无机材料学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (7): 809-816.DOI: 10.15541/jim20190502 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20190502
所属专题: 能源材料论文精选(四):光催化与电催化(2020)
收稿日期:2019-09-30
修回日期:2019-12-28
出版日期:2020-07-20
网络出版日期:2020-03-03
作者简介:张翊青(1995-), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: zhangyq95@163.com基金资助:
ZHANG Yiqing,ZHANG Shujuan,WAN Zhengrui,MO Han,WANG Niangui( ),ZHOU Liqun(
),ZHOU Liqun( )
)
Received:2019-09-30
Revised:2019-12-28
Published:2020-07-20
Online:2020-03-03
Supported by:摘要:
开发高效廉价的催化剂对于清洁能源经济至关重要, 将氨硼烷的催化水解用于氢能源开发前景广阔。本工作首先采用简单回流法制备BiVO4纳米片, 再通过浸渍还原法制备出Ru/Fe不同摩尔比的RuFe@BiVO4催化剂, 并在室温下用于催化氨硼烷水解产氢。通过比较载体BiVO4、Ru@BiVO4、Fe@BiVO4、RuFe@BiVO4以及无载体的RuFe纳米粒子的催化产氢速率发现, 在所有的催化剂中, Ru1Fe0.1@BiVO4具有最高的催化活性, 非贵金属Fe能显著增强Ru的催化性能, 这与RuFe之间强的电子效应以及RuFe纳米粒子与载体BiVO4间的双功能效应密切相关, 其活化能(Ea)为43.7 kJ·mol-1, 转化频率(TOF)为205.4 molH2·molRu·min-1。
中图分类号:
张翊青,张淑娟,万正睿,莫晗,王念贵,周立群. RuFe纳米粒子修饰片状BiVO4协同催化氨硼烷水解产氢[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(7): 809-816.
ZHANG Yiqing,ZHANG Shujuan,WAN Zhengrui,MO Han,WANG Niangui,ZHOU Liqun. RuFe Nanoparticles Modified Sheet-like BiVO4 : High-efficient Synergistic Catalyst for Ammonia Borane Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(7): 809-816.
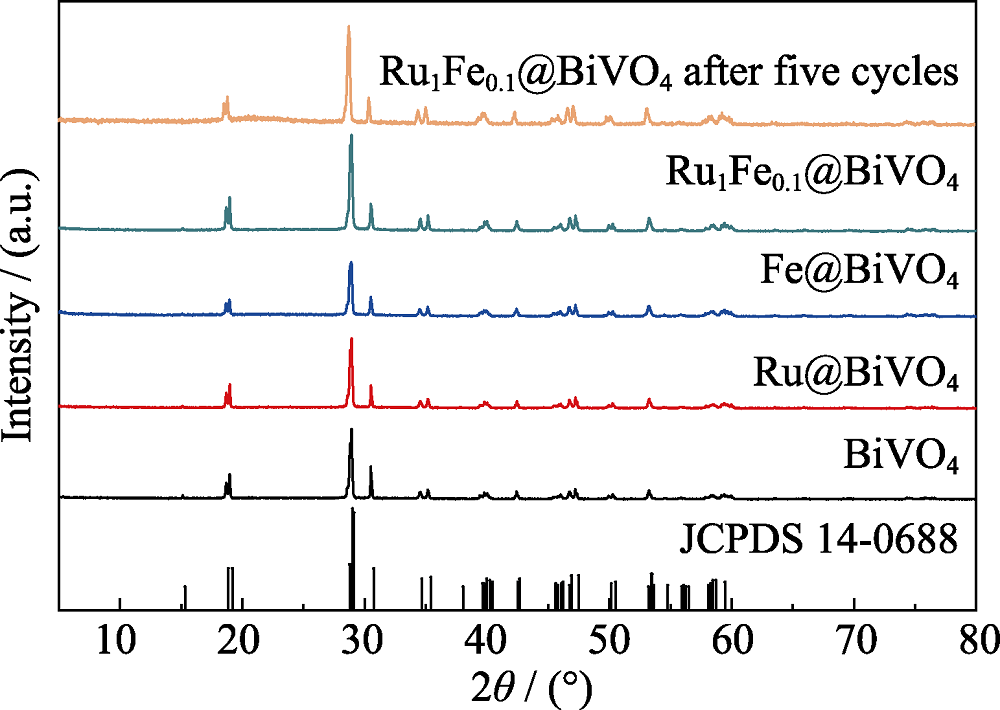
图1 BiVO4、Ru@BiVO4、Fe@BiVO4、Ru1Fe0.1@BiVO4和五次循环后Ru1Fe0.1@BiVO4的XRD图谱
