晶体材料已广泛应用于能源、环境、信息、医疗、军事等领域, 在人类社会发展中起着举足轻重的作用[1]。我国人工晶体材料的研究开创于20世纪50年代中期, 经历从无到有、从实验室研发到大规模产业化, 进展相当迅速[2]。近年来, 随着高新技术的飞速发展, 大尺寸、高品质晶体材料已成为制约相关行业发展的瓶颈。2021年, 中国科学技术协会在第二十三届中国科协年会闭幕式上发布了10个对科学发展具有导向作用的前沿科学问题,其中中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院提出的“如何突破大尺寸晶体材料的制备理论和技术”居十个前沿科学问题的首位, 说明大尺寸晶体材料制备方面的基础科学问题已经成为制约该行业快速发展的关键[3]。
材料结晶是一个物质发生相变的复杂过程[4],晶体生长的典型方法包括气相、溶液和熔体法, 均涉及到籽晶在生长界面处的成核和生长过程[5]。晶体生长过程涉及复杂的物理和化学问题, 大尺寸晶体生长更涉及到不同尺度上的相变、界面变化、缺陷形成与增殖机理。工业生产层面亟需根据晶体生长原理和技术建立可靠的结晶工艺, 设计可计量的智能化、数字化晶体生长装备。化学、物理学、数学、材料学和工程等相关领域科学家共同努力提出了晶体平衡形态理论、界面理论模型、结晶生长的化学键合理论等来解决晶体生长过程中工程问题。材料结晶模型是以相图为基础, 确定材料的组成与相关物理化学参数, 结合材料结晶理论和生长方法共同制备大尺寸晶体材料[6]。基础科学研究领域还需要研究晶体材料的多尺度结晶生长新理论, 准确定量描述成核与生长过程, 综合考虑晶体生长过程中的跨尺度热力学和动力学。
结晶过程中的原位观测与测量技术可为发展结晶理论和控制晶体品质提供重要的实验证据。计算模拟结晶过程解决了某些过程无法实验验证的难题。本文主要总结结晶过程中采用的原位方法和多尺度计算模拟技术,期望在大尺寸晶体材料生长过程中能够结合计算模拟与原位表征, 最终实现量化整个晶体生长周期, 为优化生长工艺和控制品质提供数据支持。
1 结晶生长的化学键合理论及大尺寸稀土晶体快速生长方法
晶体生长理论包括热力学和动力学两大方面, 经过多年的发展形成了很多优秀的理论成果。由于结晶过程的复杂性, 很难为实际晶体生长提出一个完备的理论模型。在国家标准《人工晶体材料术语》(GB/T 39131-2020)[7]中规定了部分晶体和生长机理的定义, 例如:
1)结晶生长的化学键合理论是指利用三相区描述生长过程, 在过渡相区, 结晶学结构和结晶环境共同决定生长界面处的离子/分子排布, 进一步决定化学键合模式。
2)多尺度结晶生长界面处溶液/熔体中晶体组成之间不同聚集态的能量分布诱导的结晶过程。
3)快速生长是指在动力学控制的实际生长中, 优化生长参数使生长界面处晶体组成间聚集态的能量分布接近于热力学生长状态, 从而提高生长速率, 并接近于热力学生长速率。
4)稀土晶体是指稀土元素可以完整占据结晶学结构中某一格点的晶体。
图1
2 原位显微技术研究晶体生长过程
2.1 原位光学显微镜
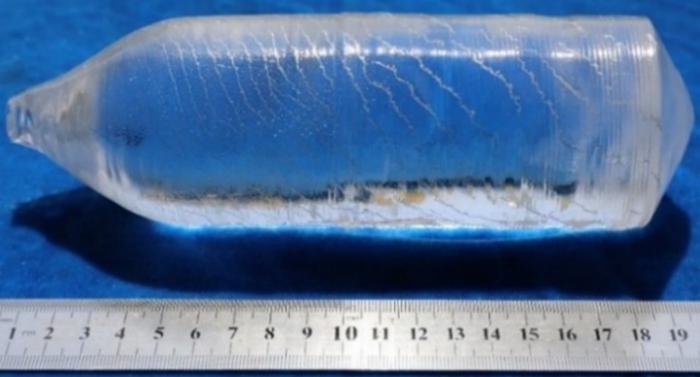
图2
图2
KDP生长结晶的原位光学显微镜照片
Fig. 2
In-situ optical microscope crystallization images of KDP growth
(a) By optical microscope; (b) By camera
另一种使用激光作为光源的显微镜也可以原位表征高温晶体的生长行为。高温激光共聚焦扫描显微镜(High-temperature laser scanning confocal microscopy)使用卤素灯作为加热源, 具有快速升温(1200 K/min)和降温(3000 K/min)的功能。近年来其常被用来原位研究高温熔体的结晶和生长行为, 例如不同气氛、不同降温速率条件下的凝固和相转变机制[12]。
2.2 电子显微镜
扫描电子显微镜(Scanning electronic microscopy, SEM)是材料研究的主要表征手段, 相比较光学显微镜可以在更小尺度观测材料特征。通过合适的结晶腔室设计, SEM可以原位观测到晶体生长过程的界面形貌和形态转变, 帮助探究晶体成核与生长机理。利用原位SEM观察分子束外延砷化镓和硅生长的初始阶段, 可以显示10 nm~100 μm范围内的原子台阶和二维岛。实验成功观测了取决于吸附原子扩散长度和台阶尺寸的不同生长模式, 真实空间图像分为二维岛成核、台阶流和不稳定台阶流[13]。通过环境SEM观测到六方冰晶在过饱和水蒸气环境中通过台阶生长形成。这些台阶来自两个不同的起源, 即螺钉位错位和初始台阶[14]。但是受技术限制, 用SEM观测高温熔体结晶过程还鲜有报道。
透射电子显微镜(Transmission electron microscope, TEM)比SEM具有更高的电子能量, 可以进行原子分辨率表征[15]。相较于原位SEM, 原位TEM可以获取更多的微观信息。该技术在溶液法纳米材料结晶机理研究得到了广泛应用, 但对高温熔体结晶研究相对较少[16]。采用HRTEM(High resolution transmission electron microscope)观察浮区硅熔融凝固过程中的结晶行为, 发现在高温下形成的点缺陷簇[17]。{111}液固界面通过一对具有几个原子高度的台阶的横向移动来扩展, 而{100}液固界面可以保持平坦的形貌并在两个端面之间延伸。在大约20层台阶处观察到结晶的{111}液-固界面。
SEM和TEM只能在高真空条件下进行, 所以实验样品需要在强电子束下保持稳定, 并且高温下的原位实验过程中必须保证样品位置不变, 这些因素限制了可探究的结晶体系。
2.3 原子力显微镜
原子力显微镜(Atomic force microscope, AFM)通过固体探针与样品表面之间的原子间相互作用力来研究样品的表面结构[18]。AFM可以研究结晶过程中的台阶、表面缺陷、形貌演化以及生长动力学等。但是AFM空间和时间分辨率比电子显微镜要差, 还要注意AFM探针尖可能会对结晶体系产生影响。
3 原位光谱技术研究晶体生长过程
3.1 红外光谱
作为一种振动光谱, 傅里叶变换红外光谱(Fourier transform infrared, FTIR)能反映材料化学键的变化信息[22-23]。再加上设备的易操作性, FTIR可作为研究晶体生长机制的原位监测技术。采用衰减全反射傅里叶变换红外光谱(Attenuated total internal reflectance Fourier transform infrared, ATR-FTIR)可以在结晶过程中原位测量溶液的浓度、过饱和度、溶解度以及介稳极限, 并且具有足够的准确度[24]。Xue等[25-26]利用ATR-FTIR研究了NH4H2PO4(ADP)、KH2PO4(KDP)的结晶过程。原位ATR-FTIR可以实时记录结晶过程中基团的变化及键的断裂与形成, 如ADP、KDP等晶体, 为水溶液中分子晶体结晶过程及其化学键性质提供一定策略。并且,原位ATR-FTIR能够观测到晶体结构变化[27], 鉴定结晶过程中的结构转变, 这有利于研究结晶过程中的系统动力学[28-29]。
