|
|
Research Progress of Perovskite Layer Structured Piezoelectric Ceramics with Super High Curie Temperature
ZHOU Zhi-Yong, CHEN Tao, DONG Xian-Lin
2018 Vol. 33 (3): 251–258
 Abstract
Abstract(
1974 )
 HTML
HTML(
103)
 PDF
PDF(879KB)(
3412
)
Perovskite-layer structured (PLS) piezoelectric ceramics have the characteristics of ultra high Curie temperature and good thermal stability, thus PLS ceramics have become one of the hot topics in the field of high temperature piezoelectric ceramics. The present article reviews the research progress on PLS piezoelectric ceramics from the aspects of crystal structure, processing technologies, doping modifications, and forming solid solutions in order to overcome their disadvantages of poor sinterability and low piezoelectricity. Meanwhile, this review summarizes and compares the effects of processing technologies and doping modifications on the sinterability and piezoelectricity of PLS ceramics. Furthermore, the origin of the spontaneous polarization of PLS ferroelectircs is briefly described. The mechanism of ferroelectric phase transition and the approaches to improvement of piezoelectric properties for PLS piezoelectric ceramics are proposed for research work in the near future.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Property of Alumina Aerogel
YANG Jing-Feng, WANG Qi-Hua, WANG Ting-Mei
2018 Vol. 33 (3): 259–265
 Abstract
Abstract(
2502 )
 HTML
HTML(
95)
 PDF
PDF(709KB)(
5949
)
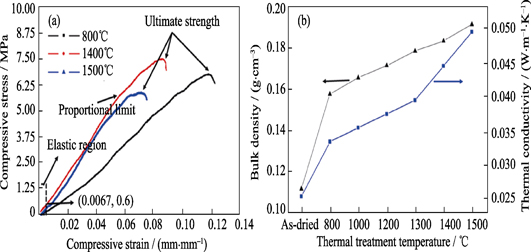
Alumina aerogel has wide application prospect in high temperature thermal insulation and catalytic fields due to its high specific surface area, high porosity, and better thermal stability than silica aerogel. However, the complicated synthetic process and the low strength of alumina aerogel restrict their application. In this review, the synthetic process of alumina aerogel is firstly introduced. Some problems existed in the Sol-Gel process, the characteristics of various drying methods, and the latest drying methods developed by researchers are pointed out. Then, some representation achievements in the performance improvements on specific surface area, thermal stability, thermal conductivity and compressive strength of alumina aerogel in recent years are summarized. Finally, the development and application of alumina aerogel in high temperature catalytic and thermal insulation fields are introduced, their development tendency is prospected, and some issues on the study of alumina aerogel are highlighted.
|
|
|
Wet Oxidation Process to Al0.98Ga0.02As Layer for the Vertical-Cavity-Surface-Emitting-Laser Fabrications
LIN Tao, ZHANG Tian-Jie, LI Jing-Jing, GUO En-Min, NING Shao-Huan, DUAN Yu-Peng, LIN Nan, QI Qiong, MA Xiao-Yu
2018 Vol. 33 (3): 266–272
 Abstract
Abstract(
1072 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(834KB)(
3490
)
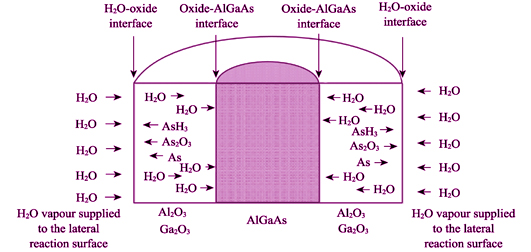
To study the wet oxidation process and mechanism in the Vertical-Cavity-Surface-Emitting-Laser (VCSEL) fabrications, a special material structure was designed and grown by the Metal-Organic Chemical Vapor Deposition(MOCVD) method. The samples formed by photolithography and dry etching were subjected to wet oxidation for different time, and the oxidation degree was determined by the surface morphology and the cross-sectional structure. In this study, a linear tendency was revealed between oxidation depth and oxidation time during a relatively short oxidation period, then it transformed into parabolic tendency and gradually became saturated with increasing oxidation time. Moreover, it was found that the oxidation rate of Al0.98Ga0.02As was higher than that of Al0.9Ga0.1As layer by one order of magnitude, and the speed of oxidation processing was accelerated as the Al0.9Ga0.1As layer thickened. Finally, the lateral oxidation process of Al0.98Ga0.02As layer in the confined space was interpreted by a modified one-dimensional Deal-Grove model.