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of BiVO4, Ru@BiVO4, Fe@BiVO4, Ru1Fe0.1@BiVO4 and Ru1Fe0.1@BiVO4 after five cycles
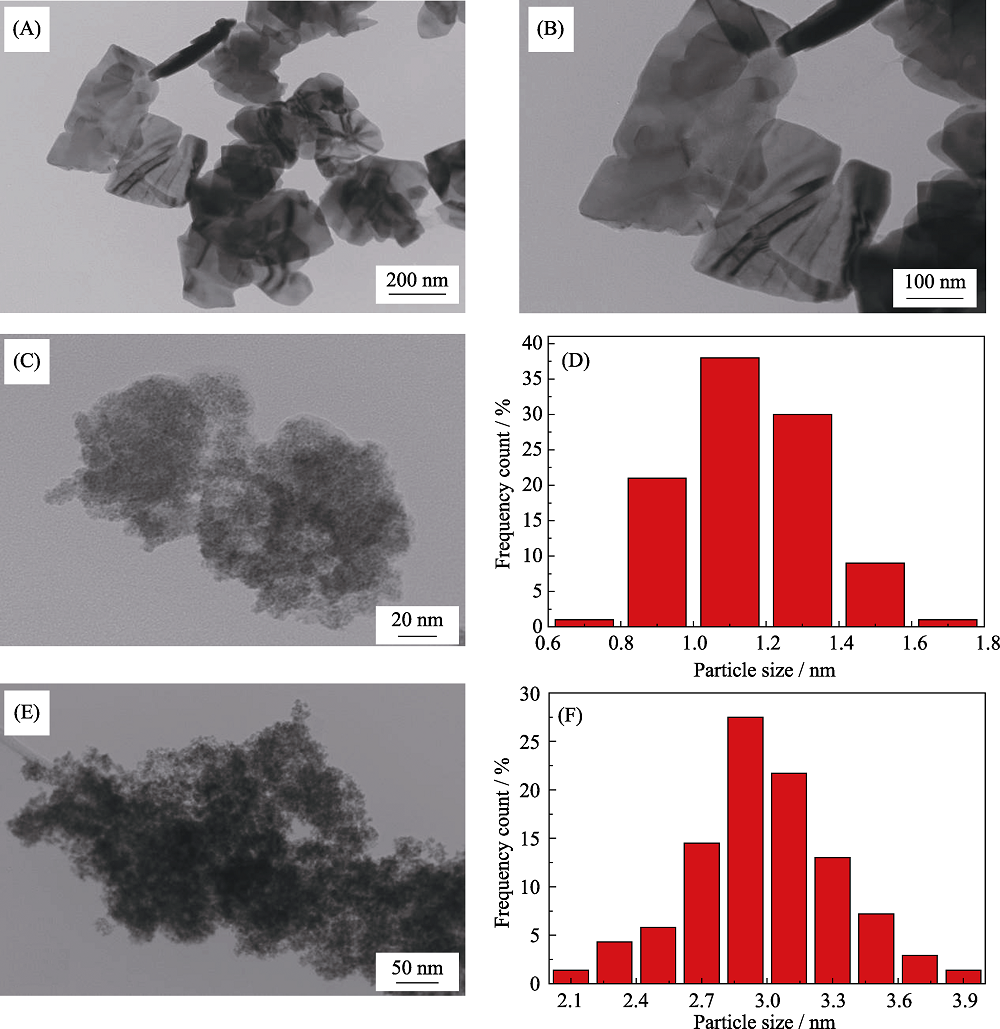
图2 BiVO4(A, B)、Ru1Fe0.1@BiVO4(C)和RuFe纳米粒子(E)的TEM照片; Ru1Fe0.1@BiVO4(D)、RuFe纳米粒子(F)的粒径分布图
Fig. 2 TEM images of BiVO4 (A, B), Ru1Fe0.1@BiVO4 (C) and RuFe NPs (E); particle size distributions of Ru1Fe0.1@BiVO4 (D) and RuFe NPs (F)
| Catalyst | Initial ratio of Ru : Fe | Actual ratio of Ru : Fe | Actual Ru loading/wt% |
|---|---|---|---|
| RuFe@BiVO4 | 1 : 0.10 | 1 : 0.12 | 4.21 |
表1 RuFe@BiVO4催化剂中元素的ICP-AES分析结果
Table 1 ICP-AES analyses results of RuFe@BiVO4 catalyst
| Catalyst | Initial ratio of Ru : Fe | Actual ratio of Ru : Fe | Actual Ru loading/wt% |
|---|---|---|---|
| RuFe@BiVO4 | 1 : 0.10 | 1 : 0.12 | 4.21 |
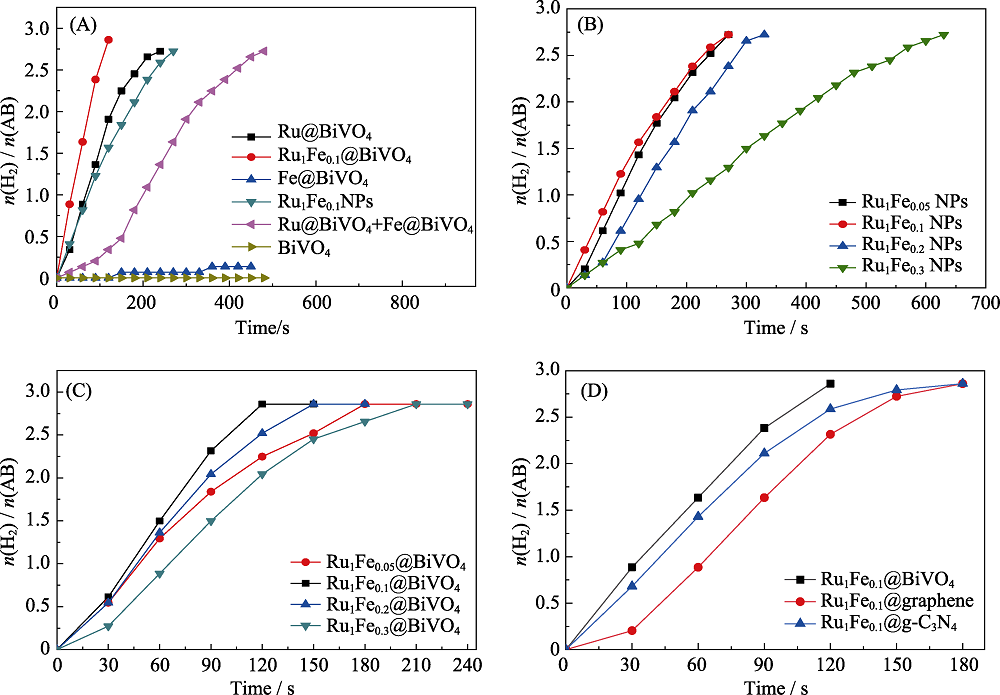
图6 不同催化剂对AB水解产氢速率图
Fig. 6 Plots of n(H2)/n(AB) vs. time from the hydrolysis of AB (18.5 mg) (A) Catalysts with the same nanoparticles loadings; (B) Ru1Fex NPs; (C) Ru1Fex@BiVO4 ; (D) Catalysts with different supporters
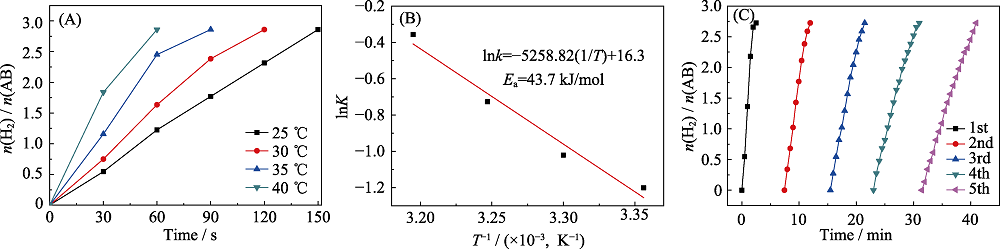
图8 温度对Ru1Fe0.1@BiVO4催化水解氨硼烷的影响曲线(A)及其相应的阿伦尼乌斯图(B), 催化剂五次循环稳定性(C)
Fig. 8 Plots of n(H2)/n(AB) vs. time for the hydrolysis of AB catalyzed by Ru1Fe0.1@BiVO4 at different temperatures(A) and corresponding Arrhenius plots (B), and cycling test for the Ru1Fe0.1@BiVO4 within five cycles (C)
