无机材料学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (2): 217-224.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250209 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20250209
曹娟1,2( ), 吴西士1,3(
), 吴西士1,3( ), 刘泽华1,3, 裴兵兵1,3, 韩建燊1,3, 刘欢1,3, 杨亦天1,3, 吴海波1,3, 黄政仁1,3(
), 刘泽华1,3, 裴兵兵1,3, 韩建燊1,3, 刘欢1,3, 杨亦天1,3, 吴海波1,3, 黄政仁1,3( )
)
收稿日期:2025-05-14
修回日期:2025-06-27
出版日期:2026-02-20
网络出版日期:2025-07-16
通讯作者:
吴西士, 副研究员. E-mail: wuxishi@nimte.ac.cn;作者简介:曹 娟(2000-), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: caojuan@nimte.ac.cn
基金资助:
CAO Juan1,2( ), WU Xishi1,3(
), WU Xishi1,3( ), LIU Zehua1,3, PEI Bingbing1,3, HAN Jianshen1,3, LIU Huan1,3, YANG Yitian1,3, WU Haibo1,3, HUANG Zhengren1,3(
), LIU Zehua1,3, PEI Bingbing1,3, HAN Jianshen1,3, LIU Huan1,3, YANG Yitian1,3, WU Haibo1,3, HUANG Zhengren1,3( )
)
Received:2025-05-14
Revised:2025-06-27
Published:2026-02-20
Online:2025-07-16
Contact:
WU Xishi, associate professor. E-mail: wuxishi@nimte.ac.cn;About author:CAO Juan (2000-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: caojuan@nimte.ac.cn
Supported by:摘要:
碳化硅(SiC)陶瓷因其优异的力学性能以及抗高温蠕变、耐酸碱腐蚀、高热导率等优良性能在半导体、核能、航空航天、海洋等领域得到广泛应用。然而, 脆性陶瓷材料的断裂强度通常表现出显著的离散性, 导致可靠性降低, 限制了其在工程结构中的应用。本研究通过调节晶粒尺寸, 提升了常压固相烧结碳化硅(SSiC)陶瓷的断裂强度可靠性。系统研究了晶粒尺寸对SSiC陶瓷力学性能、断裂强度Weibull分布以及裂纹扩展阻力曲线(R曲线)特征的影响, 深入分析了SSiC陶瓷断裂强度可靠性的调控机理。结果表明: 随着烧结温度从2100 ℃升高至2200 ℃, SSiC陶瓷平均晶粒尺寸从3.01 µm增大至8.45 µm, 晶粒尺寸分布均匀性系数从0.70减小至0.62; 同时, 随着平均晶粒尺寸从8.45 µm减小至3.01 µm, SSiC陶瓷断裂强度Weibull模数从8.5逐渐增大至12.2, 增幅达到44%, 表明晶粒细化对提高断裂强度可靠性具有积极作用。其主要原因在于高密度晶界网络通过裂纹分叉与桥接效应分散应力集中, 同时均匀的晶粒分布和较小的缺陷尺寸提升了裂纹扩展的能量阈值, 从而表现出上升的R曲线行为。本研究通过调控晶粒尺寸明显改善了SiC陶瓷的断裂强度可靠性, 有望推动SiC陶瓷材料更广泛的工程化应用。
中图分类号:
曹娟, 吴西士, 刘泽华, 裴兵兵, 韩建燊, 刘欢, 杨亦天, 吴海波, 黄政仁. 晶粒尺寸对常压固相烧结SiC陶瓷断裂强度Weibull分布的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(2): 217-224.
CAO Juan, WU Xishi, LIU Zehua, PEI Bingbing, HAN Jianshen, LIU Huan, YANG Yitian, WU Haibo, HUANG Zhengren. Influence of Grain Size on Weibull Distribution of Fracture Strength in Atmospheric-pressure Solid-phase Sintered SiC Ceramics[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2026, 41(2): 217-224.