|
|
|
Au Film Electrodes on CdZn Te Surface: Preparation and Ohmic Contact Property
XIE Jing-Hui, LIU Yu-Cong, WANG Chao, YIN Zi-Wei, CHEN Jia-Dong, DENG Hui-Yong, SHEN Yue, WANG Lin-Jun, ZHANG Jian-Guo, DAI Ning
2018 Vol. 33 (3): 273–278
 Abstract
Abstract(
1023 )
 HTML
HTML(
16)
 PDF
PDF(515KB)(
1561
)
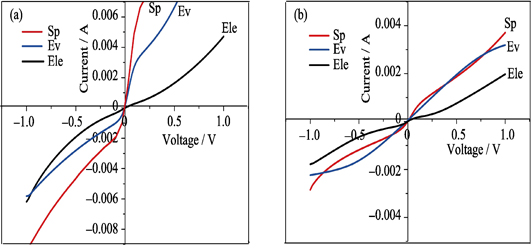
Tellurium cadmium zinc (CdZnTe) is a kind of II - VI wide band-gap semiconductor compound, which is a promising material to fabricate the X- or γ-ray detectors. Its Ohmic contact property significantly influences the detector performance. In order to study the influence of preparation technology on Ohmic contact properties of the electrode, Au film electrodes were deposited by sputtering deposition, vacuum evaporation and electroless deposition. By analyzing I-V curves, SEM and AC impedance spectra, microstructure and Ohmic contact properties of the samples were studied. The results show that surtace of the sample prepared by the electroless deposition is smooth and dense showing lower contact barrier and better Ohmic contact properties smooth and Ohmic contact properties of the electrodes. After annealing at 100℃, the Ohmic coefficient of the Au electrode prepared by electroless deposition increases from 0.883 to 0.915, and the barrier height reduces from 0.492 eV to 0.487 eV, displaying improved. AC impedance spectroscopy shows that it is the change of impurity-doping and defects of CdZnTe surface at the interface that attribute to the lowest contact barrier of the Au electrode prepared by electroless deposition.
|
|
|
Preparation and Property of CuInS2/ZnS Core-shell Quantum Dots in Aqueous Phase
ZHOU Bei-Ying, CHEN Dong, LIU Jia-Le, JIANG Wan, LUO Wei, WANG Lian-Jun
2018 Vol. 33 (3): 279–283
 Abstract
Abstract(
1163 )
 HTML
HTML(
20)
 PDF
PDF(639KB)(
2271
)
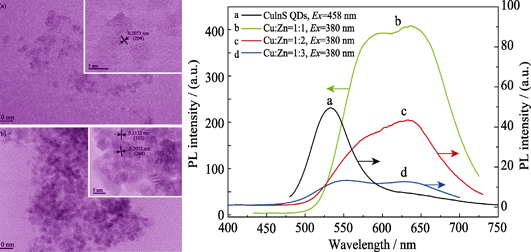
Owing to the absence of Cd, Pb, Te and other toxic elements, and the widely tunable fluorescence emission spectra from visible to near infrared light, CuInS2 quantum dots (QDs), as a new type of I-III-VI semiconductor materials, have been applied in biological detection and analysis imaging. In this study a fast and low temperature method was proposed to synthesize CuInS2 and its ZnS core-shell structure QDs with low toxicity raw materials. The ZnS outer layer suppresses the surface defects to improve the luminescence properties of CuInS2 QDs, and further reduces biological toxicity. CuInS2 QDs exhibited an obvious emission peak at 530 nm when the molar ratio of Cu∶In was 1∶1. With the increase of In content, the luminescence peak presents a gradual redshift. After coated with ZnS shell, the luminous intensity of QDs obviously increased and the emission peak red shifted. Further more, when the molar ratio of Cu∶Zn was 1∶1 and the reflux time was 45 min, the luminescent properties of the synthesized CuInS2/ZnS QDs were optimized. This synthesis method takes the advantages of energy saving, high production efficiency, and excellent environmental friendship, showing wide application potential.