| Catalyst | TOF/(molH2?molRu?min-1) | Ea/(kJ?mol-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ru NPs | 26.7 | 66.5 | [ |
| RuCu(1 : 1)/γ-Al2O3 | 16.4 | 52 | [ |
| RuCo(1 : 11)/γ-Al2O3 | 32.9 | 47.0 | [ |
| RuCuCo@MIL-101 | 241.2 | 48.0 | [ |
| Ru@g-C3N4 | 313.0 | 37.4 | [ |
| RuCu/graphene | 135.0 | 30.6 | [ |
| Ru1Fe0.1@BiVO4 | 205.4 | 43.7 | This study |
表2 不同钌基催化剂用于AB水解脱氢的催化活性
Table 2 Catalytic activities of different Ru-based catalysts used for the hydrolytic dehydrogenation of AB
| Catalyst | TOF/(molH2?molRu?min-1) | Ea/(kJ?mol-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ru NPs | 26.7 | 66.5 | [ |
| RuCu(1 : 1)/γ-Al2O3 | 16.4 | 52 | [ |
| RuCo(1 : 11)/γ-Al2O3 | 32.9 | 47.0 | [ |
| RuCuCo@MIL-101 | 241.2 | 48.0 | [ |
| Ru@g-C3N4 | 313.0 | 37.4 | [ |
| RuCu/graphene | 135.0 | 30.6 | [ |
| Ru1Fe0.1@BiVO4 | 205.4 | 43.7 | This study |
| [1] |
EDWARDS P P, KUZNETSOV V L, DAVID W I F, et al. Hydrogen and fuel cells: towards a sustainable energy future. Energy Policy, 2008,36(12):4356-4362.
DOI URL |
| [2] | EBERLE U, FELDERHOFF M, SCHUETH F. ChemInform abstract: chemical and physical solutions for hydrogen storage. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2009,40(48):6608-6630. |
| [3] |