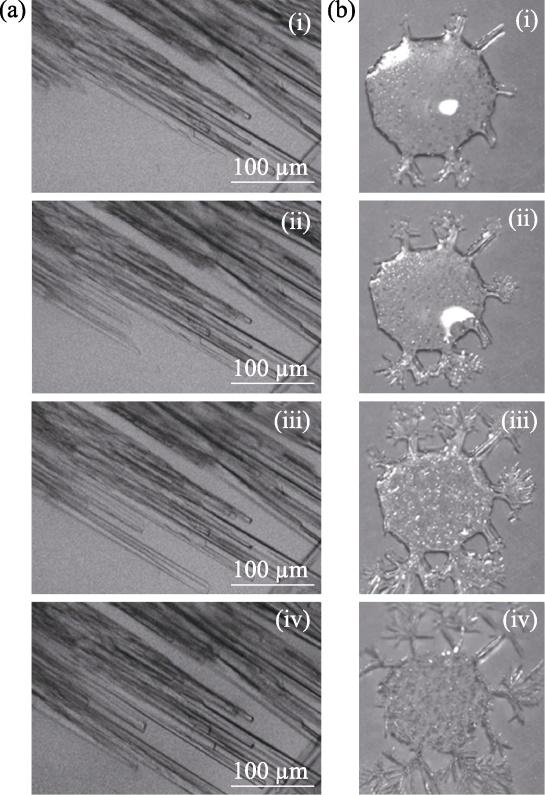
图3
图3
水合碳酸钙结晶的红外光谱[31]
Fig. 3
Crystallization spectrum of hydrated calcium carbonate[31]
(a) FTIR spectra of calcium carbonate monohydrate (blue spectrum) and aCCM (black spectrum); (b) Schematic representation of different vibrational modes; (c) FTIR spectra of aCCM recrystallized in acetonitrile mixture after different intervals; (d) Rectangle area in (c) showing hydroxyl stretching band region during recrystallization of aCCM after different intervals
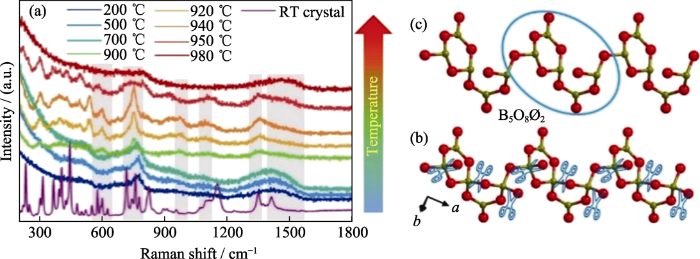
3.2 拉曼光谱
在高温溶液晶体的生长过程中, 尤其是在固液界面相邻液相区的晶体生长边界层, 其微观结构对于晶体生长机理和习性至关重要, 原位拉曼光谱以其可以原位观察、微尺度分析、可在高温下测量等优点,成为研究晶体生长微观边界层理论的重要工具[34]。
图4
图4
LCB晶体生长拉曼光谱及微观结构演变
Fig. 4
Raman spectra and microstructure evolution of LCB crystal growth
(a) Raman spectra of LCB crystals at room temperature and LCB-grown raw material powders at different temperatures; (b, c) Molecular structural evolution in LCB-grown melts[38]
3.3 差分反射光谱
4 原位同步辐射技术研究晶体生长过程
4.1 能量色散X射线衍射
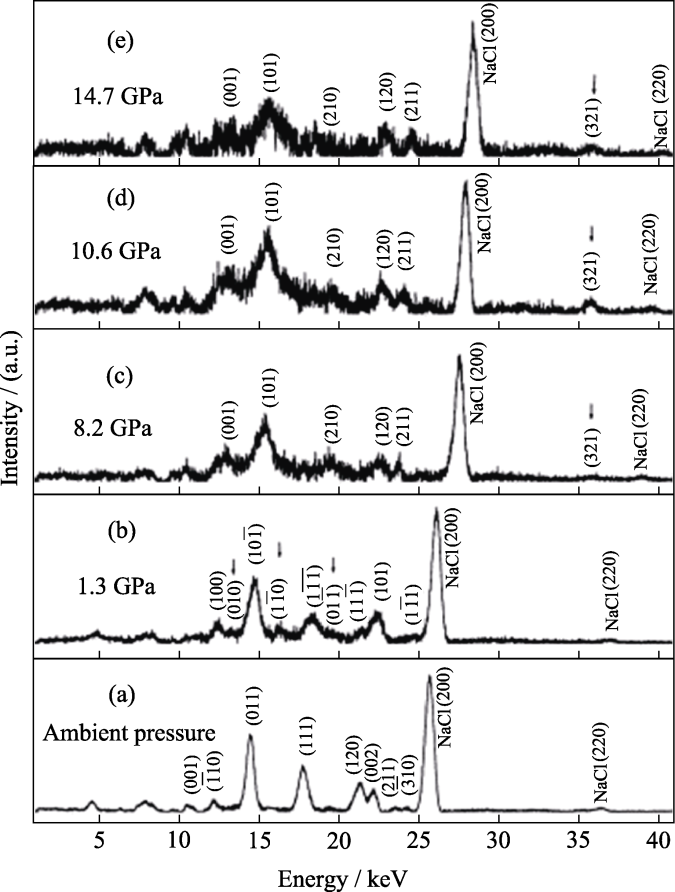
与传统的实验室X射线源相比, 能量色散X射线衍射(Energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, EDXRD)多采用强度明显更高的同步辐射X射线源, 更容易监测结晶过程的中间体和前驱体[52]。EDXRD使用高强度的同步辐射带来了高时间分辨率, 允许在几秒钟的时间尺度上从毫克级别的样品中获取光谱。这一特点使EDXRD可以对其他大多数原位技术无法表征的水热结晶进行监测, 并能够对其中不同化合物形成的演变过程进行表征。除此之外, 在考虑结晶边界条件的同时, EDXRD可以获取反应进展的详细信息, 绘制反应进度与时间的变化图像。
Beale等[53]采用水热法在低于200 ℃的温度下制备了不同相的钼酸铋, 并用EDXRD对这些相进行了研究, 发现α和β结晶相是直接从无定形凝胶混合物中形成的, 没有中间相, 证明该水热合成过程优于传统固态路线。同样地, Zhou等[54]利用EDXED技术监测了水热法合成纳米结构钨酸铋的过程。Ma等[55]利用EDXRD可以在高压下进行原位监测的特点, 研究了压力诱导三聚氰胺的结构相变。通过分析与优化原位EDXRD在不同压力探测的三聚氰胺的光谱图(图5), 研究人员构建了在不同压力下三聚氰胺的晶体结构。确定三聚氰胺从环境压力到14.7 GPa的压力范围内, 分别发生了从单斜结构到三斜结构(1.3 GPa)再到正交结构(8.2 GPa)的结构相变, 为高压环境条件下获取晶体结构提供了合理可行的方案。
图5
使用EDXRD仅能监测到结晶相, 无法监测液相中无定形相以及极小的前驱体, 来自液相中的无定形相及分子的信息可以通过扩展X射线吸收精细结构(Extended X-ray absorption finestructure, EXAFS)获得。因此, 针对水热法, 通过EDXRD及EXAFS两种方法互补则可以更好地理解其中的结晶机理[56]。
4.2 X射线吸收精细结构谱
X射线吸收精细结构谱(X-ray absorption fine structure, XAFS)分为近边吸收结构谱(X-ray absorption near edge structure, XANES)和扩展X射线吸收精细结构谱(Extended X-ray absorption finestructure, EXAFS)。该技术可以获取到电子和原子局部结构信息, 空间分辨率可达1 nm[57]。XANES对应吸收边前到吸收边后50 eV的能量范围, 主要探测吸收原子价态、立体配位及化学键等信息, 采集时间较短且吸收信号清晰, 可以快速鉴别元素的化学种类; EXAFS对应吸收边后50 eV以上的能量范围, 主要探测原子种类、配位数、键长和无序度等信息[58]。
原位XAFS技术可以在真空、环境压力或高压条件下使用, 是研究结晶过程中元素变化的重要技术手段[59]。XAFS也被用于探究在晶体掺入特定元素过程中, 该元素在晶体表面特定位置分布以及在晶体中的局部配位环境变化[60]。Zhang等[61]利用原位XANES探测了KTP晶体生长过程中出现的灰色轨迹区域的形成机制, 确定了Ti3+的影响因素, 最终解决了该灰轨问题, 生长出高质量的晶体。Yao等[62]使用原位时间分辨XAFS光谱研究AuCl还原合成Au分散纳米晶体, 并提出了动力学三步机制, 包括金纳米晶体的初始成核、缓慢生长以及最终聚结。原位XAFS可广泛应用于研究过渡金属纳米晶体的液相合成动力学。
4.3 小角X射线散射
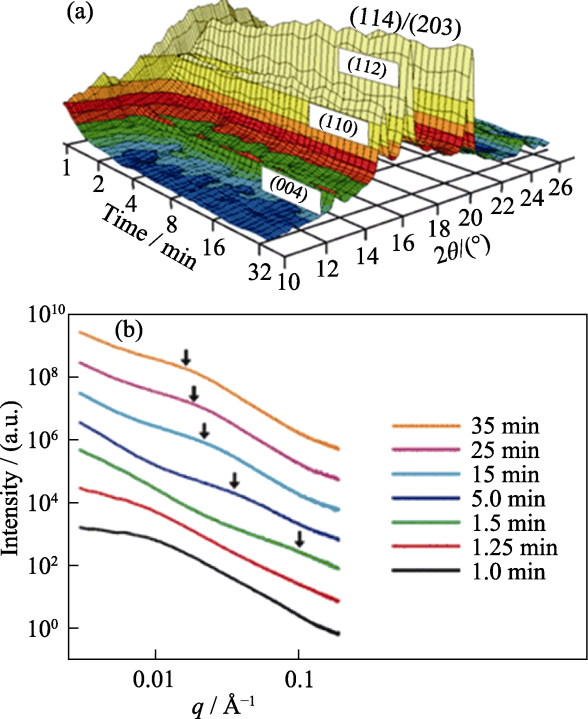
