|
|
Progress on Fabrication of Nanoporous Carbon via CDC Method
DUAN Li-Qun, MA Qing-Song, CHEN Zhao-Hui
2013 Vol. 28 (10): 1051–1056
 Abstract
Abstract(
790 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(368KB)(
1861
)
Nanoporous carbon possesses great potential in many areas, such as adsorption, separation, catalyst support and so on for its favorable performances (excellent biocompatibility, good conductivity, high specific surface area, etc.). The carbide-derived carbons (CDC) methods have a series of advantages, such as well-tuned specific surface area in large-scale, well-controlled pore structure and graphitization degree, lower synthesis temperature, near net shape transformation compared with other methods, which arouse interests from researchers. This article aims to summarize the current development of nanoporous carbon via CDC methods from principles to application and its prospect is also introduced.
|
|
|
Tribological Behaviors and Anti-wear Mechanisms of Carbon/Carbon-silicon Carbide Composites
ZHOU Hai-Jun, DONG Shao-Ming, HE Ping, HU Jian-Bao, WU Bin
2013 Vol. 28 (10): 1057–1061
 Abstract
Abstract(
952 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(911KB)(
2322
)
C/C-SiC composites were prepared by liquid silicon infiltration (LSI) process. The tribological properties were investigated using MMW-1A and MM-1000 test machine, respectively. Under experimental conditions, the rotation speed had limited impact on the tribological properties of C/C-SiC composites when the pressure was 0.48 MPa. The pressure had approximately the same effect on the wear rate when the rotation speed was 0.3 m/s. The wear mechanism was mainly abrasive grain wear. While under real brake conditions, the coefficient of friction (COF) of C/C-SiC composites reached 0.50 and the wear rate was up to 5.95 mg/times. The COF curves showed the typical saddle shapes brake curves. Abrasive grain wear mechanism and adhere wear mechanism appeared in the early and last stages in real brake conditions.
|
|
|
Effect of Particle Size on Densification and Mechanical Properties of Hot-pressed Boron Carbide
DU Xian-Wu, ZHANG Zhi-Xiao, WANG Wei-Min, FU Zheng-Yi, WANG Hao
2013 Vol. 28 (10): 1062–1066
 Abstract
Abstract(
1148 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(495KB)(
1574
)
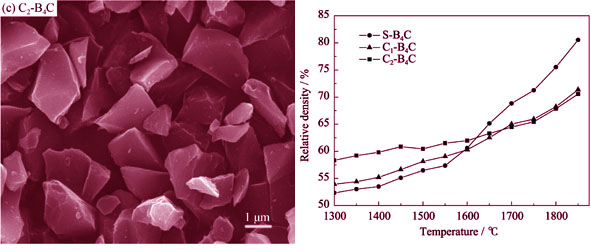
Monolithic B4C ceramics were prepared by hot-pressing using three types of B4C powders with average particle of 3.5 μm, 1.5 μm and 200 nm, respectively. The effect of particle size on densification and microstructure of sintered ceramics was studied. The activation energy difference of the starting powders in the initial sintering stage was obtained in terms of dwelling time as a function of linear shrinkage and plastic deformation mechanism. The result shows that at the same process, the diffusion activation energy and densification initial temperature of the powders decrease with the mean particle size decreasing, and the time of plastic flow in the initial sintering stage is also shortened markedly, while the relative density and densification rate are higher. The microstructure and mechanical properties of sinterd samples are also improved with mean particle size decreasing. The relative density of 90.5% and hardness of (17±1.8) GPa are achieved for the B4C ceramics sintered from the powders with mean particle size of 200 nm for 1 h at 1850℃.