|
|
|
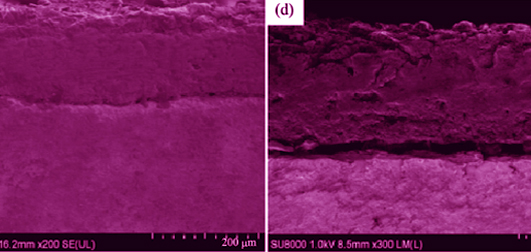
Influence of Reaction Time on Hydrogen Resistance Film on the Surface of ZrH1.8 in Aluminate System
ZHANG Peng-Fei, YAN Shu-Fang, CHEN Wei-Dong, LI Shi-Jiang, ZHAO Li, WANG Hong-Xing
2018 Vol. 33 (3): 284–288
 Abstract
Abstract(
660 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(1503KB)(
1373
)
Micro-arc oxidation process was conducted on ZrH1.8 in the electrolyte composed of NaAlO2 to fabricate hydrogen resistance film. The as-prepared film was then characterized by field emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and vacuum dehydrogenation experiment. The influences of reaction time on thickness, micro-morphology, structure, and hydrogen resistance properties of the hydrogen resistance film on the surface of ZrH1.8 were investigated. The results show that the thickness of the surface film increases from 78.4 μm to 152.8 μm with the oxidation time changing from 7.5 min to 15 min. The film is composed of M-ZrO2, T-ZrO2 and C-ZrO2, and the oxidation time has no obvious influence on its structure. The film comprises of an exterior loose layer and an interior layer by substrate. When the oxidation time is 10 min, the obtained film is compact and uniform, and has a moderate thickness, showing an excellent hydrogen permeation resistance, of which the Permeation Reduction Factor (PRF) value reaches up to the maximum of 20.
|
|
|
Surfactant Dependence of Nanostructured NiCo2S4 Films on Ni Foam for Superior Electrochemical Performance
ZHANG Guo-Xiong, CHEN Yue-Mei, HE Zhen-Ni, LIN Chuan, CHEN Yi-Gang, GUO Hai-Bo
2018 Vol. 33 (3): 289–294
 Abstract
Abstract(
1149 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(786KB)(
1426
)
Nanostructured NiCo2S4 films on Ni foams were successfully synthesized through a facile method, involving hydrothermal growth of NiCo-precursor and subsequent sulfidation process of NiCo2S4. The influence of different surfactants were investigated, including morphology, phase structure and electrochemical performance of NiCo2S4 electrodes. With the addition of surfactants during the hydrothermal processes, the nanostructured NiCo2S4 self-organized and agglomerated into nanosheets, showing outstanding influence on the morphology by the surfactants. Among these electrodes, the NiCo2S4 electrode modified with SDS exhibited an optimal capacitance of 2893 F/g at 0.5 A/g, a superior rate capability of 1890.6 F/g even at 10 A/g, and good cycling stability of 96.1% over 1000 cycles. These results indicate that nanosheet NiCo2S4 would be promising electrode materials for supercapacitor applications.
|
|
|
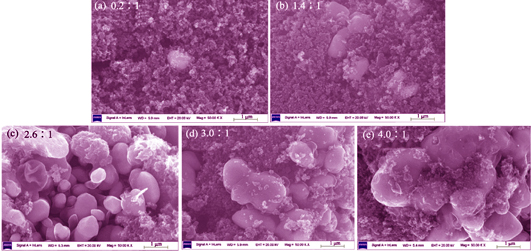
Fe-N Modified Carbon Black as a High-performance and Cost-effective Cathode Catalyst in Microbial Fuel Cells
XIE Yang-En, WANG Ding-Ling, MA Zhao-Kun, SONG Huai-He, XU Pei
2018 Vol. 33 (3): 295–300
 Abstract
Abstract(
844 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(496KB)(
1607
)
Carbon black is a high conductive and cheap catalyst for oxygen reduction, which can be used as cathode catalyst of microbial fuel cells. However, pure carbon black has low catalytic activity which does not meet the requirement in practical field. In order to improve the catalytic performance of carbon black, ferric chloride (FeCl3) and melamine, as sources of Fe and N respectively, were mixed with carbon black at a certain ratio and co-carbonized. Results show that the output power density reaches the highest value (1395 mW/m2) with the mass ratio of 2.6∶1 (FeCl3-melamine/carbon black), which is 59% higher than that of the widely used Pt/C catalyst (876 mW/m2). SEM images show that some elliptic or columnar crystals are formed on the surface of carbon black, which is testified to be Fe3C crystal by XRD and XPS. Meanwhile, pyridinic and quaternary nitrogen generated by carbonization provides more active sites on the catalyst surface, thus improving the catalytic performance of composite catalyst. With the increasing ratio of Fe-N, the conductivity and the surface area of composite catalyst decrease gradually, which limits the catalytic performance. All those data demonstrated that the catalyst generated by FeCl3, melamine and carbon black is an exceptional cost-effective cathode catalyst which can be used in scale-up MFCs.