小角X射线散射(Small angle X-ray scattering, SAXS)、异常小角X射线散射(Anomalous small angle X-ray scattering, ASAXS)以及广角X射线散射(Wide angle X-ray scattering, WAXS)一般用于原位监测纳米级晶体。SAXS及ASAXS可以获取到有关颗粒的大小、形状和方向等信息, WAXS可以识别和量化纳米微晶的晶向等晶体结构信息[63]。因此, 可以在同一个实验中结合SAXS、ASAXS及ASAXS获取不同长度尺度上的晶体结构[64]。Bots等[65]通过原位SAXS/WAXS探究了无定形碳酸钙(Amorphous calcium carbonate, ACC)的结晶机制和动力学, 并根据WAXS及SAXS数据获得ACC结晶球霰石的反应程度信息(图6), 有助于充分理解ACC到球霰石再到方解石结晶的基本途径。
图6
图6
ACC结晶时间分辨的WAXS及SAXS数据图[65]
Fig. 6
Time-resolved WAXS and SAXS data of ACC crystallization[65]
(a) 3D representation of the time resolved WAXS modes in the experiment; (b) Stacked time series of the SAXS modes with time in minutes, and the arrows indicating positions of peaks caused by scattering from the growing vaterite crystallites, 1 Å =0.1 nm
Zhou等[66]利用原位同步加速器SAXS和WAXS探究了70~90 ℃范围内拉伸的无定形聚乳酸(Polylactic acid, PLA)的应变冷结晶行为和结构演变。根据原位SAXS及WAXS显示的非晶相衍射峰等数据推断出拉伸应变诱导的晶体结构变化。PLA在70 ℃拉伸时, 首先出现介晶体, 然后形成晶体; 在80 ℃下拉伸时, 以较低的应变和较高的结晶速率诱导晶体。随着应变增加, 结晶度和晶体取向增大。90 ℃拉伸时的结构演变与80 ℃时相似, 但结晶开始时间更早, 结晶速率更高。最终研究认为应变诱导的介晶/晶体和薄片是由原本存在于PLA玻璃中的中间相形成的。Cravillon等[67]使用组合的时间分辨SAXS/WAXS实时监测了沸石咪唑酸盐框架晶体的快速成核及生长, 利用同步辐射做到在各种长度尺度上具有高时间分辨率[68-69]。通过这种方式观测到的成核前簇和纳米晶体, 意味着其可能不遵循经典成核理论的复杂结晶过程, 这对全面了解该类晶体结晶机理有巨大帮助。
4.4 中子技术
但相较于X射线而言, 中子通量过低, 很难探测快速反应和过程。Walton等[73]利用ND进行原位跟踪, 进一步阐明钛酸钡的水热结晶机理。他们使用高入射通量的探测器更快地收集数据, 并从中提取钛酸钡形成的结晶曲线, 从而获得定量的动力学信息。随着中子衍射技术的进一步发展, 更快速的数据收集会使其成为原位结晶研究中不可或缺的技术。
4.5 其它技术
单一的原位监测技术仅能获得部分晶体生长过程的相关信息, 在以往的探究中, 不同的原位方法相结合能够获取不同尺度上的全面图像, 从而得到晶体生长过程的广泛结论[77]。许多原位方法相互之间受不同的样品环境条件限制, 如何合理设计结合不同原位技术监测晶体生长过程, 也是发展结晶理论及控制结晶生长过程的重点方向之一。
5 结合机器学习的在线晶体生长技术
图7
6 多尺度计算模拟
图8
6.1 原子/分子尺度的模拟
6.1.1 第一性原理方法
在无机材料的制备方面, 通过第一性原理方法求得体系的薛定谔方程, 可以获得无机材料基态电子密度和能量本征值。通过对本征值的处理, 可以获得无机材料的大部分基态性质和部分激发态性质, 例如缺陷性质、稳定结构、带隙、弹性模量等。
缺陷强烈影响材料的物理性能, 并对其应用性能产生决定性影响。第一性原理方法适合研究原子尺度上晶体材料的点缺陷[81],它已经成为一种强大的方法, 可以补充实验, 并作为预测工具识别和表征缺陷。通过电子结构计算对晶体材料中的点缺陷进行理论建模。目前已经发展了一种通用的热力学量, 例如形成能、熵和过剩体积等来研究材料的点缺陷性质。如图9所示, 陈昆峰等[82]采用密度泛函理论(Density functional theory, DFT)对铌酸锂晶体的缺陷形成能进行了计算, 并对不同缺陷模型(NbLi4+、VLi−、NbLi4++VNb5−)的XRD模式进行了模拟。结果表明, 在相同成分铌酸锂样品中, Nb反位缺陷是与Li空位共存的最稳定点缺陷。
图9
图9
铌酸锂结构、缺陷、不同点缺陷的形成能与费米能的函数关系[82]
Fig. 9
Lithium niobate structure, defects and formation energy of different point defects as a function of Fermi energy[82]
(a, b) Crystallographic structures of stoichiometric LN and congruent LN with anti-site NbLi4+ and VLi− defects. Green octahedra indicate NbO6 and LiO6; (c) Formation energies of different point defects (NbLi4+, VLi−, and NbLi4+ + VNb5−) in LN as a function of Fermi energy
图10
6.1.2 基于经验势的模拟方法
分子动力学方法是在经典力学的框架下, 将原子核和电子作为整体, 不考虑量子效应, 求解体系中每个原子的牛顿方程, 获得体系在坐标和动量空间中的演化轨迹[88]。对于平衡体系的模拟, 在远大于体系本征弛豫时间的范围内进行时间平均,可以获得无机材料的多种宏观物理性质, 例如热熔、密度、热膨胀系数等。对于非平衡体系的模拟, 在坐标和动量空间进行动力学演化轨迹的分析, 获得无机材料的微观结构和相关性质的演变过程, 从而揭示其内在机理。
在无机材料晶体生长领域, 由于固液界面埋藏于液体中, 原位探测面临巨大挑战, 分子动力学模拟对分析晶体生长动力学机制发挥关键作用。利用分子动力学方法, 建立了多种晶体生长动力学模型。最先提出的是扩散模型(WF模型)[90], 该模型认为晶体生长的动力学过程主要由原子扩散决定, 并解释了随着过冷度增大生长速度降低的趋势。随后Broughton等[91]利用分子动力学模拟建立了碰撞模型, 该模型认为原子热运动是决定晶体生长动力学过程的关键。最近的研究发现, 如图11所示, 在晶体生长过程中界面原子以集体运动的模式从无序状态转变为有序状态, 并且该过程不存在热力学势垒, 因而实现了超快生长[91]。虽然随着过冷度的增加, 原子扩散和热运动能力都在减弱, 一般体系的生长速度都会减小,但是在最近的分子动力学模拟中, 如图12所示, 人们发现在无生长势垒的胶体颗粒体系中, 即使在深过冷状态下, 体系仍然能保持较高的生长速度[93]。