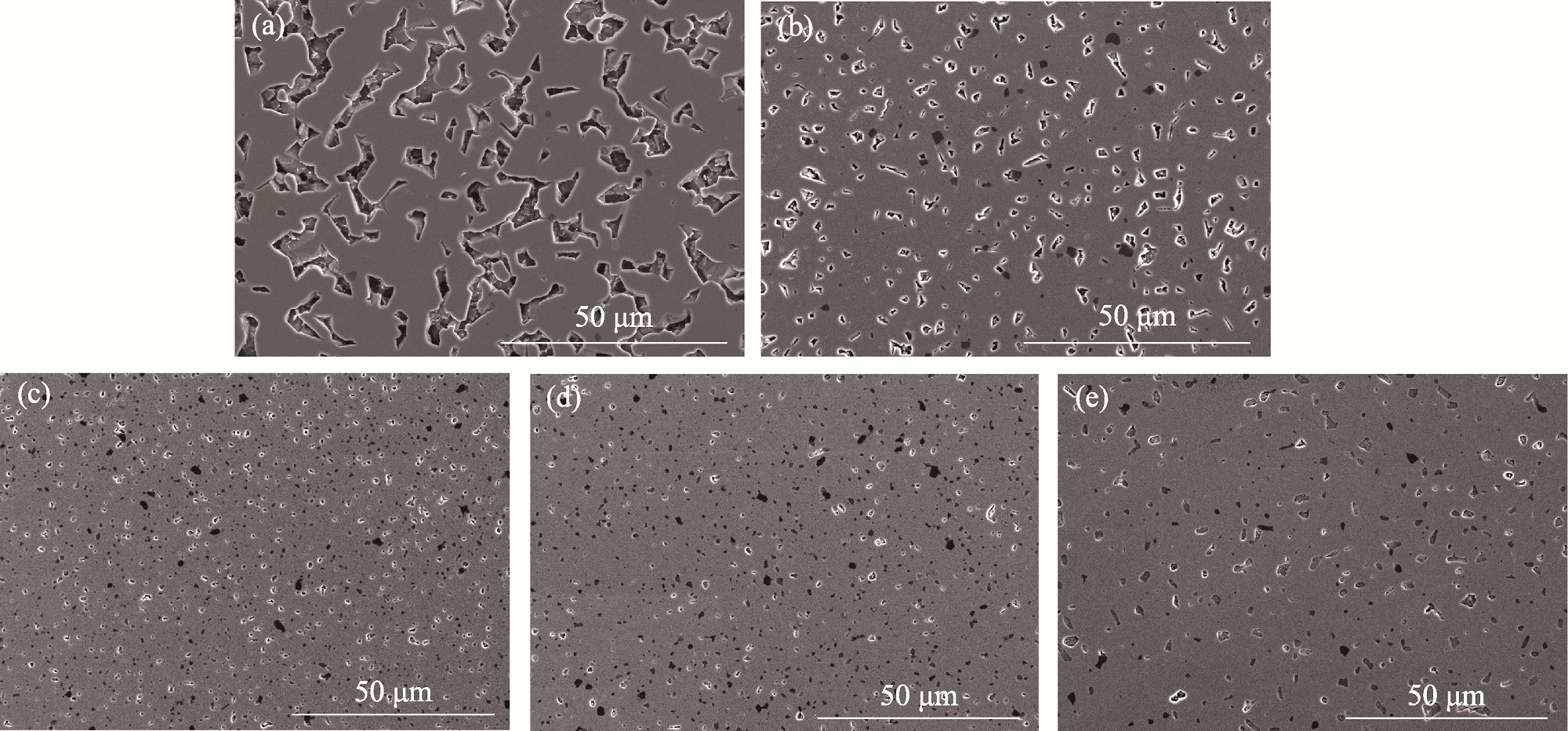
图3 不同温度烧结得到的SSiC陶瓷抛光表面形貌
Fig. 3 Polished surface morphologies of SSiC ceramics sintered at different temperatures (a) 2000 ℃; (b) 2050 ℃; (c) 2100 ℃; (d) 2150 ℃; (e) 2200 ℃
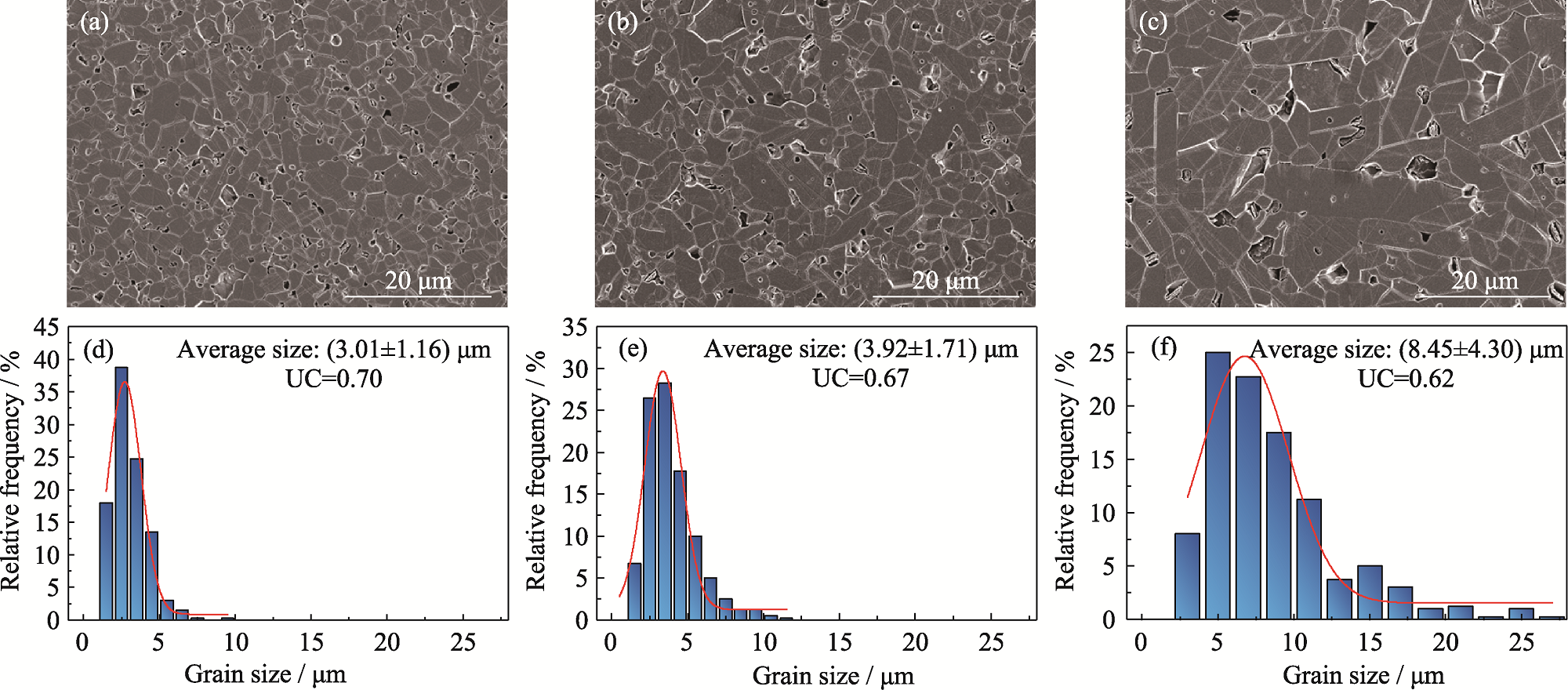
图4 熔融NaOH腐蚀后SSiC表面形貌(a~c)及晶粒分布(d~e)
Fig. 4 (a-c) Surface morphology and (d-e) grain distribution of SSiC after molten NaOH corrosion (a, d) SSiC-2100; (b, e) SSiC-2150; (c, f) SSiC-2200
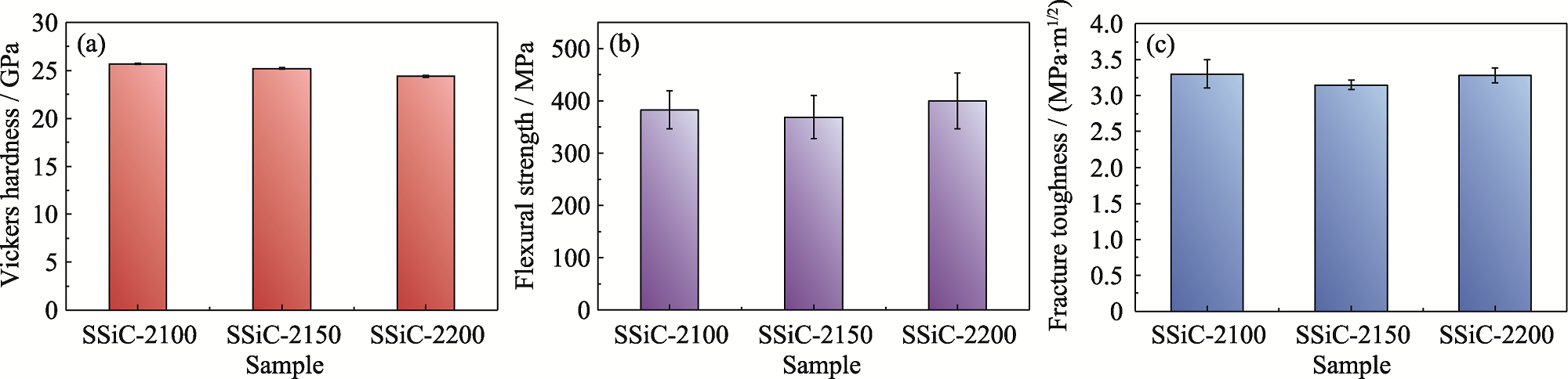
图5 不同晶粒尺寸SSiC陶瓷的力学性能