|
|
|
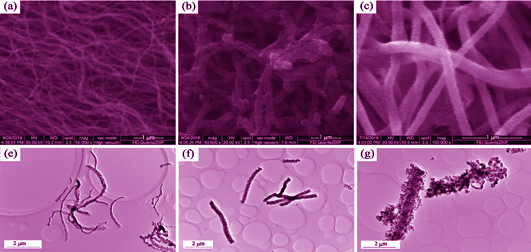
Synthesis and Electrochemical Performance of Fe2O3 Nanofibers as Anode Materials for LIBs
CAI Jian-Xin, LI Zhi-Peng, LI Wei, ZHAO Peng-Fei, YANG Zhen-Yu, YU Ji
2018 Vol. 33 (3): 301–306
 Abstract
Abstract(
1226 )
 HTML
HTML(
20)
 PDF
PDF(554KB)(
1783
)
Due to high theoretical specific capacity and low cost, Fe2O3 has become an attractive research field in anode materials for lithium-ion batteries (LIBs). In this study, by using PVP/FeCl3 solutions with different concentrations as precursors, Fe2O3 nanofibers with different diameters were prepared by electrospinning technology and anneal treatment. In addition, Fe2O3 nanoparticles were prepared by hydrothermal synthesis method. The crystalline structure, morphology and electrochemical performances of the composites were investigated by X-ray diffraction, thermogravimetric analysis, infrared spectrum, scanning electron microscope, transmission electron microscope, and charge-discharge tests. Results showed that Fe2O3 nanofibers has better electrochemical performance than Fe2O3 nanoparticles. Fe2O3 nanofibers with diameter of 160 nm exhibited the highest rate and cycle performance as anode material in LIBs. It was found that the Fe2O3 electrode could deliver a discharge capacity of 827.3 mAh/g at 0.1 A/g current density and 439.1 mAh/g at 2 A/g after 70 cycles.
|
|
|
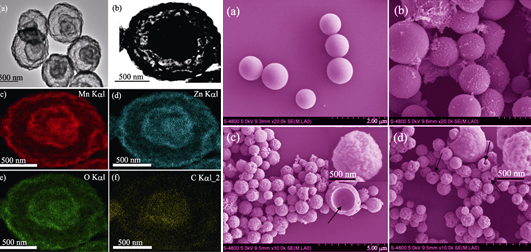
Semi-hollow/Solid ZnMn2O4 Microspheres: Synthesis and Performance in Li Ion Battery
LI Bo, HAO Wen, WEN Xiao-Gang
2018 Vol. 33 (3): 307–312
 Abstract
Abstract(
928 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(1076KB)(
1688
)
Porous semi-hollow/solid ZnMn2O4 microspheres were controllably synthesized via template and solvothermal methods respectively. The as-synthesized samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM) and transmission electron microscope (TEM). It is found that the solvent ratio exerts a crucial effect on the morphology and microstructure of solid ZnMn2O4 microspheres. The porous solid ZnMn2O4 microspheres could be obtained when the volume ratio of ethylene glycol to deionized water was 3 : 1. The semi-hollow ZnMn2O4 microspheres with a double-layer ZnMn2O4 shell and a small C core could be synthesized via a template-solvothermal method and post-calcination process. The electrochemical properties of as-prepared semi-hollow/solid ZnMn2O4 microspheres as anode materials of lithium-ion batteries were investigated. Semi-hollow ZnMn2O4 microspheres exhibit higher initial discharge capacity, better rate capacity and cycling performance than solid ZnMn2O4 microspheres.