图11
图12
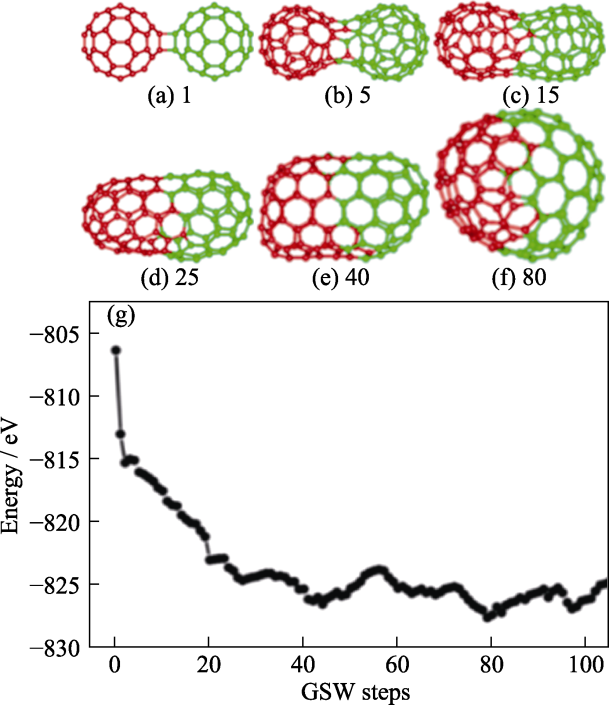
图13
图13
通过路径搜索方法研究C60二聚体结合的最佳路线[94]
Fig. 13
Structural snapshots and relationship between energy and GSW of the optimal route for C60 dimer binding by the path search method[94]
(a-f) Structural snapshots and relationship between energy and GSW steps; (g) GSW in the 0, 5, 15, 25, 40, and 80 GSW steps. Red and green represent two carbon atoms in C60, respectively
6.2 介观尺度的模拟
相场模拟方法的研究对象是体系在介尺度的动力学演化非平衡过程, 是探究无机材料介尺度相貌和组织结构演变的重要手段。该方法以经典热力学和动力学为基础, 根据Ginzburg-Landau理论建立材料组织演化计算数值模型[95]。该方法将体系视为连续的“场”, 通常用一组“场”来描述体系的局部性质, 而体系的总自由能是“场”的泛函, 在体系总自由能降低的驱动下, 通过求解动力学方程获得“场”的演化,从而获得材料体系的微观组织形貌、元素扩散和畴结构的动力学变化特征。
枝晶的生长演化对材料的微观组织形貌有重要影响, 例如锂电池中枝晶的生长会改变电极局部形貌, 尖锐的枝晶可能刺破隔膜造成电池内部短路, 导致安全问题。Hong和Viswanathan开发了一个基于巨势非线性相场模型(Grand potential-based nonlinear phase-field model)[96], 在二维空间上研究了大/小过电位下锂枝晶的动态形态演化, 揭示了离子输运和电化学反应之间的竞争会导致截然不同的生长模式。基于此研究,他们提出了一种具有较高局部离子浓度的“成分梯度电解质”,作为潜在抑制枝晶形成的方法。
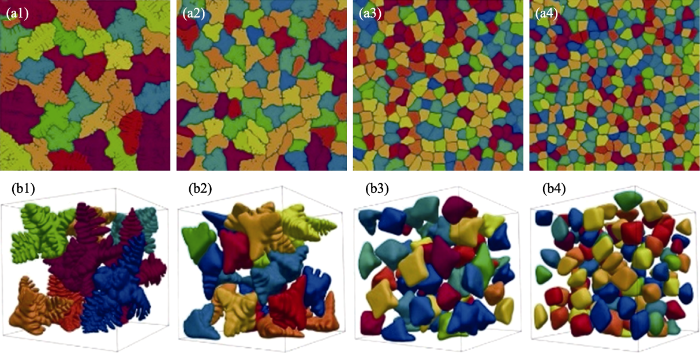
图14
图14
在0.1 K/s的冷却速度下, Al-1% Cu合金凝固的相场模拟[97]
Fig. 14
Phase-field simulation of the solidification of Al-1% Cu alloy at a cooling rate of 0.1 K/s[97]
(a1-a4) Solid fraction of the 2D system at 0.9; (b1-b4) Substantial fraction of the 3D system at 0.2; (b1-b4)3D systems corresponding to (a1-a4), respectively, containing different numbers of grains
6.3 宏观尺度的模拟
有限元模拟方法是一种解决应力分析、热传导、电磁学和流体力学等工程应用问题的宏观尺度模拟方法[98], 它通过离散化的数值计算近似求解某些复杂边界条件和初值条件下的偏微分方程组, 获得体系相关特征和性质。目前,该方法在无机材料制备的热场、流场分析中有广泛应用。
无机材料是在多场耦合下制备的, 例如单晶硅。在工业规模的设备中模拟硅的直拉法生长过程中的传热和氧掺入, 需要对整个系统的传导、对流和径向传热进行耦合模拟, 并模拟熔体中的湍流对流等。Lipchin和Brown[99]提出了一种杂化热传导的热毛细模型和Jones-Launder低雷诺湍流模型, 用于模拟整个直拉系统的传热和熔体中的湍流对流。该方法具有很好的鲁棒性, 揭示了晶体和坩埚旋转对传热和湍流的影响。
7 总结与展望
多尺度晶体材料制备的制备过程经历成核和生长阶段, 时空尺度上包括多个过程:原子分子-团簇-晶核-体块晶体, 温度场-流体场-物质输运-生长界面推移, 点-线-面缺陷形成与延伸。多尺度晶体材料生长的复杂性也增加了完全复原生长时空过程的难度, 目前原位结晶表征技术只能展现生长过程的一个或几个方面。在更小的空间和时间尺度上, 以及多尺度耦合方面, 采用计算模拟方法研究晶体生长过程更具有优势。建立实际生长环境的原位/在线表征技术以及计算模拟方法, 将是未来的发展趋势, 特别是结合机器学习、大数据等手段, 会使大尺寸无机材料制备的迭代周期大大缩短。这也将带来生长理论、生长装备、生长技术以及大尺寸无机材料品质的快速发展和提升。
参考文献
Advance in theory and technology of rapid growth of large-size crystals
Omni-functional crystal: advanced methods to characterize the composition and homogeneity of lithium niobate melts and crystals
Fast growth of cerium-doped lutetium yttrium orthosilicate single crystals and their scintillation properties
Recent advances in nonlinear optical rare earth structures
Recent advances and perspectives on melt structures of large-size functional oxcide crystals
Chemical bonding theory of single crystal growth and its application to fast single crystal growth of rare earth inorganic materials
In situ observation of melting/dissolution, nucleation and growth of NdBa2Cu3Ox by high temperature optical microscopy
In situ measurement of the growth rate of YBa2Cu3Ox single crystals