Fig. 5 Mechanical properties of SSiC ceramics with different grain sizes (a) Vickers hardness; (b) Flexural strength; (c) Fracture toughness
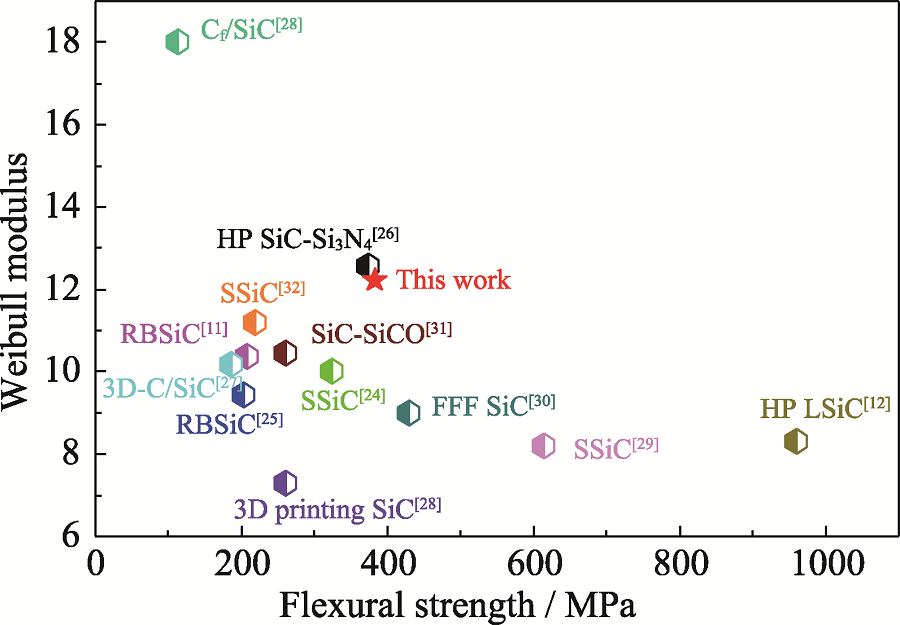
图8 文献中SiC基陶瓷材料弯曲强度及其Weibull模数与本工作对比[11-12,24 -32]
Fig. 8 Flexural strength and Weibull modulus of SiC-based ceramic materials reported in the literature versus in this work[11-12,24 -32]
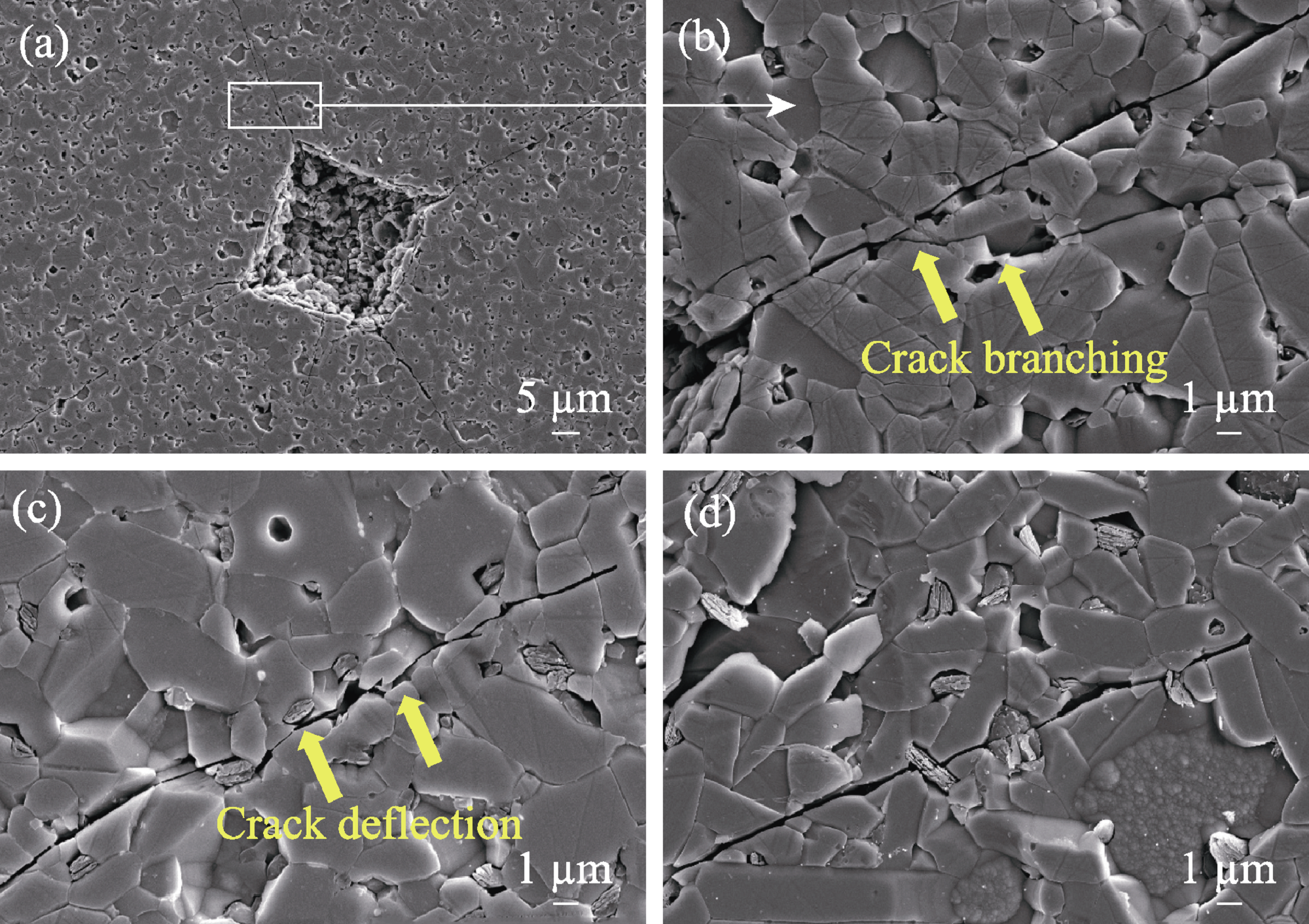
图11 不同晶粒尺寸SSiC陶瓷表面压痕裂纹扩展路径
Fig. 11 Surface indentation crack propagation path of SSiC ceramics at different grain sizes (a, b) SSiC-2100; (c) SSiC-2150; (d) SSiC-2200
| [1] |
HE R J, ZHOU N P, ZHANG K Q, et al. Progress and challenges towards additive manufacturing of SiC ceramic. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2021, 10(4): 637.
DOI |
| [2] |
HAO B Q, FAN L, LI K Y, et al. Hot oscillatory pressing of SiC ceramics with B4C and C as sintering additives. Ceramics International, 2024, 50(24): 53628.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
XIONG L J, WU Y J, CHEN Z F, et al. A combined stereolithography and a pressureless sintering method to prepare SiC ceramics. Ceramics International, 2025, 51(2): 2701.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
DING G J, HE R J, ZHANG K Q, et al. Dispersion and stability of SiC ceramic slurry for stereolithography. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(4): 4720.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
BAO Y W, SUN Y, KUANG F H, et al. Development and prospects of high strength pre-stressed ceramics. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(4): 399.