|
|
|
Preparation and Electrochemical Performance of Ordered Mesoporous Si/C Composite for Anode Material
WANG Jing, CHENG Zhi-Ning, GUO Yu-Zhong, HUANG Rui-An, WANG Jian-Hua
2018 Vol. 33 (3): 313–319
 Abstract
Abstract(
1061 )
 HTML
HTML(
14)
 PDF
PDF(804KB)(
1741
)
Using SBA-15 of SiO2 template as precursor, a bundle-shaped ordered mesoporous nanoarchitecture Si/C composite (OMP-Si/C) was successfully assembled 2D-directionally by a magnesiothermic reduction reaction (MRR) route and the ensuing carbon-coating modification processing, and the MRR process of the SBA-15 was investigated in depth, the electrochemical performance of as-prepared OMP-Si/C composites was tested. Analysis based on XRD data reveals the presence of a reaction path of Mg2Si intermediate phase in MRR process, on which a T-t (reaction temperature-reaction time) phase transition diagram is proposed. DSC/TG analysis shows that Mg particles may melt below its melting point (648℃) upon reaction, and in liquid-solid reaction pattern react with SiO2 via melting-reaction teamwork. Observed from FE-SEM, SBA-15 column units are validated to assemble into a lotus-root-chain-bundle shaped nanoarchitecture of ordered mesoporous silicon, which can effectively offset the drastic volume change of Si material inherent in the charge/discharge process, and exhibit excellent cycling stability and rate capability. Based on the micro-fluid field assembling mechanism, the two-dimensional directional assembly process can be reasonably interpreted.
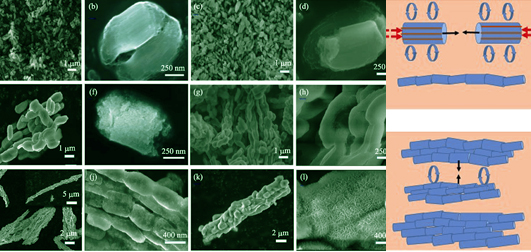
|
|
|
LiNixCoyMn1-x-yO2 Cathode Material Synthesized through Construction of E-pH Diagram and Its Electrochemical Performance
LI Ling, LI Yun-Jiao, XU Bin, LU Wei-Sheng, SU Qian-Ye, CHEN Yong-Xiang, LI Lin
2018 Vol. 33 (3): 320–324
 Abstract
Abstract(
1327 )
 HTML
HTML(
11)
 PDF
PDF(421KB)(
2365
)
The thermodynamic data of various species in Li-Ni-Co-Mn-H2O system is obtained by thermodynamics calculation, and E-pH diagrams for Li-Ni-Co-Mn-H2O system with activity 1.00 at 25℃ and 200℃ were constructed. From E-pH diagrams, it shows that there is no predominant region of the LiNixCoyMn1-x-yO2 composite oxide in pH range of 3~13 at 25℃. However, the stability region of various species expands towards the low pH and low potential zones as the temperature increases. When pH is between 9.7~13.0 at 200℃, synthesis of LiNixCoyMn1-x-yO2 via aqueous process is thermodynamically possible, and high temperature is favorable. Experimental results showed that the composite precursor (LNCM) with α-NaFeO2 structure was successfully prepared in aqueous solution by using (Ni0.5Co0.2Mn0.3)(OH)2 as precursor and LiOH·H2O as raw material. LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2 cathode materials were then obtained by post heat treatment and following tests exhibited excellent cycling performance. These experimental results are in consistent with the information given in E-pH diagram of the Li-Ni-Co-Mn-H2O system, and the as-prepared LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2 cathode materials show excellent cycling performance.
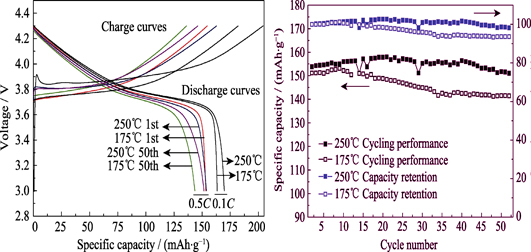
|
|
|
Preparation of Si/Mullite/Yb2SiO5 Environment Barrier Coating (EBC) by Plasma Spray-Physical Vapor Deposition (PS-PVD)
ZHANG Xiao-Feng, ZHOU Ke-Song, LIU Min, DENG Chun-Ming, NIU Shao-Peng, XU Shi-Ming
2018 Vol. 33 (3): 325–330
 Abstract
Abstract(
1216 )
 HTML
HTML(
14)
 PDF
PDF(923KB)(
2112
)
Environmental barrier coating (EBC) Si/3Al2O3-2SiO2/Yb2SiO5 was prepared by plasma spray-physical vapor deposition (PS-PVD) on SiC/SiC ceramic matrix composites. The surface and interface of tri-layered EBC were characterized by SEM. And the phase transformation of the mullite coating was analyzed by XRD. The interaction of feedstock powder and high temperature plasma jet was investigated. Furthermore, the deposition mechanism of EBC was studied. Experimental results dermonstrated that EBC with low porosity and good bonding can be obtained by PS-PVD. EBC withont micro-crack was observed on the surface of Si coating in contrast to coating mullite and Yb2SiO5 coating. The size of crack in mullite surface was larger than that in Yb2SiO5 coating. Low porous EBC was deposited by liquid droplet accompanied by gas and solid state through PS-PVD. Yb2SiO5 coating was dense and formed laminar structure, mainly resulting from liquid droplet deposition. Additionally, nano-grains were observed in Yb2SiO5 coating which resulted from both homogeneous and heterogeneous nucleation of vapor phase. And sub-micron/micron grains were obtained from semi-molten and splashed particles.