CHANDRA M, XU Q. A high-performance hydrogen generation system: transition metal-catalyzed dissociation and hydrolysis of ammonia-borane. Journal of Power Sources, 2006,156(2):190-194.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
YANG J, SUDIK A, WOLVERTON C, et al. High capacity hydrogen storage materials: attributes for automotive applications and techniques for materials discovery. Chemical Society Review, 2010,39(2):656-675.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
GROCHALA W, EDWARDS P P. Thermal decomposition of the non-interstitial hydrides for the storage and production of hydrogen. Chemical Reviews, 2004,104(3):1283-1316.
DOI URL PMID |
| [6] |
SUN D, MAZUMDER V, ÖNDER METIN, et al. Catalytic hydrolysis of ammonia borane via cobalt palladium nanoparticles. ACS Nano, 2011,5(8):6458-6464.
DOI URL PMID |
| [7] |
CHEN G, DESINAN S, RENZO R, et al. Synthesis of Ni-Ru alloy nanoparticles and their high catalytic activity in dehydrogenation of ammonia borane. Chemistry - A European Journal, 2012,18(25):7925-7930.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
QU XIAO-PENG, YU ZHI-QIANG, LI ZE-PING, et al. CoRh nanoparticles supported on ZIF-67 as highly efficient catalysts for hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia boranes for chemical hydrogen storage. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(51), 30037-30047.