In-situ observation of crystallization and growth in high-temperature melts using the confocal laser microscope
23-In Situ Observation of Crystal Growth by Scanning Electron Microscopy
In situ observation of ice formation from water vapor by environmental SEM
In situ TEM observation of crystal structure transformation in InAs nanowires on atomic scale
In situ transmission electron microscopy investigation of structural transformation in III-V nanowires is essential for providing direct insight into the structural stability of III-V nanowires under elevated temperature. In this study, through in situ heating investigation in a transmission electron microscope, the detailed structural transformation of InAs nanowires from wurtzite structure to zinc-blende structure at the catalyst/nanowire interface is witnessed on the atomic level. Through detailed structural and dynamic analysis, it was found that the nucleation site of each new layer of InAs and catalyst surface energy play a decisive role in the growth of the zinc-blende structure. This study provides new insights into the growth mechanism of zinc-blende-structured III-V nanowires.
In situ kinetic observations on crystal nucleation and growth
In-situ HRTEM observation of the melting-crystallization process of silicon
Atomic force microscopy in the study of macromolecular crystal growth
Ex situ investigation of surface topography of as-grown potassium dihydrogen phosphate crystals by atomic force microscopy
Surface topography of rapidly grown KH2PO4 crystals with additives: ex situ investigation by atomic force microscopy
In situ TEM and AFM investigation of morphological controls during the growth of single crystal BaWO4
FTIR spectroscopy of nanodiamonds: methods and interpretation
Evaluation of chemometric models in an FTIR study of the gas phase during atmospheric- pressure CVD of tin oxide thin films
ATR FTIR spectroscopy for in situ measurement of supersaturation
In situ IR spectral identification of NH4H2PO4 structural evolution during crystallization in water-ethanol mixed solvent
In situ IR spectral observation of NH4H2PO4 crystallization: structural identification of nucleation and crystal growth
Hydrogen bonding nature during ADP crystallization
Crystallization behaviors of KDP and ADP
In situ ATR-IR observation of nucleation and crystal growth of KH2PO4 in aqueous solution
Microdynamic changes of moisture- induced crystallization of amorphous calcium carbonate revealed via in situ FTIR spectroscopy
Amorphous calcium carbonate monohydrate containing a defect hydrate network by mechanochemical processing of mono-hydrocalcite using ethanol as auxiliary solvent
Calcium carbonate monohydrate-like ACC was made by ball-milling with ethanol as auxiliary solvent. IR and solid-state NMR, diffraction and total scattering show that defects of the hydrate network due to partial displacement of water by ethanol are crucial for amorphization.