|
|
|
Removal of Microalgae in Ballast Water by Coal-based Porous Carbon Membrane
SONG Cheng-Wen, TAO Ping, SONG Xue-Kai, WU Shuai-Hua, SHAO Mi-Hua, GAO Guang-Rui, FENG Yi-Ning, WANG Tong-Hua
2013 Vol. 28 (10): 1067–1071
 Abstract
Abstract(
802 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(434KB)(
1147
)
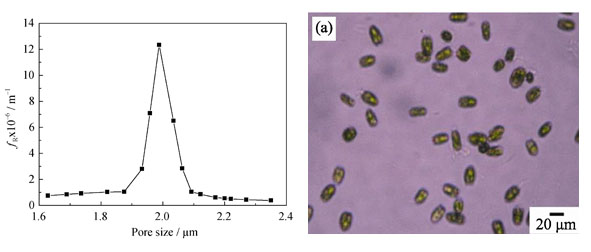
Introduction of invasive species via ballast water has been identified as one of the greatest threats to oceans. The coal-based porous carbon membrane with low cost for removal of microalgae in ballast water was prepared by carbonization of tubular carbonaceous precursor obtained by extrusion method. Scanning electron microscopy and bubble-pressure method were employed to investigate the morphology and pore structure characteristics of carbon membrane. Effects of microalgae size, transmembrane pressure and crossflow velocity on the steady-state flux were also studied. The results indicate that the as-prepared carbon membrane has smooth surface, rich and uniform porous structure, which are beneficial for removing microalgae in ballast water. A decrease in steady-state flux is observed as the microalgae size increases. High transmembrane pressure is more prone to block the membrane pore and results in the decrease of the steady-state flux. High crossflow velocity is favorable to increase the steady-state flux owing to the inhibition of fouling layer development through the high shear stress on membrane surface. After being treated by coal-based carbon membrane, no microalgae are detected. It indicates that coal-based carbon membrane is of great potential to ballast water treatment.
|
|
|
Preparation and Formation Mechanism of New PdHx-Pd/C Catalyst through Hydrazine-reducing Method under Atmospheric Pressure and H2-free Conditions
HUAN Chang-Yong, MA Lei, L- De-Yi, ZHENG Yi-Fan, JI Lai-Jun, LI Xiao-Nian
2013 Vol. 28 (10): 1072–1078
 Abstract
Abstract(
991 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(583KB)(
2014
)
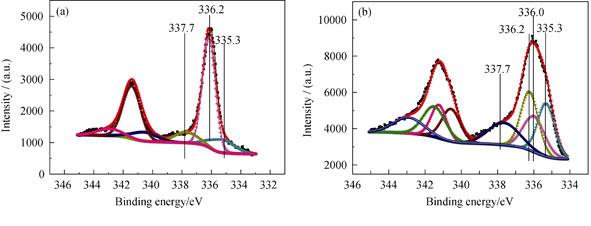
PdHx is an important reactive species for the Pd/C catalyst. Without H2, it can not exist stably at room temperature. This species is usually prepared through reaction of Pd with H2 under certain pressure. PdHx-Pd/C catalyst was prepared through hydrazine-reducing method under atmospheric pressure and H2-free conditions. The microstructure, morphology and chemical state of PdHx and Pd particles were investigated by XRD, TEM and XPS characterization methods. The formation mechanism of PdHx particles in the hydrazine-reducing method was proposed. Experimental results show that the average particle size of PdHx is 3.9 nm, and the d spacing of PdHx(111) is slightly larger than that of Pd(111). The PdHx particles derive from the reduction process of PdO by hydrazine. Their particle size is closely related to the particle size and structural imperfection of PdO. The PdHx-Pd/C catalyst demonstrates better catalytic performance than the conventional Pd/C catalyst in the amination reaction to produce 2, 6-dimethylaniline under H2-free condition.
