本工作通过反相溶剂扩散法成功生长出厘米级尺寸的Cs3Cu2I5单晶, 全面表征了其光学和闪烁性能, 并与利用布里奇曼法生长的Cs3Cu2I5单晶进行性能对比研究。利用溶液法生长的Cs3Cu2I5单晶不仅不潮解、无自吸收, 而且在X射线和γ射线辐照下具有高光产额以及低余辉特性。结果表明:利用溶液法和熔体法生长的Cs3Cu2I5单晶光学和闪烁性能相当。
1 实验方法
1.1 原料
CsI(99.999%, 购自Alfa)、CuI(99.999%, 购自Acros)、N,N-二甲基甲酰胺(DMF, ≥99.5%, 购自Greagent)、二甲基亚砜(DMSO, ≥99.0%, 购自Greagent)、甲醇(MeOH, 水含量≤5×10-5, 99.8%, 购自Adamas)。除非另有说明, 所有的试剂和溶剂都没有进行纯化。
1.2 晶体生长
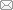
在N2氛围下, 称取CsI (0.7794 g, 3 mmol)和CuI (0.3809 g, 2 mmol)溶解于12 mL的DMF/DMSO (体积比1 : 1)混合溶液中。然后加热至65 ℃并搅拌12 h至完全溶解, 形成前驱体溶液。用0.25 μm的聚四氟乙烯膜过滤至新的40 mL的透明玻璃容器中, 形成澄清的前驱体溶液。将该透明玻璃容器裹覆保鲜膜并扎孔, 置于盛有12 mL MeOH的100 mL密闭大瓶中。最后在65 ℃下恒温生长7 d, 得到透明棒状单晶(图1)。将良性溶剂与反相溶剂MeOH的体积比由1 : 1优化为5 : 3, 其它生长参数保持不变, 生长9 d得到厘米级块状Cs3Cu2I5单晶。
图1
图1
用反相溶剂扩散法生长Cs3Cu2I5晶体示意图
Fig. 1
Schematic diagram of Cs3Cu2I5 crystal grown by anti, solvent diffusion method
1.3 性能测试
使用Bruker D8 Advance X射线衍射仪, 在Mo Kα射线辐射下, 对研磨后的Cs3Cu2I5粉末进行粉末X射线衍射(XRD)分析。
使用Horiba FluoroMax-plus型荧光光谱仪测试了Cs3Cu2I5的室温激发和发射光谱。激发光源为氙灯。Cs3Cu2I5晶体的吸收和透过光谱由PE Lambda 950型分光光度计测得, 测试范围为200~800 nm。光致发光衰减动力学由牛津仪器公司FLS980型光谱仪的OptistatDN系统测得。
稳态X射线发射光谱是采用JF-10型携带式诊断X射线机作为激发源, 使用的管电压为50 keV, 管电流为0.5 mA, 利用积分球收集发射光, 通过光纤将收集到的光导入荧光光谱仪并采集数据。利用光谱仪的动力学模式测试其稳态X射线余辉性能, 以BGO和CsI:Tl晶体作为参比样品, 测试时间范围为100 s。使用ROSBTL 3DS热释光光谱仪测试晶体的热释光曲线, 温度范围为300~580 K, 加热速率为0.5 K/s。γ射线辐照下的脉冲高度谱由在137Cs辐照下, 滨松R2059光电倍增管收集发光信号, 高压为-1800 V, 成形时间为10 μs, 增益为4, 用单光子法标定绝对光输出。闪烁衰减曲线采用137Cs作为激发光源, 滨松R2059光电倍增管收集发光信号, 最终通过Tektronix DPO 5104数字荧光示波器采集。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 晶体生长与物相分析
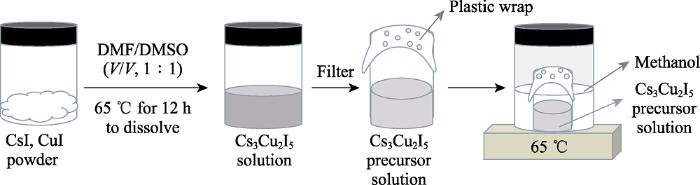
利用反相溶剂MeOH缓慢扩散至前驱体溶液中, 降低Cs3Cu2I5在良性溶剂DMF/DMSO中的溶解度, 从而形成过饱和溶液, 促进晶核形成和晶体生长, 最终生长出毫米级尺寸的棒状Cs3Cu2I5单晶, 如图2(a)所示。通过减小反溶剂与良溶剂体积比, 减小反溶剂的扩散速率, 减缓晶体生长速率, 最终生长出的厘米级块状Cs3Cu2I5单晶, 如图2(b)所示。Cs3Cu2I5单晶在254 nm紫外灯辐照下, 晶体发出明亮的蓝光。图2(c, d)分别为利用溶液法和熔体法生长的Cs3Cu2I5单晶测试用样品。Cs3Cu2I5晶体中阴离子多面体[Cu2I5]3-的结构如图2(e)所示。Cs3Cu2I5是空间群为Pnma的正交晶系。Cu+离子占据四面体体心位点和三角形面心位点。两个Cu+离子和周围的五个I-组成一个[Cu2I5]3-多面体, 每个多面体都被Cs+隔开, 形成0D结构。溶液法生长的晶体粉末XRD图谱和Cs3Cu2I5单晶的XRD标准卡片对比, 如图2(f)所示。粉末的XRD衍射峰位置与标准卡片基本吻合[11], 且未出现多余的杂峰, 表明合成了纯Cs3Cu2I5物相。
图2
图2
Cs3Cu2I5晶体照片和结构
Fig. 2
Photographs and structures of Cs3Cu2I5 crystals
(a-b) Photographs of millimeter-sized rod-like Cs3Cu2I5 crystals and centimeter-sized bulk Cs3Cu2I5 crystals grown by solution method under sunlight and 254 nm ultraviolet light; (c) Photographs of Cs3Cu2I5 crystals grown by solution method for comparative study; (d) Photographs of Cs3Cu2I5 crystals grown by melt method for comparative study; (e) Structure of [Cu2I5]3- where blue and purple spheres represent Cu and I atoms, respectively; (f) X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) pattern of crystals grown by solution method