In situ infrared measurements of film and gas properties during the plasma deposition of amorphous hydrogenated silicon
FTIR in-situ studies of the gas-phase reactions in chemical-vapor-deposition of SiC
High temperature Raman spectroscopy study on the microstructure of the boundary layer around a growing LiB3O5 crystal
Study on the crystallization rates of beta- and epsilon-form HNIW in in-situ Raman spectroscopy and FBRM
In situ investigation of BaBPO5 crystal growth mechanism by high-temperature Raman spectroscopy
The analysis of morphology evolution in KABO crystal growth
In situ Raman spectroscopy studies on La2CaB10O19 crystal growth
Hydrogen bonding dependent mesoscale framework in crystalline Ln(H2O)9(CF3SO3)3
Fabrication and spectral properties of Tm3+-doped novel bismuthate glasses
Estimating crystal growth rates using in situ ATR-FTIR and Raman spectroscopy in a calibration-free manner
Molecular paradigm dependent nucleation in urea aqueous solution
Nucleation-dependant chemical bonding paradigm: the effect of rare earth ions on the nucleation of urea in aqueous solution
Rare earth ions can be used to construct a variety of novel structures and are favorable to chemical bonding regulation and design. In this study, the chemical bonding paradigm between rare earth ions (Ln) and urea molecules in an aqueous solution can be tracked by the evolution of C[double bond, length as m-dash]O, NH, and CN vibration bands during the urea nucleation stage. Rare earth ions such as La, Gd, and Lu can manipulate the nucleation time of urea via regulating the nucleation-dependant N-C[double bond, length as m-dash]OH-N hydrogen-bonding between urea molecules. Two types of chemical bondings between Ln and urea molecules have been confirmed, which are LnO[double bond, length as m-dash]C-N and LnNH-C. Compared with LnNH-C, Ln prefers to coordinate with the O[double bond, length as m-dash]C bond in urea. With a higher concentration of rare earth ions in the solution, some N-C[double bond, length as m-dash]OH-N hydrogen bonds are broken as a consequence of the incorporation of Ln into the lattice, resulting in the decreased symmetry of local urea molecules in the crystalline nuclei and the consequent Ln concentration-dependent nucleation time of urea. Moreover, using the ionic electronegativity scale of Ln, the different effects of La, Gd, and Lu on urea nucleation can be further distinguished. The present study provides basic data for unrevealing the chemical bonding regulation role of rare earth ions in the formation of hydrogen bonded materials, which may give insight into the design and fabrication of novel materials utilizing rare earth ions to adjust the chemical bonding process.
Physical chemistry of crystalline (K,NH4)H2PO4 in aqueous solution: an in situ molecule vibration spectral observation of the early formation stage
In-situ micro-Raman spectroscopy study of gypsum crystallization driven by chemical reaction
In-situ monitoring of the formation of crystalline solids
Optical differential reflectance spectroscopy of ultrathin epitaxial organic films
This Perspective does not have the ambition to entirely review the subject of optical spectroscopy on thin organic films. What we will try to achieve instead is to give an overview on optical reflectance spectroscopy of highly ordered organic thin films in the thickness range from submonolayers to several monolayers, as a tool to study the absorption behavior of such films. By doing so, we will emphasize the relations between the physical layer structure and the resulting optical properties. More specifically, we intend to show on the basis of particular examples what physical effects can be favorably examined by means of real-time optical spectroscopy, i.e., applied during the actual film growth, especially differential reflectance spectroscopy (DRS). Epitaxial organic films on inorganic substrates (insulators and conductors) will be in focus, and also the perspectives of investigating organic-organic heteroepitaxial layers will be addressed.
In situ differential reflectance spectroscopy of thin crystalline films of PTCDA on different substrates
Pentacene crystal transition during the growth on SiO2 studied by in situ optical spectroscopy
Growth of pentacene on alpha-Al2O3(0001) studied by in situ optical spectroscopy
Direct observation of monolayer MoS2 prepared by CVD using in-situ differential reflectance spectroscopy
The in-situ observation is of great significance to the study of the growth mechanism and controllability of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDCs). Here, the differential reflectance spectroscopy (DRS) was performed to monitor the growth of molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) on a SiO2/Si substrate prepared by chemical vapor deposition (CVD). A home-built in-situ DRS setup was applied to monitor the growth of MoS2 in-situ. The formation and evolution of monolayer MoS2 are revealed by differential reflectance (DR) spectra. The morphology, vibration mode, absorption characteristics and thickness of monolayer MoS2 have been confirmed by optical microscopy, Raman spectroscopy, ex-situ DR spectra, and atomic force microscopy (AFM) respectively. The results demonstrated that DRS was a powerful tool for in-situ observations and has great potential for growth mechanism and controllability of TMDCs prepared by CVD. To the best of the authors’ knowledge, it was the first report in which the CVD growth of two-dimensional TMDCs has been investigated in-situ by reflectance spectroscopy.
Kinetic study of the intercalation of cobaltocene by layered metal dichalcogenides with time-resolved in situ X-ray powder diffraction
In situ study of the formation of crystalline bismuth molybdate materials under hydrothermal conditions
In situ X-ray diffraction study of the hydrothermal crystallization of hierarchical Bi2WO6 nanostructures
Crystal structures of C3N6H6 under high pressure
Combined in situ EDXRD/EXAFS investigation of the crystal growth of [Co(C6H18N4)][Sb2S4] under solvothermal conditions: two different reaction pathways leading to the same product
New technique for investigating noncrystalline structures-Fourier analysis of extended X-ray-absorption fine structure
Structural study of electrochemically deposited Cu on p-GaAs(100) in H2SO4 solution by in situ surface-sensitive X-ray absorption fine structure measurements
Redox properties of nanostructured lanthanide-doped ceria spheres prepared by microwave assisted hydrothermal homogeneous co-precipitation
In this work, nanostructured LnxCe(1-x)O2-δ (Ln: Gd and Pr; x = 0.1 and 0.2) spheres were synthesized by microwave assisted hydrothermal homogeneous co-precipitation and their properties were characterized by synchrotron radiation XRD, X-ray absorption near-edge spectroscopy (XANES) and scanning and high-resolution electron microscopy (SEM and HRTEM). In situ XRD and XANES experiments were carried out under reducing and oxidizing conditions in order to investigate the redox behaviour of these materials. The nanostructured mixed oxide spheres were found to have a cubic crystal structure (Fm3m space group). The spheres were composed of nanoparticles with an average crystallite size of about 10 nm. The Ln(0.1)Ce(0.9)O2-δ compositions exhibited the highest specific surface area (∼ 60 m(2) g(-1)). In situ XRD experiments showed an increase in lattice parameters upon reduction, which was attributed to the reduction of Ce(4+) and Pr(4+) cations to Ce(3+) and Pr(3+), which have larger radii, and to the associated increase in VO concentration. This increase in lattice parameters was considerably more pronounced for PrDC than GDC, and was explained by the considerably larger change in ionic radius for Pr upon reduction. XANES absorption experiments at the Ce and Pr L3-edge showed that the changes observed upon reduction of the Pr-containing samples resulted mostly from the formation of Pr(3+) rather than Ce(3+), and supported the previously reported proposal that Pr(3+) has a stabilizing effect on Ce(4+).