|
|
|
Synthesis of Porous-Bi2WO6 and Its Photocatalytic Oxidative Desulfurization (Photo-ODS) Activity of Simulation Fuel
WANG Dan-Jun, YUE Lin-Lin, GUO Li, FU Feng, XUE Gang-Lin
2013 Vol. 28 (10): 1079–1086
 Abstract
Abstract(
1198 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(1039KB)(
6319
)
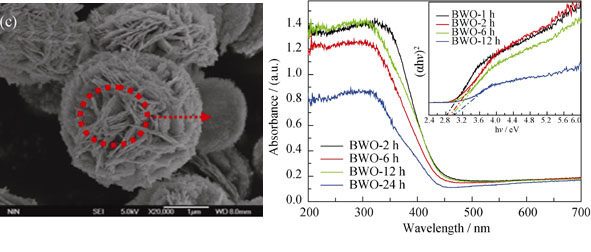
Porous-Bi2WO6 was synthesized by a hydrothermal process. The phase composition, morphology, surface area/pore size distribution and optical properties of as-synthesized Bi2WO6 sample were investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD), filed-scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM), transmission electron mcroscope (TEM), energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS), UV-Vis absorption spectrum (UV-Vis-DRS), and low-temperature N2 adsorption/desorption techniques. Furthermore, the photocatalytic oxidative desulfurization (Photo-ODS) activity of as-synthesized Bi2WO6 samples was also investigated. The experimental results reveal that reaction temperature and reaction time have a significant effect on the morphology and structure of Bi2WO6 under the strong acidic medium. After 2 h of reaction at 190℃, the as-obtained sample exhibits a novel nest-like 3D Bi2WO6 microcrystal with scales of 3-4 μm. HR-SEM reveals that the 3D nest-like Bi2WO6 microcrystal composes of many small secondary nanoplates. XRD and EDS results confirm that the as-synthesized D nest-like Bi2WO6 microcrystal is orthorhombic pure-Bi2WO6. N2 adsorption/desorption isotherms and the pore distribution result show that nest-like 3D Bi2WO6 microcrystal has pores in the size of 6-8 nm and the BET surface area is calculated to be as much as 17.49 m2/g. The photocatalytic experimental result illustrates that as-synthesized 3D nest-like porous Bi2WO6 microcrystals exhibit an excellent photocatalytic performance to photocatalytic oxidative desulfurization for simulated fuel oil under sun-like light irradiation. Under the conditions of 100 mL/min air flow, 1.2 g/L photocatalyst amount, and visible-light irradiation for 180 min, the desulfurization rate of simulated fuel oil reaches 91.2%, and the stability of photoctalyst is also good.
|
|
|
Preparation and Non-linear Optical Properties of Mesoporous Silica Film Incorporated with Gold Nanowires
ZHANG Qian, SHAN Feng, LU Xue-Min, LU Qing-Hua
2013 Vol. 28 (10): 1087–1092
 Abstract
Abstract(
872 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(4557KB)(
1003
)
An Au-loaded oriented mesoporous silica film was prepared by hot air flow method and its non-linear optical properties were investigated. Amino groups were first introduced to the oriented mesochannels’ surface based on a chemical reaction, and gold nanowires were incorporated into the oriented mesochannels via the reduction by H2 after the interaction between the amino groups and auric chloride acid. The hybrid film presents obviously non-linear optical properties according to Z-scan measurement. The hybrid film shows anisotropy, which is consistent with the fact that the nanowires are aligned. So the film is expected to be applied in the new optical devices.