2.2 光学性能
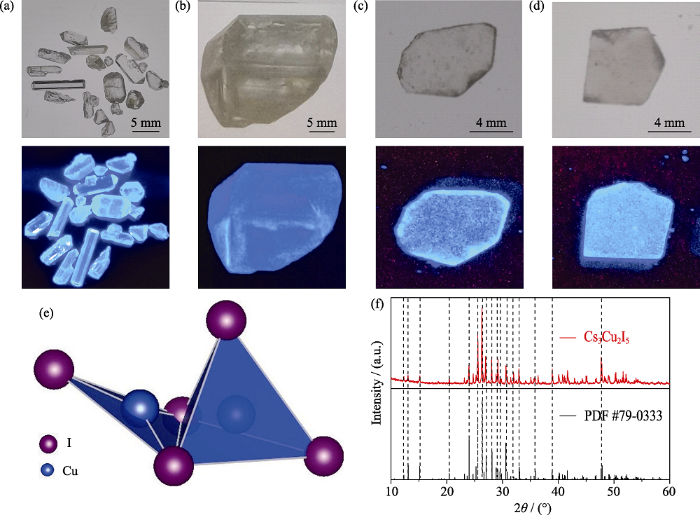
为了研究溶液法生长的Cs3Cu2I5单晶的光学性能, 测试了其吸收光谱、荧光激发/发射光谱和荧光衰减动力学。从图中可以观察到一个位于309 nm的吸收峰(图3(a)), 通过对吸收截止边拟合得到其光学带隙为3.68 eV, 与利用熔体法生长的Cs3Cu2I5单晶的3.77 eV的光学带隙接近[11]。晶体在380~780 nm范围内的透过率均大于68%, 展现出优异的透光性(图3(b))。激发光谱中有一个308 nm的主峰和280 nm的肩峰, 发射峰位置在448 nm(图3(c)), 与利用熔体法生长的Cs3Cu2I5单晶峰位450 nm相近[11]。此外, 由荧光光谱可知, 溶液法制备的Cs3Cu2I5晶体几乎没有自吸收, 具有1.37 eV的大斯托克斯位移。溶液法生长的Cs3Cu2I5单晶只有一个发光中心(图3(d)), 该发光中心来源于单个无机团簇[Cu2I5]3-的自陷激子发射[14]。图3(e)为监测308 nm激发波长和448 nm发射波长下测试得到的时间分辨荧光光谱。采用单指数衰减函数拟合, 得到荧光衰减时间为943 ns, 略短于通过熔体法生长的Cs3Cu2I5单晶968 ns的荧光衰减时间[11]。
图3
图3
Cs3Cu2I5晶体的光学性能
Fig. 3
Optical properties of Cs3Cu2I5 crystals
(a) Absorption spectra of Cs3Cu2I5 crystals grown by solution method; (b) Transmittance spectra of Cs3Cu2I5 crystals grown by solution method; (c) Photoluminescence excitation (PLE) and emission (PL) spectra of Cs3Cu2I5 crystals grown by solution method; (d) PL and PLE contour mappings of Cs3Cu2I5 crystals grown by solution method; (e) Photoluminescence decay profiles of Cs3Cu2I5 crystals grown by solution method when λex=308 nm and λem=448 nm excited by nanoLED
2.3 闪烁性能
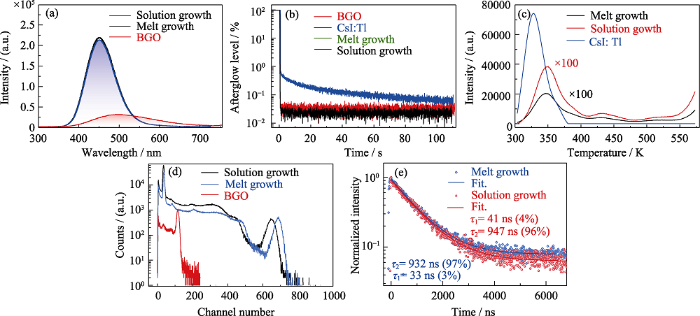
溶液法和熔体法生长的Cs3Cu2I5单晶的X射线激发发射光谱如图4(a)所示。在稳态X射线激发下, 二者的发射峰均位于448 nm。在相同测试条件下, 以相同尺寸的BGO晶体作为参比样品, 通过对比发射光谱的积分面积, 计算得到溶液法和熔体法生长的晶体的光产额均为32000 photons/MeV。图4(b)为晶体在X射线诱导下的余辉曲线。在稳态X射线辐照下, 与商用BGO和CsI : Tl单晶相比, 通过溶液法和熔体法生长的Cs3Cu2I5晶体都具有更低的余辉。为了研究溶液法和熔体法生长的Cs3Cu2I5晶体的缺陷特征, 以4 mm×4 mm×1 mm的CsI : Tl晶体作为参比样品, 测试它们的热释光曲线。如图4(c) 所示, 相同测试条件下, 在300~580 K的温度范围内, 溶液法与熔体法生长的Cs3Cu2I5单晶的热释光发光强度比CsI:Tl单晶低两个数量级。这说明与CsI:Tl单晶相比, 溶液法与熔体法制备的Cs3Cu2I5单晶具有更低的缺陷浓度。
图4
图4
Cs3Cu2I5晶体的闪烁性能
Fig. 4
Scintillation properties of Cs3Cu2I5 crystals
(a) X-ray excited RL spectra of Cs3Cu2I5 crystals grown by solution method and melt method with BGO as reference sample; (b) X-ray afterglow curves of Cs3Cu2I5 grown by solution method and melt method compared with that of BGO and CsI:Tl; (c) Thermoluminescence glow curves of Cs3Cu2I5 grown by solution method and melt method compared with that of CsI:Tl; (d) Pulse height spectra of Cs3Cu2I5 grown by solution method and melt method under 137Cs gamma-ray radiation as well as that of BGO; (e) Scintillation decay profiles of Cs3Cu2I5 grown by solution method and melt method under 137Cs gamma-ray radiation===Colorful figures are available on website