Coprecipitation of chromate with calcite: batch experiments and X-ray absorption spectroscopy
Growth and optical properties of gray-track-resistant KTiOPO4 single crystals
Insights into initial kinetic nucleation of gold nanocrystals
Understanding the initial nucleation mechanism of monodisperse nanocrystals (NCs) during synthesis process is an important prerequisite to control the desired sizes and to manipulate the properties of nanoscale materials. The acquisition of information for the small nanocluster nucleation process, however, still remains challenging. Here, using a continuous-flow in situ X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) spectroscopy for time-resolved studies, we have clarified the initial kinetic nucleation of Au clusters under the grain size of 1 nm for the classical Au NCs synthesis via the reduction of AuCl(4)(-) in aqueous solution. The in situ XAFS results present the experimental revelation of the formation of intermediate Cl(3)(-)Au-AuCl(3)(-) dimer and the subsequent higher complexes 'Au(n)Cl(n+x)' in the initial nucleation stage. We propose a kinetic three-step mechanism involving the initial nucleation, slow growth, and eventual coalescence for the Au NCs formation, which may be helpful for the synthesis of metallic nanomaterials.
In situ synchrotron SAXS/XRD study on the formation of ordered mesoscopic hybrid materials with crystal-like walls
A kinetic study of the phase conversion of layered cobalt hydroxides
Mechanistic insights into the crystallization of amorphous calcium carbonate (ACC)
Direct investigations on strain-induced cold crystallization behavior and structure evolutions in amorphous poly(lactic acid) with SAXS and WAXS measurements
Fast nucleation and growth of ZIF-8 nanocrystals monitored by time-resolved in situ small-angle and wide-angle X-ray scattering
In situ small-angle and wide-angle X-ray scattering investigation on nucleation and crystal growth of nanosized zeolite A
Time-resolved in situ synchrotron X-ray study and large-scale production of magnetite nanoparticles in supercritical water
In situ studies of the Sol-Gel synthesis of materials
Structure and stability of SnO2 nanocrystals and surface-bound water species
Nucleation and growth of nanocrystals in glass-ceramics: an in situ SANS perspective
Real time observation of the hydrothermal crystallization of barium titanate using in situ neutron powder diffraction
The hydrothermal crystallization of barium titanate, BaTiO3, has been studied in situ by time-resolved powder neutron diffraction methods using the recently developed Oxford/ISIS hydrothermal cell. This technique has allowed the formation of the ferroelectric ceramic to be followed in a noninvasive manner in real time and under genuine reaction conditions. In a first set of experiments, Ba(OD)2-8D2O was reacted with two different titanium sources, either crystalline TiO2 (anatase) or amorphous TiO2-H2O in D2O, at 100-140 degrees C and the reaction studied using the POLARIS time-of-flight neutron powder diffractometer, at the ISIS Facility. In a second series of experiments, the reaction between barium chloride and crystalline TiO2 (anatase) in NaOD/D2O was studied at temperatures between 100 and 200 degrees C and at different deuterioxide concentrations using the constant-wavelength D20 neutron powder diffractometer at the Institut Laue Langevin. Quantitative growth and decay curves were determined from analysis of the integrated intensities of Bragg reflections of starting materials and product phases. In both sets of experiments the rapid dissolution of the barium source was observed, followed by dissolution of the titanium source before the onset of crystallization of barium titanate. Using a nucleation-growth model we are able to simulate the growth curve of barium titanate at three temperatures. Our results indicate the predominance of a homogeneous dissolution-precipitation mechanism for the hydrothermal formation of barium titanate, rather than other possible mechanisms that have been discussed in the literature. Analysis of the line widths of the Bragg reflections in the neutron diffraction data indicates that the particle size of the BaTiO3 product phase prepared from the amorphous TiO2-H2O is smaller than that prepared from crystalline TiO2 (anatase).
An in-situ characterization of II-VI molecular-beam epitaxy
Microscopic description of the polyamorphic phases of triphenyl phosphite by means of multidimensional solid-state NMR Spectroscopy
The structural properties of a second, apparently amorphous phase (aII) of the molecular glass former triphenyl phosphite were studied by means of multidimensional solid-state NMR spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction. Phase aII was prepared by annealing the supercooled liquid in the temperature range 210 K <or= T(a) <or= 230 K. In addition to 1D (1)H and (31)P spectra and spin-lattice relaxation data, we used (31)P radio-frequency-driven spin-diffusion exchange spectroscopy to analyze the arrangement of neighboring TPP molecules on both a local and intermediate scale. For the first time, our results give a detailed microscopic description of phase aII. For T(a) > 223 K a nano- or microcrystalline material is formed, whereas for T(a) < 223 K phase aII is homogeneous and disordered. Our data strongly suggest that some of the TPP molecules in phase aII tend toward a parallel alignment. The regions, where the molecules preferentially align appear to be spatially separated and consist of only a few molecules. Whereas the mean cubic expansion of an individual region does not change within the experimental error, the percentage of correlated molecules increases with rising T(a). Based on our results, phase aII can consistently be described as a second liquid, where a part of the molecules exhibit structural correlations. The transformation of the supercooled liquid into phase aII is therefore considered as a liquid-liquid phase transition.
Interface diagnostics: in-situ determination of crystal-melt interface shape evolutions via probing growth interface electromotive force
Unraveling the crystallization mechanism of CoAPO-5 molecular sieves under hydrothermal conditions
The hydrothermal crystallization of CoAPO-5 molecular sieves has been studied using time-resolved in-situ SAXS/WAXS, UV-vis, Raman, and XAS. Data collected during heating to 180 degrees C allowed the observation of different steps occurring during the transformation of the amorphous gel into a crystalline material from a macroscopic and atomic perspective. Raman spectroscopy detected the initial formation of Al-O-P bonds, whereas SAXS showed that these gel particles had a broad size distribution ranging from ca. 7 to 20 nm before crystallization began. WAXS showed that this crystallization was sharp and occurred at around 160 degrees C. Analysis of the crystallization kinetics suggested a one-dimensional growth process. XAS showed that Co(2+) transformed via a two-stage process during heating involving (i) a gradual transformation of octahedral coordination into tetrahedral coordination before the appearance of Bragg peaks corresponding to AFI, suggesting progressive incorporation of Co(2+) into the poorly ordered Al-O-P network up to ca. 150 degrees C, and (ii) a rapid transformation of remaining octahedral Co(2+) at the onset of crystallization. Co(2+) was observed to retard crystallization of AFI but provided valuable information regarding the synthesis process by acting as an internal probe. A three-stage, one-dimensional crystallization mechanism is proposed: (i) an initial reaction between aluminum and phosphate units forming a primary amorphous phase, (ii) progressive condensation of linear Al-O-P chains forming a poorly ordered structure separated by template molecules up to ca. 155 degrees C, and (iii) rapid internal reorganization of the aluminophosphate network leading to crystallization of the AFI crystal structure.