|
|
|
Preparation and Photovoltaic Performance of SnS Sensitized Nanocrystallite TiO2 Photoanode
ZHANG Xiao-Ping, LAN Zhang, CHEN Lin, GAO Su-Wen, WU Wan-Xia, QUE Lan-Fang, ZHANG Xiao-Pei
2013 Vol. 28 (10): 1093–1097
 Abstract
Abstract(
1039 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(577KB)(
1573
)
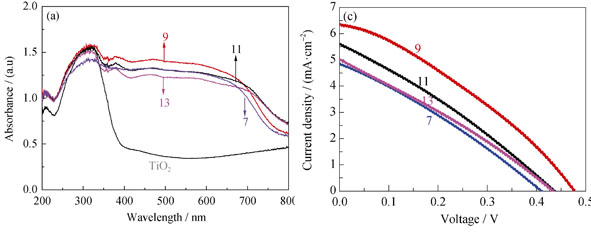
A simple method of successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction (SILAR) was employed to prepare SnS sensitized nanocrystallite TiO2 photoanodes. The characteristics of these photoanodes, such as surface morphology, crystal structure, UV-Vis adsorption and diffusion properties, were measured with XRD, TEM, UV-Vis adsorption and diffusion spectra, respectively. The photovoltaic performances of SnS sensitized solar cells with these photoanodes were measured. The effects of counter electrodes with polyaniline or platinum catalyst and liquid electrolytes with iodine or sulfur redox couple on the photovoltaic performance were also studied. The cells assembled with these different components showed different photovoltaic performance. It was found that the cell assembled with the photoanode fabricated by 9 times of SILAR circulation, the counter electrode with polyaniline-stainless steel net, and the liquid electrolyte containing sulfur redox couple showed the highest photovoltaic performance. The short-circuit current density, open-circuit voltage, fill factor, and power conversion efficiency could reach 4.59 mA/cm2, 0.547 V, 0.505 and 1.27%, respectively.
|
|
|
Ferromagnetism Induced by Defects in Cr-doped TiO2 Nanopowders
ZHAO Qian, WU Ping
2013 Vol. 28 (10): 1098–1102
 Abstract
Abstract(
871 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(433KB)(
1439
)
Rutile Ti1-xCrxO2 (x=0, 0.04, 0.08) nanopowders were synthesized by the Sol-Gel method. Magnetic measurements indicate that as-prepared Cr-doped rutile TiO2 nanopowders exhibit room-temperature ferromagnetism with saturation magnetizations Ms of 0.55×10-3 and 1.6×10-3 emu/g, respectively, for samples x=0.04 and 0.08. And their coercive forces Hc are 220 and 40 Oe, respectively. The saturation magnetizations Ms increase with increasing Cr doping concentration. Annealed nanopowders in Ar atmosphere are superparamagnetic. The tight scan Cr2p by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy spectra (XPS) indicates that Cr ions are in the +3 state for all samples. Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectra indicates that Cr3+ ions contribute only to paramagnetism. Based on above analysis, slight ferromagnetism of Cr-doped TiO2 nanopowders at room temperature originates from structural defects introduced by doping Cr ions, where oxygen vacancies play an important role.
|
|
|
Preparation of SrTiO3 Cubes by Molten Salt Method and Its Surface Ions Modification with Cu(II) Clusters
LONG Zhen, WEI Xian-Hua, QIU Xiao-Qing
2013 Vol. 28 (10): 1103–1107
 Abstract
Abstract(
967 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(470KB)(
1518
)
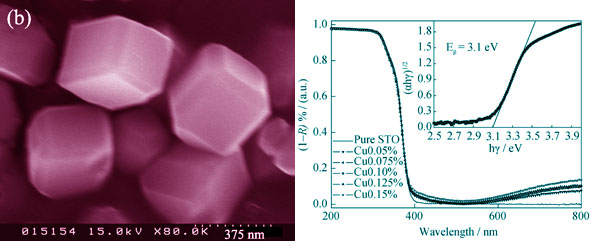
Pure SrTiO3 cubes with perovskite structure were prepared by a molten salt method. The novel visible light active photocatalysts were obtained as a result of surface modification of SrTiO3 cubes with Cu ions by an impregnation technique. The as-prepared samples were characterized by an inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometer, X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscope (XPS), and UV-Vis diffuse reflectance spectroscope (DRS). The decomposition of gaseous 2-propanol was chosen as a probe to evaluate the photocatalytic activities of the samples in air. The results show that the visible light photocatalytic activities of the samples can be significantly enhanced by grafting amorphous Cu(II) clusters on the surfaces of SrTiO3. Under visible light irradiation, electrons in the valance band of SrTiO3 are transferred to the surfaced Cu(II) clusters, leaving holes with strong oxidizing power in the valance band and producing Cu(I) clusters. The Cu(I) clusters can efficiently reduction oxygen molecules via a multi-electron reduction process to consume the excited electrons. On the other hand, the generated holes can decompose the organic compounds. As a result, the complete decomposition of gaseous 2-propanol into CO2 can be achieved over the Cu(II)-SrTiO3 under visible light irradiation.
