无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (3): 314-322.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240396 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20240396
所属专题: 【信息功能】发光材料与器件(202506)
潘泽晟1,2( ), 游雅萍1,2, 郑雅1,2, 陈海杰1,2(
), 游雅萍1,2, 郑雅1,2, 陈海杰1,2( ), 王连军1,2(
), 王连军1,2( ), 江莞1,2
), 江莞1,2
收稿日期:2024-08-30
修回日期:2024-10-28
出版日期:2025-03-20
网络出版日期:2025-03-12
通讯作者:
王连军, 教授. E-mail: wanglj@dhu.edu.cn;作者简介:潘泽晟(1998-), 男, 博士研究生. E-mail:panzes@mail.dhu.edu.cn
基金资助:
PAN Zesheng1,2( ), YOU Yaping1,2, ZHENG Ya1,2, CHEN Haijie1,2(
), YOU Yaping1,2, ZHENG Ya1,2, CHEN Haijie1,2( ), WANG Lianjun1,2(
), WANG Lianjun1,2( ), JIANG Wan1,2
), JIANG Wan1,2
Received:2024-08-30
Revised:2024-10-28
Published:2025-03-20
Online:2025-03-12
Contact:
WANG Lianjun, professor. E-mail: wanglj@dhu.edu.cn;About author:PAN Zesheng (1998-), male, PhD candidate. E-mail: panzes@mail.dhu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
紫光激发白光发光二极管(Light Emitting Diode, LED)具有色温可调、视觉友好等优点, 已经受到了广泛关注。但是, 适用于紫光(400~420 nm)激发的高性能荧光材料尚未取得大规模应用, 其中荧光材料的耐候性是评判其是否具有商业化应用潜力的重要因素之一。然而, 目前针对荧光材料耐候性的研究却十分缺乏。本研究首先采用固相反应法制备了K2CaPO4F:Eu2+、K1.3Al11O17+δ:Eu2+和Ca2YHf2Al3O12:Ce3+,Tb3+三种LED用紫光激发稀土发光材料。然后开展了荧光粉在高温高湿、水浸泡、LED芯片紫光辐照等条件下的耐候性实验, 研究了其耐候性以及失效机理。最后, 将三种荧光粉与400 nm紫光芯片组合, 制备了白光LED器件。结果表明, 相较于同体系荧光粉, 本研究所制备的荧光粉不仅在发光性能方面有所优化, 而且对材料在不同使用环境下的耐候性表征更为全面。所制备的白光LED器件的显色指数为93.6、色温为5151 K、色坐标为(0.34, 0.36), 展现出优质的白光照明性能, 且白光LED器件的耐候性相对于单一荧光粉有所提升。上述研究表明, 对荧光材料及其对应的LED器件进行耐候性评估是至关重要的。本工作率先开展了紫光激发LED用荧光材料的耐候性研究, 对于推动其应用具有指导和借鉴意义。
中图分类号:
潘泽晟, 游雅萍, 郑雅, 陈海杰, 王连军, 江莞. 面向紫光激发白光LED用荧光材料的耐候性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 314-322.
PAN Zesheng, YOU Yaping, ZHENG Ya, CHEN Haijie, WANG Lianjun, JIANG Wan. Stability of Phosphors for White LED Excitable by Violet Light[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 314-322.