DOI |
| [6] | 龚江宏. 陶瓷材料脆性断裂的显微结构效应. 现代技术陶瓷, 2021, 42(Z2): 287. |
| [7] |
BOARDMAN S, PACKARD C E. Linking flexural strength and strength-limiting flaws in additively manufactured alumina with print parameter variations. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2024, 107(2): 1185.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
LIU C, AENGENHEISTER S, HERZOG S, et al. Application of Weibull theory to laser surface textured Al2O3. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(2): 1415.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
STEFAN F, NICO L, WALTER K, et al. Size effect of carbon fiber-reinforced silicon carbide composites (C/C-SiC): part 1-bending load and statistical effects. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(14): 6805.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
WEI C C, LIU Z, ZHANG Z Y, et al. High toughness and R-curve behaviour of laminated SiC/graphite ceramics. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(14): 22973.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
CHAUGULE P S, DU W C, KAMATH R R, et al. Reliability comparisons between additively manufactured and conventional SiC-Si ceramic composites. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2024, 107(5): 3117.
DOI URL |
| [12] | MATSUNAGA N, HIRATA Y, NAKAHAMA K, et al. Enhancement of strength of SiC by heat-treatment in air. Journal of Ceramic Processing Research, 2009, 10(3): 319. |
| [13] |
ROHIT M, YOUNGWOOK K. Effects of initial α-phase content on properties of pressureless solid-state sintered SiC ceramics. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2021, 19(2): 703.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
LI S, XIE Z P. Preparation of zirconia ceramics with high density and fine grains by oscillatory pressure sintering. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(02): 207.
DOI |
| [15] |
KUMAR K, KIM M J, PARK Y J, et al. Twofold increase in Weibull modulus of hot-pressed Si3N4 ceramic by modified pressing profile. Materials Today Communications, 2022, 32: 103979.
DOI URL |
| [16] | 胡传奇, 刘海林, 黄小婷, 等. 反应烧结碳化硅的显微结构和力学性能分析. 中国陶瓷工业, 2020, 27(5): 7. |
| [17] |
OSUCHUKWU O A, SALIHI A, IBRAHIM A, et al. Weibull analysis of ceramics and related materials: a review. Heliyon, 2024, 10(12): e32495.
DOI URL |
| [18] | 刘镇.高韧性层状氮化硅陶瓷材料的制备及性能研究. 淄博: 山东理工大学硕士学位论文, 2021. |
| [19] |
COOK R F, LAWN B R, FAIRBANKS C J. Microstructure- strength properties in ceramics: I, effect of crack size on toughness. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1985, 68(11): 604.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
ANSTIS G R, CHANTIKUL P, LAWN B R, et al. A critical evaluation of indentation techniques for measuring fracture toughness: I, direct crack measurements. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1981, 64(9): 533.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
DAI P Y, WANG Y Z, LIU G L, et al. Fabrication of highly dense pure SiC ceramics via the HTPVT method. Acta Materialia, 2011, 59(16): 6257.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
ZHANG C G, HU X Z, SERCOMBE T, et al. Prediction of ceramic fracture with normal distribution pertinent to grain size. Acta Materialia, 2018, 145: 41.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
ZHANG Z F, SHA J J, ZU Y F, et al. Fabrication and mechanical properties of self-toughening ZrB2-SiC composites from in-situ reaction. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2019, 8(4): 527.
DOI |
| [24] | WEI S, XIE Z P, XUE W J, et al. How does pore-induced crack change as temperatures decrease from 293 K to 77 K. Ceramics International, 2015, 41(10): 15246. |
| [25] |
AROATI S, CAFRI M, DILMAN H, et al. Preparation of reaction bonded silicon carbide (RBSC) using boron carbide as an alternative source of carbon. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2011, 31(5): 841.