|
|
|
Electrolyte Thickness Control and Its Effect on YSZ/Ni-YSZ Dual-layer Hollow Fibres
GONG Xun, MENG Xiu-Xia, YANG Nai-Tao, TAN Xiao-Yao, YIN Yi-Mei, MA Zi-Feng
2013 Vol. 28 (10): 1108–1114
 Abstract
Abstract(
1009 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(1222KB)(
1680
)
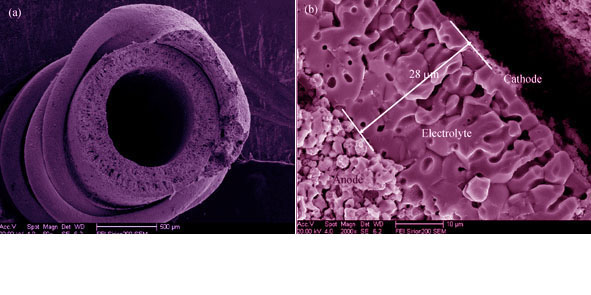
Electrolyte/anode (YSZ/NiO-YSZ) dual-layer hollow fibres were developed by a co-spinning process based on phase inversion technique for fabrication of micro tubular solid oxide fuel cells (MT-SOFCs). After being calcined at 1450℃ in ambient air and reduced at 700℃ in H2 for 4 h, the precursors were transformed into dual layer YSZ/Ni-YSZ hollow fibers. Full MT-SOFCs were fabricated by dip-coating with La0.8Sr0.2MnO3-δ (LSM) ink on the outer surface of YSZ/NiO-YSZ dual layer hollow fibers and sintering at 1200℃. The results show that the YSZ membranes of the dual-layer hollow fibers possess thicknesses of 6, 13, 18 and 28 μm when the spinning rates of electrolyte dopes are 0.5, 1, 1.5 and 2 mL/min and the anode dope keeps on a constant rate of 10 mL/min. The bending strength and the gas-tightness of the dual-layer hollow fibers increase with the increase of electrolyte thickness. However, the electrical conductivity and porosity of the dual-layer hollow fibers are less influenced by YSZ thickness. The maximum power density of single MT-SOFC with an electrolyte layer of 28 μm is 75 mW/cm2, while the output of an MT-SOFC with a 6 μm-thick YSZ membrane is up to 329 mW/cm2, both operated at 800?℃ using 20 mL/min H2 as fuel and 30 mL/min air as oxidant.
|
|
|
Properties of Cu-based Oxygen Carrier Used for Chemical Looping Oxygen Production
WANG Kun, YU Qing-Bo, XIE Hua-Qing, QIN Qin, LI Jiu-Chong
2013 Vol. 28 (10): 1115–1120
 Abstract
Abstract(
721 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(676KB)(
1265
)
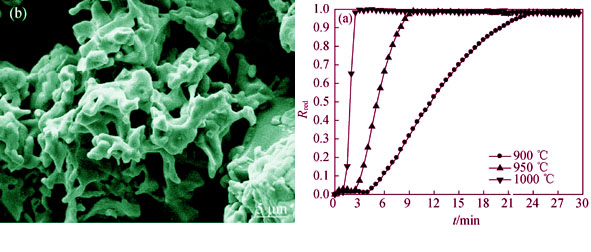
The optimal reaction temperatures were investigated via the temperature programmed thermogravimetry, and the effects of particle size, gas flow rate and reaction temperature on reduction and oxidation reactions were studied via isothermal thermogravimetry by using STA409PC thermal analyzer. BET, SEM and XRD were also used to analyze the specific surface area, surface morphology and phases of the prepared oxygen carriers. The results show that the Cu/Si oxygen carrier has the high reactivity of releasing and adsorbing oxygen when the temperatures are higher than 850℃ and 400℃. The reaction rates have increased with gas flow rate increase and particle size decreasing, but the increase tendency is not apparent. The reaction rates increase greatly with the temperature increase. The oxygen carrier has excellent stability under 900℃ oxygen reduction and 700℃ oxygen oxidation conditions. Phases and surface morphology of oxygen carriers were measured by X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscope before and after experiments. The main phases of oxygen carrier are composed of CuO and SiO2 in fresh and oxidized samples, Cu2O and SiO2 in reduced samples, which reveal that the oxygen carrier is stable when using the preparation process and under the operation conditions. The porous structure of cycled oxygen carrier is much more apparent than fresh samples and particles do not appear to disintegrate after 23 cycles.