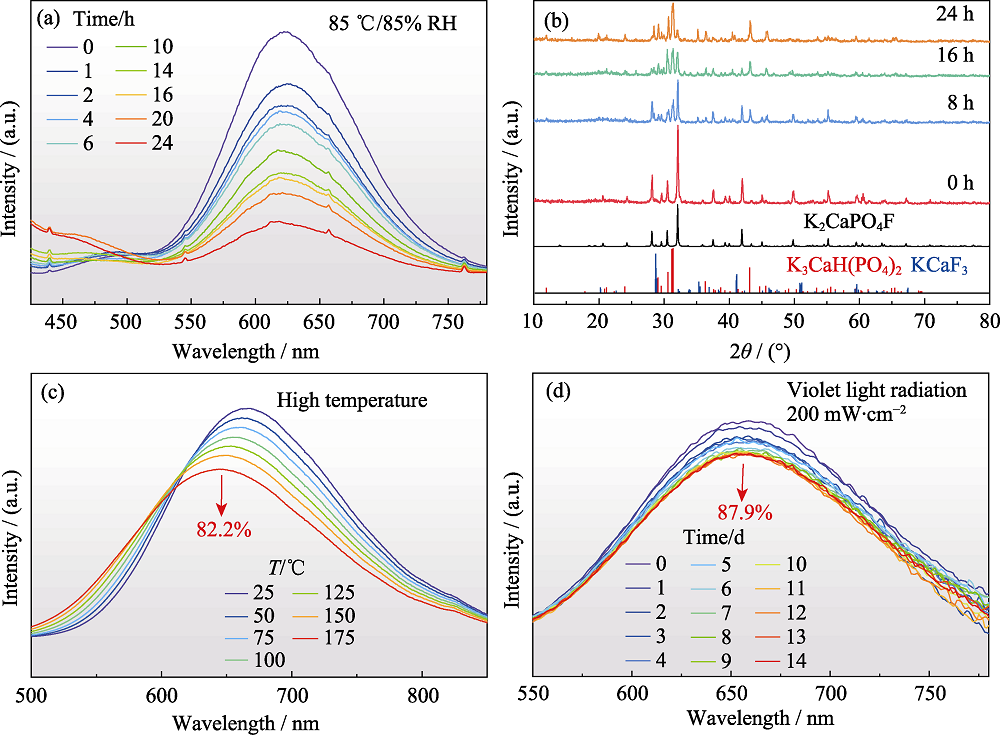
图1 K2CaPO4F:Eu2+荧光粉的耐候性能
Fig. 1 Environmental stability of K2CaPO4F:Eu2+ phosphor (a) PL spectra when kept in 85 ℃/85% RH condition for different duration time; (b) XRD patterns when kept in 85 ℃/85% RH condition for different duration time; (c) Temperature-dependent PL spectra; (d) PL spectra when radiated under 200 mW·cm-2 of violet light for different duration time. Colorful figures are available on website
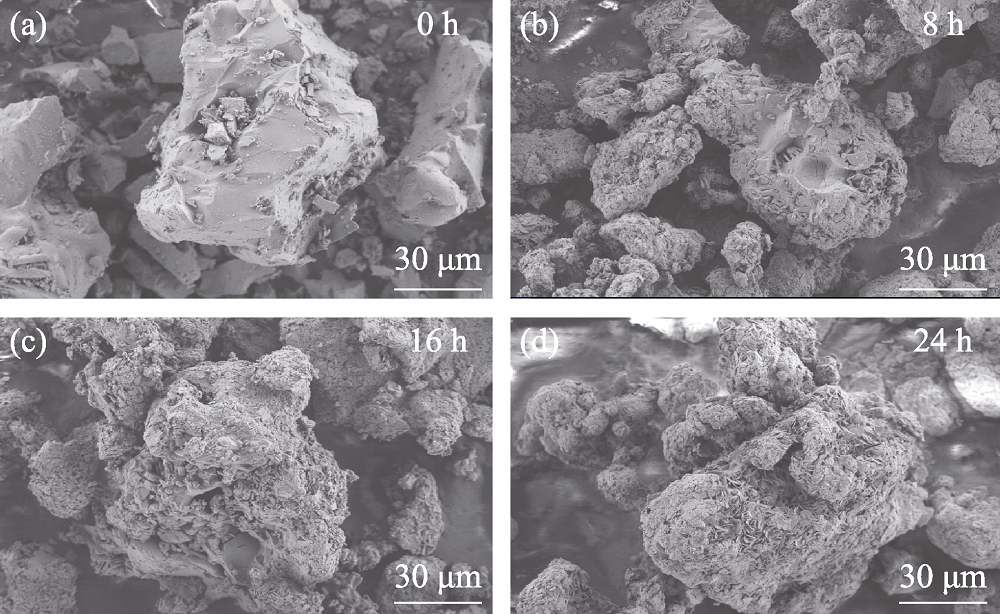
图2 K2CaPO4F:Eu2+荧光粉在85 ℃/85% RH条件下老化不同时间后的SEM照片
Fig. 2 SEM images of K2CaPO4F:Eu2+ phosphor when kept in 85 ℃/85% RH condition for different duration time (a) 0 h; (b) 8 h; (c) 16 h; (d) 24 h
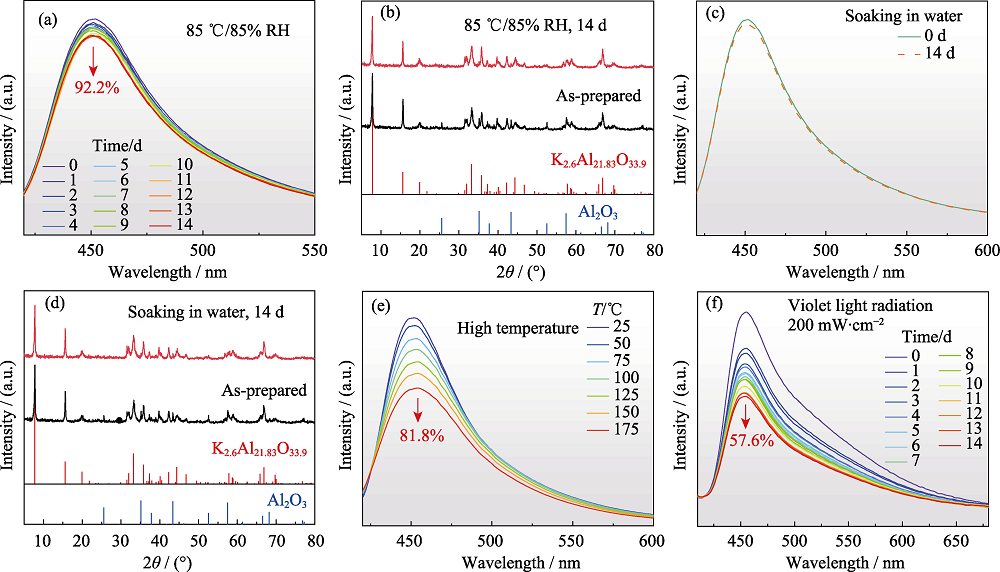
图3 K1.3Al11O17+δ:Eu2+荧光粉的耐候性能
Fig. 3 Environmental stability of K1.3Al11O17+δ:Eu2+ phosphor (a) PL spectra when kept in 85 ℃/85% RH condition for different duration time; (b) XRD patterns before and