脱炭素社会に向けて新技術! -AI利用で高品質な6インチのSiC結晶成長の開発を圧倒的な開発スピードで実現
[
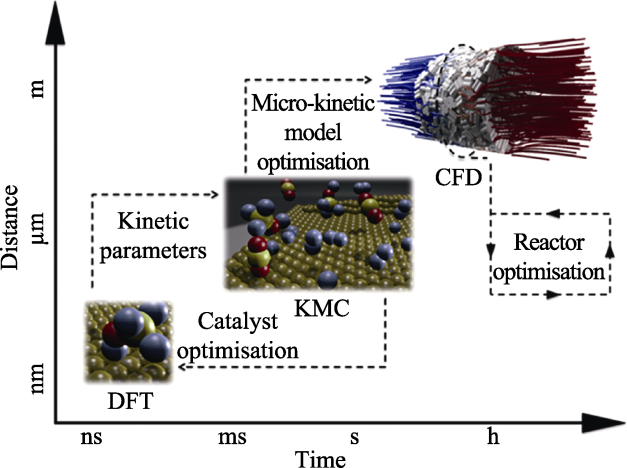
Ab initio multiscale process modeling of ethane, propane and butane dehydrogenation reactions: a review
Olefins are among the most important structural building blocks for a plethora of chemical reaction products, including petrochemicals, biomaterials and pharmaceuticals. An ever-increasing economic demand has urged scientists, engineers and industry to develop novel technical methods for the dehydrogenation of parent alkane molecules. In particular, the catalysis over precious metal or metal oxide catalysts has been put forward as an alternative way route to thermal-, steam- and fluid catalytic cracking (FCC). Multiscale system modeling as a tool to theoretically understand processes has in the past decade period evolved from a rudimentary measurement-complementing approach to a useful engineering environment. Not only can it predict various experimentally obtained parameters, such as conversion, activity, and selectivity, but it can help us to simulate trends, when changing applicative operating conditions, such as surface gas temperature or pressure, or even support us in the search for the type of materials, their geometrical properties and phases for a better functional performance. An overview of the current set state of the art for saturated organic short chain hydrocarbons (ethane, propane and butane) is presented. Studies that combine at least two different dimensional scales, ranging from atomistic-, bridging across mechanistic mesoscale kinetics, towards reactor- or macroscale, are focused on. Insights considering reactivity are compared.
Electronic Structure:Basic Theory and Practical Methods
First-principles calculations for point defects in solids
Microstructure and defect characteristics of lithium niobate with different Li concentrations
Li vacancies and Nb antisites are stable point defects in congruent lithium niobate. The intrinsic point defects induce the Li/Nb cation mixing, the formation of temperature-dependent defect microstructures, and disorder within the LiNbO3 lattice frame.
Superconductive sodalite- like clathrate calcium hydride at high pressures
\n Hydrogen-rich compounds hold promise as high-temperature superconductors under high pressures. Recent theoretical hydride structures on achieving high-pressure superconductivity are composed mainly of H\n 2\n fragments. Through a systematic investigation of Ca hydrides with different hydrogen contents using particle-swam optimization structural search, we show that in the stoichiometry CaH\n 6\n a body-centered cubic structure with hydrogen that forms unusual “sodalite” cages containing enclathrated Ca stabilizes above pressure 150 GPa. The stability of this structure is derived from the acceptance by two H\n 2\n of electrons donated by Ca forming an “H\n 4\n ” unit as the building block in the construction of the three-dimensional sodalite cage. This unique structure has a partial occupation of the degenerated orbitals at the zone center. The resultant dynamic Jahn–Teller effect helps to enhance electron–phonon coupling and leads to superconductivity of CaH\n 6\n. A superconducting critical temperature (T\n \n c\n \n ) of 220–235 K at 150 GPa obtained from the solution of the Eliashberg equations is the highest among all hydrides studied thus far.\n
A intrinsic n-type versus p-type doping asymmetry and the defect physics of ZnO
Oxygen vacancies in ZnO
Native point defects in ZnO
Understanding Molecular Simulation:from Algorithms to Applications
Applications of the Monte Carlo method in statistical physics
Crystallization rates of a Lennard-Jones liquid
The mechanism of the ultrafast crystal growth of pure metals from their melts
Pure metals can have ultrafast growth rates from their melts, such as a crystal of pure nickel that grows at a rate reaching 70 m s(-1). These extraordinary growth rates suggest that metallic crystals might provide the next generation of phase-change materials. The huge crystal growth rates of metals are the consequence of kinetics without activated control, in sharp contrast to the prediction of the 'classic' theory of crystal growth. While the existence of barrierless growth kinetics is now well established in atomic melts, the physical explanation for the absence of an activation barrier to ordering remains unclear. It is something of a paradox that diffusion in the liquid metal is governed by thermal activation while the movement of the same atoms organizing into a crystal is not. Here we use computer simulations of crystallization in pure metals to explicitly resolve the origin of the barrierless growth kinetics.
Fast crystal growth at ultra-low temperatures
It is believed that the slow liquid diffusion and geometric frustration brought by a rapid, deep quench inhibit fast crystallization and promote vitrification. Here we report fast crystal growth in charged colloidal systems under deep supercooling, where liquid diffusion is extremely low. By combining experiments and simulations, we show that this process occurs via wall-induced barrierless ordering consisting of two coupled steps: the step-like advancement of the rough interface that disintegrates frustration, followed by defect repairing inside the newly formed solid phase. The former is a diffusionless collective process, whereas the latter controls crystal quality. We further show that the intrinsic mechanical instability of a disordered glassy state subject to the crystal growth front allows for domino-like fast crystal growth even at ultra-low temperatures. These findings contribute to a deeper understanding of fast crystal growth and may be useful for applications related to vitrification prevention and crystal-quality control.
Energy-driven kinetic Monte Carlo method and its application in fullerene coalescence
Phase-field simulations of lithium dendrite growth with open-source software
Revisiting dynamics and models of microsegregation during polycrystalline solidification of binary alloy
Finite Element Simulations with ANSYS Workbench 2022: Theory, Applications, Case Studies