为了进一步考察溶液法制备Cs3Cu2I5晶体作为γ射线闪烁体的辐射探测性能, 利用γ射线脉冲高度谱结合单光电子峰法估算了两种方法制备的Cs3Cu2I5晶体的绝对光产额。图4(d)为溶液法和熔体法制备的Cs3Cu2I5晶体以及商用BGO(光产额为8000 photons/ MeV)作为参比样品在137Cs激发下的脉冲高度谱, 计算得到溶液法与熔体法生长的Cs3Cu2I5晶体的绝对光输出分别为(29000±3000) photons/MeV和(30000± 3000) photons/MeV。图4(e)为溶液法与熔体法生长的Cs3Cu2I5单晶在137Cs激发下的闪烁衰减时间曲线。利用双指数衰减函数拟合溶液法与熔体法生长的Cs3Cu2I5单晶衰减时间, 得到的主分量分别为947 ns (96%)和932 ns (97%)。主分量与荧光衰减时间相近, 该闪烁发光来源于自陷激子发光, 快分量来源有待进一步研究[11]。
3 结论
本工作采用反相溶剂扩散法生长出厘米级块状高质量Cs3Cu2I5单晶。该法制备的单晶具有优异的光学以及闪烁性能, 可用于X射线和γ射线探测。该晶体具有蓝光宽带发射, 来源于自陷激子发光, 因此具有1.37 eV的大斯托克斯位移。稳态X射线辐照下, 该单晶光产额为32000 photons/MeV。在137Cs源激发下, 溶液法生长的Cs3Cu2I5单晶的光产额为29000 photons/MeV, 主要闪烁衰减时间为947 ns。X射线下的余辉和热释光结果表明, 溶液法生长Cs3Cu2I5单晶具有极低的缺陷水平。这一研究结果证实了低成本溶液法可制备大尺寸高性能Cs3Cu2I5单晶。
参考文献
Broad-band emission in metal halide perovskites: mechanism, materials, and applications
Nanocrystals of cesium lead halide perovskites (CsPbX3, X = Cl, Br, and I): novel optoelectronic materials showing bright emission with wide color gamut
Properties and potential optoelectronic applications of lead halide perovskite nanocrystals
Semiconducting lead halide perovskites (LHPs) have not only become prominent thin-film absorber materials in photovoltaics but have also proven to be disruptive in the field of colloidal semiconductor nanocrystals (NCs). The most important feature of LHP NCs is their so-called defect-tolerance-the apparently benign nature of structural defects, highly abundant in these compounds, with respect to optical and electronic properties. Here, we review the important differences that exist in the chemistry and physics of LHP NCs as compared with more conventional, tetrahedrally bonded, elemental, and binary semiconductor NCs (such as silicon, germanium, cadmium selenide, gallium arsenide, and indium phosphide). We survey the prospects of LHP NCs for optoelectronic applications such as in television displays, light-emitting devices, and solar cells, emphasizing the practical hurdles that remain to be overcome.Copyright © 2017, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Advances in small perovskite- based lasers
Metal halide perovskites for X-ray imaging scintillators and detectors
Low dimensional metal halide perovskites and hybrids
All-inorganic perovskite nanocrystal scintillators
Inorganic scintillators: today and tomorrow
An X-ray computed tomography imaging agent based on long-circulating bismuth sulphide nanoparticles
Nanomaterials have become increasingly important in the development of new molecular probes for in vivo imaging, both experimentally and clinically. Nanoparticulate imaging probes have included semiconductor quantum dots, magnetic and magnetofluorescent nanoparticles, gold nanoparticles and nanoshells, among others. However, the use of nanomaterials for one of the most common imaging techniques, computed