|
|
|
Synthesis of Pt/WO3-C as Catalyst for Oxygen Reduction Reaction and Its Evaluation of Stability
GUO Fu-Rong, TIAN Jian-Hua, HU Min, SHAN Zhong-Qiang
2013 Vol. 28 (10): 1121–1126
 Abstract
Abstract(
984 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(710KB)(
1745
)
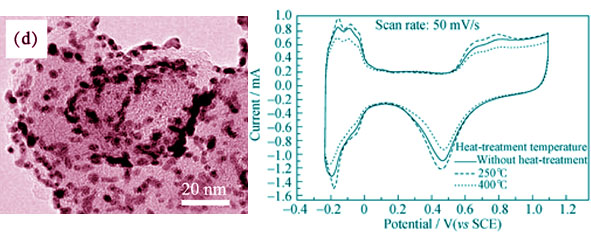
The WO3-C hybrid materials were prepared by chemical precipitation reaction of hydrochloric and sodium tungstate in carbon suspension. Pt nanoparticles were deposited by microwave-assisted polyol process on WO3-C. Influences of WO3 contents and heat-treatment temperature on the catalytic activity for oxygen reduction and the single proton exchange membrane fuel cell performance were analyzed systematically. X-ray diffraction(XRD), transmission electron microscope (TEM) and energy dispersion spectrometry (EDS) were used to characterize the Pt/WO3-C catalysts. The results show that the optimum content of WO3 is 10wt%, and heat-treatment temperature in N2 flow is 250℃. WO3 presents as monoclinic phase and about 2.77 nm Pt metal crystallites disperse on WO3-C. Cyclic voltammetry and polarization curves of single cells are investigated to measure the electrocatalytic activity. The synergistic catalytic effect is found between Pt and WO3. The Pt/WO3-C catalysts are more active for oxygen reduction than traditional Pt/C. The accelerated potential cycling test and single cell life test indicate that the Pt/WO3-C catalysts possess substantially enhanced stability in comparison with Pt/C catalysts.
|
|
|
Preparation of Mesoporous Carbon/Sulfur Composite Loaded with ZnS and Its Property for Lithium-sulfur Batteries
CHEN Long, LIU Jing-Dong, ZHANG Shi-Qun
2013 Vol. 28 (10): 1127–1131
 Abstract
Abstract(
912 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(520KB)(
1375
)
With the aim to obtain high performance cathode materials for lithium-sulfur batteries, composite of mesoporous carbon (MC) loaded with ZnS (ZnS/MC) was prepared through ultrasonic dispersion and heat treatment. The as-prepared composite was blended with elemental sulfur by heating, then cathode materials (ZnS/MC/S) was obtained. The ZnS/MC composite was characterized by XRD, SEM, EDS and N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms. The results showed that ZnS particle was uniformly loaded to the surface of MC through ultrasonic dispersion when content of ZnS was less than 17wt%. ZnS nanoparticles aggregated to form sphalerite ZnS by heat treatment or increasing content of ZnS. Cyclic voltammetry test showed that ZnS accelerated the oxidation process of polysulfides. Charge/ discharge tests indicated that the initial discharge specific capacity was 1354.6 mAh/g, while the coulombic efficiency of the first charge and discharge was 98.7%. The capacity still remained 650 mAh/g after 50 cycles.