DOI URL |
| [26] | VYSOCKA A, SPAKOVA J, DUSZA J, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of liquid-phase-sintered SiC-Si3N4 composites. Kovove Materialy, 2007, 45(4): 223. |
| [27] | SURESH K, SWEETY K, ANIL K, et al. Mechanical properties of LSI based 3D-stitched-C-SiC composites prepared by coal-tar pitch as carbon precursor. Scripta Materialia, 2007, 58(10): 826. |
| [28] |
KAUFMAN J, WYCKOFF C, LAM B, et al. Analysis of fiber-reinforced silicon carbide formed via material extrusion. Additive Manufacturing, 2024, 90: 104333.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
WANG X H, HIRATA Y. Influence of polyacrylic acid on rheology of SiC suspension and mechanical properties of densified SiC. Ceramics International, 2005, 31(5): 677.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
GAUTHE M, LORRETTE C, CHAFFRON L, et al. Fused filament fabrication of silicon carbide parts: a strategy for producing high-strength components. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2025, 45(7): 117229.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
ZHU N N, ZHANG L J, WEN G W, et al. Effect of SiC whiskers on the mechanical properties of polymer-derived ceramics prepared by digital light processing and its strengthening and toughening mechanism. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2023, 968: 171852.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
JANA D C, BARICK P, SAHA B P. Effect of sintering temperature on density and mechanical properties of solid-state sintered silicon carbide ceramics and evaluation of failure origin. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2018, 27: 2960.
DOI |
| [1] | 王康龙, 殷杰, 陈晓, 王力, 刘学建, 黄政仁. 颗粒级配对选区激光烧结打印结合常压固相烧结制备碳化硅陶瓷性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 754-760. |
| [2] | 王博, 蔡德龙, 朱启帅, 李达鑫, 杨治华, 段小明, 李雅楠, 王轩, 贾德昌, 周玉. SrAl2Si2O8增强BN陶瓷的力学性能及抗热震性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(10): 1182-1188. |
| [3] | 王新健, 朱逸璇, 张鹏, 杨文龙, 王挺, 郇宇. (Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Ti0.9Zr0.1-xSnx)O3无铅压电陶瓷的相结构与压电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(5): 513-519. |
| [4] | 李江, 丁继扬, 黄新友. 稀土离子掺杂Gd2O2S闪烁陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(8): 789-806. |
| [5] | 黄咏安, 路标, 邹艺轩, 李丹丹, 姚英邦, 陶涛, 梁波, 鲁圣国. 晶粒尺寸对细晶钛酸钡陶瓷介电、压电和铁电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(7): 767-772. |
| [6] | 黄毅华, 江东亮, 陈忠明, 刘学建, 张先锋, 廖振魁, 黄政仁. rGO/SiC复合材料的制备与性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(11): 1147-1153. |
| [7] | 刘泽华, 齐 倩, 闫永杰, 张 辉, 刘学建, 罗宏杰, 黄政仁. 残余相和烧结温度对碳化硅陶瓷抗混酸腐蚀特性的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(6): 661-666. |
| [8] | 杨 晓, 刘学建, 黄政仁, 刘桂玲, 姚秀敏. 维氏压痕对常压固相烧结碳化硅陶瓷材料力学性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2012, 27(9): 965-969. |
| [9] | 张荣军, 杨延清, 沈文涛. 三级化学气相沉积法制备SiC纤维及拉伸性能测试[J]. 无机材料学报, 2010, 25(8): 840-844. |
| [10] | 蔚 翠, 朱铁军, 肖 凯, 金 吉, 沈俊杰, 杨胜辉, 赵新兵. 快速凝固法制备ZrNiSn基Half-Heusler热电材料的微结构[J]. 无机材料学报, 2010, 25(6): 569-572. |
| [11] | 钟朝位,梁 剑,张树人,张韶华,李 波. 烧结技术对99BeO陶瓷材料结构与性能影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2010, 25(4): 415-428. |
| [12] | 刘艳辉,汪洋,孟亮. 晶粒尺寸对FeS2薄膜微应变及光吸收特性的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2007, 22(1): 143-147. |
| [13] | 吕东生,李伟善,唐仁衡,肖方明. 双辊淬冷法制备稀土镍基贮氢合金及其晶粒尺寸和电化学性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2005, 20(4): 859-863. |
| [14] | 柯华,许雪芹,王文,贾德昌,周玉. 溶胶-凝胶法制备纳米SrBi2Ta2O9的晶化过程和晶粒长大研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2005, 20(2): 373-378. |
| [15] | 郜剑英,江莞,王刚. La2O3掺杂MoSi2的SHS合成及其性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2004, 19(6): 1334-1338. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||