tomography (CT), has remained unexplored. Current CT contrast agents are based on small iodinated molecules. They are effective in absorbing X-rays, but non-specific distribution and rapid pharmacokinetics have rather limited their microvascular and targeting performance. Here we propose the use of a polymer-coated Bi(2)S(3) nanoparticle preparation as an injectable CT imaging agent. This preparation demonstrates excellent stability at high concentrations (0.25 M Bi(3+)), high X-ray absorption (fivefold better than iodine), very long circulation times (>2 h) in vivo and an efficacy/safety profile comparable to or better than iodinated imaging agents. We show the utility of these polymer-coated Bi(2)S(3) nanoparticles for enhanced in vivo imaging of the vasculature, the liver and lymph nodes in mice. These nanoparticles and their bioconjugates are expected to become an important adjunct to in vivo imaging of molecular targets and pathological conditions.
Scintillation properties of perovskite single crystals
Low-cost solution-processed scintillation radiation detection materials are pursued urgently in ionization applications. Scintillators are key conversion materials that absorb high-energy X(gamma) photons and convert them into UV-visible photons. Bulk mix organic-inorganic hybrid perovskites (CH3NH3PbCl3-xBrx) have been employed to detect X(gamma) photons using a photon-photon conversion method. Optical properties were carefully investigated by photoluminescence (PL) spectra, PL lifetime, and X-ray excited luminescence (XEL) spectra at room temperature, which can be tuned with dopant Br concentration. Two XEL peaks centered at around 456 and 479 nm have been observed for the CH3NH3PbCl2.85Br0.15 single crystal scintillator. These two peaks originated from the near band-to-band emission and self-absorption-induced re-emission. Thick crystals are able to enhance the self-absorption induced re-emission, while suppressing the near band-to-band emission.
Zero- dimensional Cs3Cu2I5 perovskite single crystal as sensitive X-ray and γ-ray scintillator
Crystal growth and scintillation properties of pure and Tl-doped Cs3Cu2I5
Solution-processed lead-free bulk 0D Cs3Cu2I5 single crystal for indirect gamma-ray spectroscopy application
Lead-free highly efficient blue-emitting Cs3Cu2I5 with 0D electronic structure
Low-temperature solution-grown CsPbBr3 single crystals and their characterization
Recent progress in the synthesis of hybrid halide perovskite single crystals
Electron-hole diffusion lengths > 175 μm in solution-grown CH3NH3PbI3 single crystals