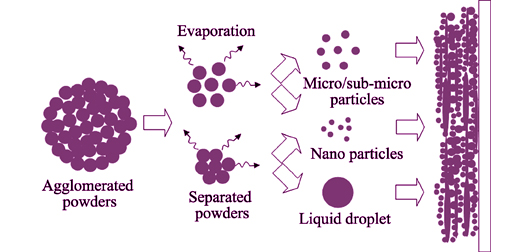
|
|
|
Metal Buffer Layer on Structure, Mechanical and Tribological Property of GLC films
LI Lei, GUO Peng, LIU Lin-Lin, SUN Li-Li, KE Pei-Ling, WANG Ai-Ying
2018 Vol. 33 (3): 331–338
 Abstract
Abstract(
864 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(1071KB)(
1278
)
Graphite-like carbon films (GLC) with different metal buffer layers (Cr, Ti, W) were fabricated by direct current magnetron sputtering technique. The effect of metal buffer layer on structure and tribological properties in artificial seawater were carefully investigated. The results show that, in contrast to Ti/GLC and W/GLC film, Cr/GLC film has the highest sp2 hybridization content, which increases from the top layer to Cr/C interface. The highest sp2 hybridization content promotes graphitization degree of the tribo-film which acts as lubrication phase in the sliding process. The results of potentiodynamic polarization tests show that, in all of three GLC films, Cr/GLC film shows superior corrosion resistance with the highest corrosion voltage (Ecorr) of -0.16 V and the lowest corrosion current (icorr ) of 4.42×10-9 A/cm2. As a result, Cr/GLC film presents the best tribological properties in artificial seawater in contrast to Ti/GLC and W/GLC films.
|
|
|
Preparation and Characterization of NaA Zeolite Membranes on Inner-surface of Four-channel Ceramic Hollow Fibers
WANG Xiao-Lei, ZHANG Yu-Ting, GAO Bing, ZHANG Chun, GU Xue-Hong
2018 Vol. 33 (3): 339–344
 Abstract
Abstract(
1023 )
 HTML
HTML(
15)
 PDF
PDF(1073KB)(
1602
)
High-performance NaA zeolite membranes were prepared on inner-surface of four-channel ceramic hollow fibers by combined counter-diffusion vacuum seeding and dynamic hydrothermal synthesis method. The as-prepared membranes were adopted to the pervaporation dehydration of 90wt% ethanol/water mixture at 75℃. Effects of seeding and synthesis conditions on morphology and separation performance of the membranes were extensively investigated in terms of flow rate of seed suspension, seeding time and synthesis temperature. These results showed that dense and uniform NaA zeolite membrane was obtained when the flow rate of seed suspension was 100 mL/h and the seeding time was 5 s. Over slow flow rate of seed suspension or too long seeding time increased the membrane thickness but generated defects on membrane surface simultaneously. When the NaA zeolite membrane was hydrothermally synthesized at 100℃ for twice, the membrane achieved the best water/ethanol separation factor of 1585 while the permeation flux was 8.8 kg/(m2·h) in the pervaporation dehydration. Lower synthesis temperature led to incomplete membrane crystallization and some defects were observed on the membrane surface. With excessive synthesis temperature defects were also detected in the cross-section of the membrane due to the over rapid crystallite rate, which resulted in poor separation performance of the membrane.