DOI URL |
| [9] | ZHANG L, ZHOU LI-QUN, YANG KUN-ZHOU, et al. Pd-Ni nanoparticles supported on MIL-101 as high-performance catalysts for hydrogen generation from ammonia borane. Journal of Alloys & Compounds, 2016,677:87-95. |
| [10] |
CHEN MENG-HUAN, ZHOU LI-QUN, LU DI, et al. RuCo bimetallic alloy nanoparticles immobilized on multi-porous MIL-53(Al) as a highly efficient catalyst for the hydrolytic reaction of ammonia borane. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018,43(3):1439-1450.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
LI JUN, ZHU QI-LONG, XU QIANG. Non-noble bimetallic CuCo nanoparticles encapsulated in the pores of metal-organic frameworks: synergetic catalysis in the hydrolysis of ammonia borane for hydrogen generation. Catal. Sci. Technol., 2015,5(1):525-530.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
ZHANG XIN-BO, YAN JUN-MIN, HAN SONG, et al. Magnetically recyclable Fe@Pt core-shell nanoparticles and their use as electrocatalysts for ammonia borane oxidation: the role of crystallinity of the core. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2009,131(8):2778-2779.
DOI URL PMID |
| [13] |
WETCHAKUN N, CHAIWICHAIN S, INCEESUNGVORN B, et al. BiVO4/CeO2 nanocomposites with high visible-light-induced photocatalytic activity. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2012,4(7):3718-3723.
DOI URL PMID |
| [14] |
ABDI F F, SAVENIJE T J, MAY M M, et al. The origin of slow carrier transport in BiVO4 thin film photoanodes: a time-resolved microwave conductivity study. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2013,4(16):2752-2757.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
DAVID W I F, WOOD I G. Ferroelastic phase transition in BiVO4 : VI. Some comments on the relationship between spontaneous deformation and domain walls in ferroelastics. Journal of Physics C: Solid State Physics, 1983,16(26):5149-5166.
DOI URL |
| [16] | WANG S, CHEN P, BAI Y., et al. New BiVO4 dual photoanodes with enriched oxygen vacancies for efficient solar-driven water splitting. Advanced Materials, 2018,30(20):8500-8504. |
| [17] |
XI G, YE J. Synthesis of bismuth vanadate nanoplates with exposed {001} facets and enhanced visible-light photocatalytic properties. Chemical Communications, 2010,46(11):1893-1895.
DOI URL PMID |
| [18] |
ZHOU L, WANG W Z, ZHANG L S, et al. Single-crystalline BiVO4 microtubes with square cross-sections: microstructure, growth mechanism, and photocatalytic property. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2007,111(37):13659-13664.
DOI URL |
| [19] | YANG K, ZHOU L, YU G, et al. Ru nanoparticles supported on MIL-53(Cr, Al) as efficient catalysts for hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of ammonia borane. Internal Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2016,41(15):6300-6309. |
| [20] |
CAO N, SU J, LUO W, et al. Ni-Pt nanoparticles supported on MIL-101 as highly efficient catalysts for hydrogen generation from aqueous alkaline solution of hydrazine for chemical hydrogen storage. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014,39(18):9726-9734.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
DAI Z R, PAN Z W, WANG Z L. Gallium oxide nanoribbons and nanosheets. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2002,106(5):902-904.
DOI URL |
| [22] | RAKAP M. PVP-stabilized Ru-Rh nanoparticles as highly efficient catalysts for hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of ammonia borane. Journal of Alloys & Compounds, 2015,649:1025-1030. |
| [23] |
TAN PING-LIAN. Active phase, catalytic activity, and induction period of Fe/zeolite material in nonoxidative aromatization of methane. Journal of Catalysis, 2016,338:21-29.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
ZHANG L, CHEN D, JIAO X. Monoclinic structured BiVO4 nanosheets: hydrothermal preparation, formation mechanism, and coloristic and photocatalytic properties. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2006,110(6):2668-2673.
DOI URL PMID |
| [25] |
WANG Y, TAN G, LIU T, et al. Photocatalytic properties of the g-C3N4/{010} facets BiVO4, interface Z-Scheme photocatalysts induced by BiVO4, surface heterojunction. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2018,234:37-49.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
NING HONG-HUI LU DI ZHOU LI-QUN, et al. Bimetallic RuM(M=Co, Ni) alloy NPs supported on MIL-110(Al): synergetic catalysis in hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane. Chinese Journal of Chemical Physics, 2018,31(1):99-109.