|
|
|
Preparation and Characterization of Gradient Sealing Material for Sodium Anode Based Battery
ZHANG Gao-Xiao, WEN Zhao-Yin, WU Xiang-Wei, ZHANG Jing-Chao
2013 Vol. 28 (10): 1132–1136
 Abstract
Abstract(
803 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(790KB)(
1381
)
A functional gradient material (FGM) based sealing was designed and applied to seal the α-Al2O3 insulator with Na-β-Al2O3 solid electrolyte of sodium anode batteries. FGMs with different component change rates were fabricated by powder stacking method. The experimental results indicated that the two dimensional feature of Na-β-Al2O3 grains greatly influenced the density of the α-Al2O3/Na-β-Al2O3 composite ceramics. It was demonstrated that the chemical diffusion of Na and Li in FGM diminished the interfaces among diffrent layers. Bending strengths of the FMGs reached (130(2), (180(3) and (225(2) MPa for the samples with component change rate of 20wt%, 10wt% and 5wt%, respectively. Moreover, the mechanical performance of the FGMs was rarely affected by heat treatment and thermal cycling, demonstrating its favorable mechanical and thermal stability.
|
|
|
Surface Modification of Apatite-wollastonite Bioactive Glass-ceramic by Grafting with RGD Peptides
ZHANG Xiang, ZHOU Da-Li, LONG Qin, ZHOU Jia-Bei, TAN Yan-Fei, LIU Shu-Jing
2013 Vol. 28 (10): 1137–1142
 Abstract
Abstract(
916 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(596KB)(
1995
)
Tripeptide of arginine-glycine-aspartic acid (RGD) has been introduced to modify of biomaterials due to its high bio-activity, which could increase the cell adhesion. In this study, the apatite-wollastonite bioactive glass-ceramic (AW) with RGD peptide (RGD-AW) was fabricated. Firstly, the amino groups were introduced to the AW surface via low temperature plasma treatment. Then, RGD peptide were immobilized on the surface of AW by combination with the amino groups. The XRD, XPS and ATR-FTIR results confirmed that the RGD peptide were fixed on the surface of AW successfully. In order to testify whether the RGD-AW were more favorable to the cells, MG63 osteblast-like cells were employed to co-culture with RGD-AW for 4 h, 1 d and 5 d in vitro. The results of fluorescence microscopy, SEM and MTT assay showed that RGD-AW could enhance the attachment and proliferation of MG63 cells significantly compared with AW.
|
|
|
Study on the Elution of the Adsorbed Serum Proteins on Biphasic Calcium Phosphate Ceramics
WANG Jing, CHEN Ying, ZHU Xiang-Dong, FAN Yu-Jiang, ZHANG Xing-Dong
2013 Vol. 28 (10): 1143–1147
 Abstract
Abstract(
930 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(461KB)(
1125
)
Two types of porous BCP ceramics were fabricated, using human serum as the model of protein solution. The effect of the different eluants and porous structure on the elution of the adsorbed serum proteins on BCP ceramics were investigated. The results showed that 400 mmol/L Na3PO4 solution had higher elution efficiency for the adsorbed serum proteins on BCP ceramics than 2 mol/L NaCl or 2% sodium dodecycl sufonate (SDS) solution. Moreover, the porous structure of BCP ceramics had a strong impact on the elution of the adsorbed serum proteins. The microporous structure could promote the adsorption of serum proteins on BCP ceramics and slowed down their release rate, but the 3D interconnected macropores were favorable for the elution and release of serum proteins from the BCP surface.
