Science, 2019, 365(6460): 1454. |
| [5] | QI Z G, LIU L, WANG S Z, et al. Progress in GaN single crystals: HVPE growth and doping. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 243. |
| [6] | ZHOU N, YANG R, ZHAI T. Two-dimensional non-layered materials. Materials Today Nano, 2019, 8: 100051. |
| [7] | AL BALUSHI Z Y, WANG K, GHOSH R K, et al. Two-dimensional gallium nitride realized via graphene encapsulation. Nature Materials, 2016, 15(11): 1166. |
| [8] | CHEN Y, LIU K, LIU J, et al. Growth of 2D GaN single crystals on liquid metals. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2018, 140(48): 16392. |
| [9] | WANG Z, WANG G, LIU X, et al. Two-dimensional wide band-gap nitride semiconductor GaN and AlN materials: properties, fabrication and applications. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2021, 9(48): 17201. |
| [10] | YU Y, WANG T, CHEN X, et al. Demonstration of epitaxial growth of strain-relaxed GaN films on graphene/SiC substrates for long wavelength light-emitting diodes. Light: Science & Applications, 2021, 10(1): 117. |
| [11] | CHEN Z, ZHANG X, DOU Z, et al. High-brightness blue light-emitting diodes enabled by a directly grown graphene buffer layer. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(30): 1801608. |
| [12] | DAENEKE T, KHOSHMANESH K, MAHMOOD N, et al. Liquid metals: fundamentals and applications in chemistry. Chemical Society Reviews, 2018, 47(11): 4073. |
| [13] | AUKARASEREENONT P, GOFF A, NGUYEN C K, et al. Liquid metals: an ideal platform for the synthesis of two-dimensional materials. Chemical Society Reviews, 2022, 51(4): 1253. |
| [14] | SCHEIDELER W J, NOMURA K. Advances in liquid metal printed 2D oxide electronics. Advanced Functional Materials, 2024, 34(40): 2403619. |
| [15] | HANDSCHUH-WANG S, WANG T, GANCARZ T, et al. The liquid metal age: a transition from Hg to Ga. Advanced Materials, 2024, 36(45): 2408466. |
| [16] | CABRERA N, MOTT N F. Theory of the oxidation of metals. Reports on Progress in Physics, 1949, 12(1): 163. |
| [17] | SYED N, ZAVABETI A, MESSALEA K A, et al. Wafer-sized ultrathin gallium and indium nitride nanosheets through the ammonolysis of liquid metal derived oxides. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(1): 104. |
| [18] | ZHANG G, CHEN L, WANG L, et al. Subnanometer-thick 2D GaN film with large bandgap synthesized by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2022, 10: 4053. |
| [19] | SZEKERES A, ALEXANDROVA S, KIROV K. The effect of O2 plasma on properties of the Si-SiO2 system. Physica Status Solidi (a), 1980, 62(2): 727. |
| [20] | KIM J J, PARK H H, HYUN S H. The evolution of microstructure and surface bonding in SiO2 aerogel film after plasma treatment using O2, N2, and H2 gases. Thin Solid Films, 2001, 384(2): 236. |
| [21] | JAIN S K, SYED N, BALENDHRAN S, et al. Atomically thin gallium nitride for high-performance photodetection. Advanced Optical Materials, 2023, 11(15): 2300438. |
| [22] | ELKASHEF N, SRINIVASA R S, MAJOR S, et al. Sputter deposition of gallium nitride films using a GaAs target. Thin Solid Films, 1998, 333(1): 9. |
| [23] | KOLEY B, LAKSHAN A, RAGHUVANSHI P R, et al. Ultralow lattice thermal conductivity at room temperature in Cu4TiSe4. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(16): 9106. |
| [24] | BUSCEMA M, ISLAND J O, GROENENDIJK D J, et al. Photocurrent generation with two-dimensional van der Waals semiconductors. Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(11): 3691. |