DOI URL |
| [27] | LI Y, DAI Y, TIAN X K. Controlled synthesis of monodisperse PdxSn100-x nanoparticles and their catalytic activity for hydrogen generation from the hydrolysis of ammonia-borane. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2015,40(30):9235-9243. |
| [28] |
WANG QI, FU FANG-YU, YANG SHA, et al. Dramatic synergy in CoPt nanocatalysts stabilized by “click” dendrimers for hydrogen evolution from hydrolysis of ammonia borane. ACS Catalysis, 2019,9(2):1110-1119.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
CAO N, LIU T, SU J, et al. Ruthenium supported on MIL-101 as an efficient catalyst for hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of amine boranes. New Journal of Chemistry, 2014,38(9):4032-4035.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
ZHOU Q, YANG H, XU C. Nanoporous Ru as highly efficient catalyst for hydrolysis of ammonia borane. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2016,41(30):12714-12721.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
RACHIERO G P, DEMIRCI U B, MIELE P. Bimetallic RuCo and RuCu catalysts supported on γ-Al2O3. A comparative study of their activity in hydrolysis of ammonia-borane. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2011,36(12):7051-7065.
DOI URL |
| [32] | YANG K, ZHOU L, XING X, et al. RuCuCo nanoparticles supported on MIL-101 as a novel highly efficient catalysts for the hydrolysis of ammonia borane. Microporous & Mesoporous Materials, 2016,225:1-8. |
| [33] |
FAN YAN-RU, LI XIAO-JING, HE XIAO-CHUN, et al. Effective hydrolysis of ammonia borane catalyzed by ruthenium nanoparticles immobilized on graphic carbon nitride. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014,39(35):19982-19989.
DOI URL |
| [34] | CAO N, KAI H U, LUO W, et al. RuCu nanoparticles supported on graphene: a highly efficient catalyst for hydrolysis of ammonia borane. Journal of Alloys & Compounds, 2014,590(27):241-246. |
| [1] | 吐尔洪·木尼热, 赵红刚, 马玉花, 齐献慧, 李钰宸, 闫沉香, 李佳文, 陈平. 单晶WO3/红磷S型异质结的构建及光催化活性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 701-707. |
| [2] | 陈瀚翔, 周敏, 莫曌, 宜坚坚, 李华明, 许晖. CoN/g-C3N4 0D/2D复合结构及其光催化制氢性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 1001-1008. |
| [3] | 胡越, 安琳, 韩鑫, 侯成义, 王宏志, 李耀刚, 张青红. RhO2修饰BiVO4薄膜光阳极的制备及其光电催化分解水性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(8): 873-882. |
| [4] | 徐晶威,李政,王泽普,于涵,何祺,付念,丁帮福,郑树凯,闫小兵. 交错能带结构钕掺杂钒酸铋形貌与光催化性能调控[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(7): 789-795. |
| [5] | 张翊青, 刘梨, 张淑娟, 万正睿, 刘红英, 周立群. NH2-UIO-66负载RuCuMo纳米催化剂的制备及其催化产氢[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(12): 1316-1324. |
| [6] | 周民杰, 张 娜, 侯朝辉. 石墨烯-ZnIn2S4纳米复合微球的制备及光催化产氢活性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(7): 713-718. |
| [7] | 王 敏, 刘 琼, 孙亚杰, 车寅生, 姜承志. 溶胶-凝胶法制备Eu3+掺杂BiVO4及其可见光光催化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2013, 28(2): 153-158. |
| [8] | 郭 佳, 朱 毅, 张渊明, 李明玉, 杨 骏. 不同结构形貌BiVO4的水热制备及可见光催化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2012, 27(1): 26-32. |
| [9] | 阎建辉,张 丽,朱裔荣,唐有根,杨海华. NiO(CoO)/N-SrTiO3异质结型复合光催化剂的制备及模拟太阳光催化产氢[J]. 无机材料学报, 2009, 24(4): 666-670. |
| [10] | 戈 磊,张宪华. 微乳液法合成新型可见光催化剂BiVO4及光催化性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2009, 24(3): 453-456. |
| [11] | 戈磊. 新型Pt/BiVO4可见光活性光催化剂的制备和表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2008, 23(3): 449-453. |
| [12] | 朱裔荣,唐有根,阎建辉,刘 强. 氮掺杂SrTiO3的制备及其可见光催化产氢活性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2008, 23(3): 443-448. |
| [13] | 张林森,王为,李振亚. Ni/AC膜电极-铝合金储氢电池的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2006, 21(5): 1103-1108. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||