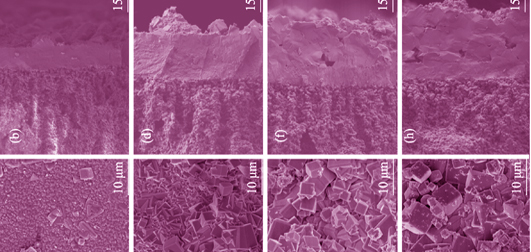
|
|
|
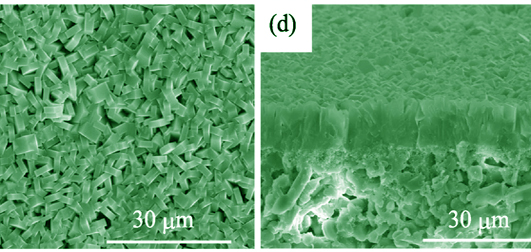
Preparation and Characterization of High Performance MFI Zeolite Membrane in Ultradilute Solution
HUANG Pan, ZHOU Liang, LI Hua-Zheng, LI Hong-Jian, YANG Jian-hua, WANG Jin-Qu
2018 Vol. 33 (3): 345–351
 Abstract
Abstract(
956 )
 HTML
HTML(
14)
 PDF
PDF(902KB)(
1581
)
High performance MFI-type zeolite membrane was successfully prepared in ultradilute solution (H2O/SiO2= 1000) on inexpensive and macroporous α-Al2O3 tubular support by secondary growth. Influences of seed size and H2O/SiO2 on morphology and pervaporation performance of the zeolite membranes were investigated. Results showed that the seed layer prepared with 0.4 μm seeds had higher crystal nucleus density which could increase the amount of the nucleation site on the support surface, resulting in a stronger induced effect on the growth of zeolite membrane. The low-concentration template and silicon source in ultradilute solution decreased the growth rate of zeolite crystals, which could reduce the zeolite membrane thickness and effectively inhibited the formation of intercrystalline defects. The flux and separation factor (αethanol/water) of the resulting MFI zeolite membrane achieved 4.09 kg/(m2·h1) and 47, respectively, for separation of 5wt% ethanol/water mixture at 60℃. Ultradilute solution and low-cost macroporous α-Al2O3 tubular support reduced the preparation cost of MFI zeolite membranes and increased the flux, showing prospect of the potential industrial application of MFI-type zeolite membrane for removal of the low-concentration organic compounds in water.
|
|
|
Charge-switchable Metal-organic Framework for Size/Charge-selective Molecular Inclusions
YUAN Bei-Bei, ZHOU Bei-Bei, ZHANG Yue-Biao, SHI Jian-Lin
2018 Vol. 33 (3): 352–356
 Abstract
Abstract(
1166 )
 HTML
HTML(
26)
 PDF
PDF(778KB)(
1715
)
Highly size/charge-selective molecular inclusions by a charge-switchable zinc-based metal-organic framework (Zn-MOF) have been achieved, which comprises of two kinds of paddle-wheel building units and four kinds of nanocages. Featuring counter anions floating in the pore and accessible coordination sites on the skeleton, Zn-MOF represents exceptional versatility in taking up anionic dyes by ion-exchange, cationic dyes by charge switch of skeleton, and neutral organic dyes by host-guest interactions. Both size and charge selectivities in the molecular inclusion by the charged nanocages in Zn-MOF provide an efficient way in designing superior porous materials with an enhanced level of compatibility and recognition.
|
|
|
Electrospun Silicon Oxycarbide Ultrafine Fibers Derived from Polycarbosilane
WU Nan, WAN Lynn Yuqin, WANG Ying-De, FRANK KO
2018 Vol. 33 (3): 357–362
 Abstract
Abstract(
1098 )
 HTML
HTML(
30)
 PDF
PDF(834KB)(
1464
)
Silicon oxycarbide (SiOC) ultrafine fibers with uniform distribution were prepared via electrospinning of polycarbosilane (PCS)/polystyrene followed by oxidation and pyrolysis at 1100℃. The diameter of SiOC fibers ranged from 500 to 900 nm through adjusting PCS concentration. The average tensile strength of SiOC fiber mat was 8.88 MPa. The obtained SiOC fibers also displayed outstanding thermal stability and chemical resistance, making them promising materials as smart filters and catalyst supports in harsh environment.
|
|