| [25] | DU Y, YIN S, LI Y, et al. Liquid-metal-assisted synthesis of patterned GaN thin films for high-performance UV photodetectors array. Small Methods, 2024, 8(2): 2300175. |
| [26] | ZHANG X, LI J, MA Z, et al. Design and integration of a layered MoS2/GaN van der Waals heterostructure for wide spectral detection and enhanced photoresponse. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(42): 47721. |
| [27] | CAI K, JIN Z W. Photodetector based on two-dimensional perovskite (PEA)2PbI4. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(9): 1069. |
| [28] | DONG S Y, TIE S J, YUAN R H, et al. Research progress on low-dimensional halide perovskite direct X-ray detectors. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(9): 1017. |
| [29] | LI F, WU J, LUO C, et al. Liquid metal based synthesis of GaN nanosheets with Ag nanoparticle modification for enhanced ultraviolet photodetection. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2025, 8(24): 12764. |
| [30] | AGGARWAL N, KRISHNA S, GOSWAMI L, et al. Inclination of screw dislocations on the performance of homoepitaxial GaN based UV photodetectors. Materials Science and Engineering: B, 2021, 263: 114879. |
| [31] | GUO Y, SONG W, LIU Q, et al. A porous GaN/MoO3 heterojunction for filter-free, ultra-narrowband ultraviolet photodetection. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2022, 10(13): 5116. |
| [32] | ZHANG J, WANG J, FAN J, et al. Ultrastable and quick response UV photodetector by high crystalline orientation wurtzite/ zinc-blende GaN superlattice. Advanced Optical Materials, 2025, 13(10): 2402779. |
| [33] | GUNDIMEDA A, KRISHNA S, AGGARWAL N, et al. Fabrication of non-polar GaN based highly responsive and fast UV photodetector. Applied Physics Letters, 2017, 110(10): 103507. |
| [1] | 安瑕, 许晟瑞, 陶鸿昌, 苏华科, 杨赫, 许钪, 谢磊, 贾敬宇, 张进成, 郝跃. Ar离子注入蓝宝石衬底诱导成核的高质量GaN外延[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(1): 91-96. |
| [2] | 卢灏, 许晟瑞, 黄永, 陈兴, 徐爽, 刘旭, 王心颢, 高源, 张雅超, 段小玲, 张进成, 郝跃. 等离子体增强原子层沉积AlN外延单晶GaN研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(5): 547-553. |
| [3] | 向晖, 全慧, 胡艺媛, 赵炜骞, 徐波, 殷江. 类石墨烯单层结构ZnO和GaN的压电特性对比研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(5): 492-496. |
| [4] | 郑雪, 江睿, 李谦, 王伟哲, 徐智谋, 彭静. 类阳极氧化铝纳米结构LED的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(5): 561-566. |
| [5] | 彭 丹, 郑学军, 谢澍梵, 罗晓菊, 王 丁. GaN/ZnO复合体的制备及光催化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(9): 956-960. |
| [6] | 李程程, 徐智谋, 孙堂友, 王智浩, 王双保, 张学明, 彭 静. GaN基LED图形衬底的性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2013, 28(8): 869-874. |
| [7] | 陈 丹, 吕建国, 黄靖云, 金豫浙, 张昊翔, 叶志镇. AZO薄膜用于GaN基LED透明电极的性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2013, 28(06): 649-652. |
| [8] | 季振国,娄 垚,毛启楠. 沉积温度对高Al含量的AlxGa1-xN薄膜的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2010, 25(4): 386-390. |
| [9] | 杨新波,徐 军,李红军,毕群玉,程 艳,苏良碧,周国清. 非极性GaN用r面蓝宝石衬底[J]. 无机材料学报, 2009, 24(4): 783-786. |
| [10] | 边继明,李效民,赵俊亮,于伟东. PLD法生长高质量 ZnO薄膜及其光电导特性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2006, 21(3): 701-706. |
| [11] | 李抒智,徐军,杨卫桥,邹军,周圣明. 用VTE方法在蓝宝石衬底上生长γ-LiAlO2薄膜[J]. 无机材料学报, 2005, 20(1): 169-174. |
| [12] | 杨卫桥,干福熹,邓佩珍,徐军,李抒智,张荣. 用MOCVD法在LiGaO2(001)上生长GaN的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2003, 18(1): 215-219. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||