|
|
|
Effect of DCTA on the Rapid Growth and Optical Characterization of KDP Crystal
ZHU Sheng-Jun, WANG Sheng-Lai, DING Jian-Xu, CHENG Xiu-Feng, WANG Zheng-Ping, XU Xin-Guang
2013 Vol. 28 (10): 1148–1152
 Abstract
Abstract(
816 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(398KB)(
1001
)
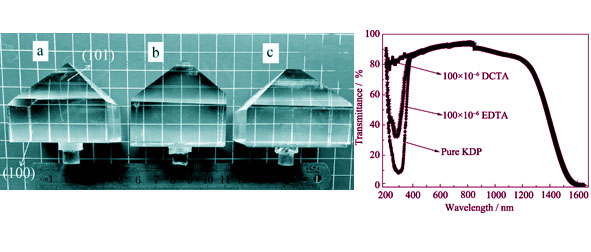
Cyclohexanediaminetetraacetic acid (DCTA) as a new additive was added into the KDP growth solution. The KDP crystal was grown from aqueous solution with 100×10-6 DCTA by the “point seed” rapid growth technique, at growth rate of about 20 mm/d. Effects of the new additive DCTA on growth habit and optical quality of the rapidly grown KDP crystal were investigated and compared with those of EDTA which was a common additive used in the rapid growth of KDP crystal. With 100×10-6 DCTA added in growth solution, the metastable temperature zone width of solution increased about 10℃ and the growth rate of (100) faces of KDP crystal accelerated by 3–10 times. Furthermore, the optical quality of crystal doped with DCTA was improved significantly: such as 2–8 times rise of UV transmittance, great mitigation of light scattering and a few exaltation of laser damage threshold. Additionally, the beneficial effects of DCTA on growth habit and optical quality of the rapidly grown KDP crystal were more significant than those of EDTA with the same concentration.
|
|
|
Crystal Structure, Phase Transition and Optical Properties of ν-PrBO3
JIN Teng-Teng, ZHANG Zhi-Jun, ZHANG Hui, ZHAO Jing-Tai
2013 Vol. 28 (10): 1153–1157
 Abstract
Abstract(
4638 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(435KB)(
1877
)
The praseodymium orthoborates λ-PrBO3 and ν-PrBO3 were synthesized from Pr6O11 and H3BO3 by solid state reaction method at 1200 and 1500℃, respectively. The crystal structure of ν-PrBO3 was refined on the basis of single-crystal X-ray diffraction data. It crystallizes in the triclinic system belonging to space group Pwith lattice parameters: a = 0.6302 (4) nm, b = 0.6521 (4) nm and c = 0.6525 (4) nm, and α = 94.312(7)°, β = 107.335(7)°, γ = 106.455(7)°, V = 0.2417(2) nm3, Z = 4. The phase transition process from λ-PrBO3 to ν-PrBO3 was also investigated. The optical band gaps of λ-PrBO3 and ν-PrBO3 are both determined to be about 4.96 eV according to the diffuse reflection spectra. There is no emission of Pr3+ in the visible range for both of λ-PrBO3 and ν-PrBO3 under X-ray and UV excitation.
|
|
|
ZrB2-SiC Coatings Prepared by Vapor and Liquid Silicon Infiltration Methods: Microstructure and Oxidation Resistance Property
ZHOU Hai-Jun, FENG Qian, KAN Yan-Mei, GAO Le, DONG Shao-Ming
2013 Vol. 28 (10): 1158–1162
 Abstract
Abstract(
1580 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(373KB)(
1955
)
Novel zirconium diboride-silicon carbide (ZrB2-SiC) coatings were prepared by vapor silicon infiltration (VSI) and liquid silicon infiltration (LSI), respectively. The static oxidation resistance properties of these coatings were evaluated and their microstructure evolution during oxidation was studied. It showed that the VSI coating had better oxidation resistance than LSI. A compact oxide scale was formed on the VSI coating, which strongly suppressed further oxidation damage during the testing. The poor oxidation resistance of the LSI coating could be mainly attributed to micro-cracks and residual silicon.
|
|