after keeping in 85 ℃/85% RH condition for 14 d; (c) PL spectra before and after soaking in water for 14 d; (d) XRD patterns before and after soaking in water for 14 d; (e) Temperature-dependent PL spectra; (f) PL spectra when radiated under 200 mW·cm-2 of violet light for different duration time. Colorful figures are available on website
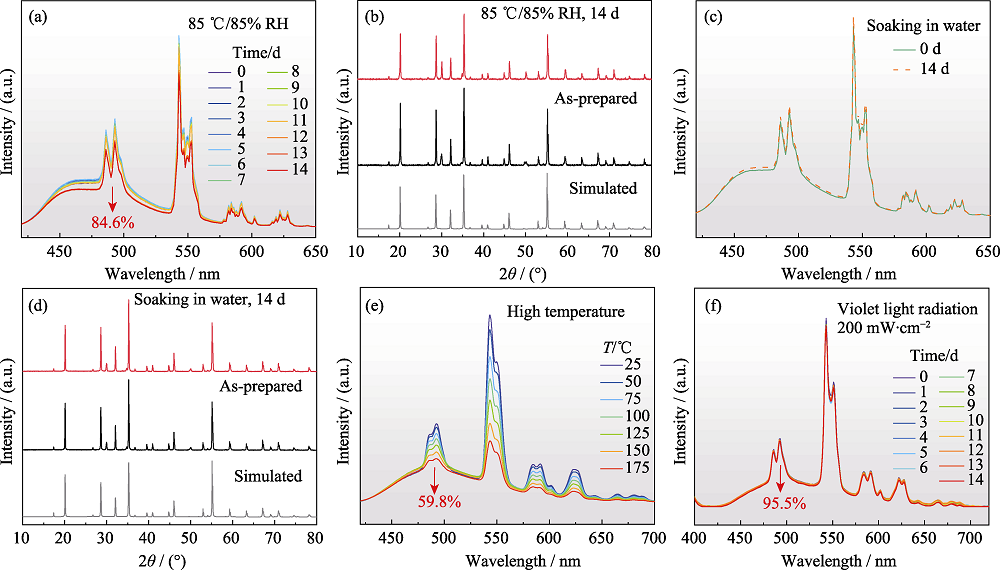
图4 Ca2YHf2Al3O12:Ce3+,Tb3+荧光粉的耐候性能
Fig. 4 Environmental stability of Ca2YHf2Al3O12:Ce3+,Tb3+ phosphor (a) PL spectra when kept in 85 ℃/85% RH condition for different duration time; (b) XRD patterns before and after keeping in 85 ℃/85% RH condition for 14 d; (c) PL spectra before and after soaking in water for 14 d; (d) XRD patterns before and after soaking in water for 14 d; (e) Temperature-dependent PL spectra; (f) PL spectra when radiated under 200 mW·cm-2 of violet light for different duration time. Colorful figures are available on website
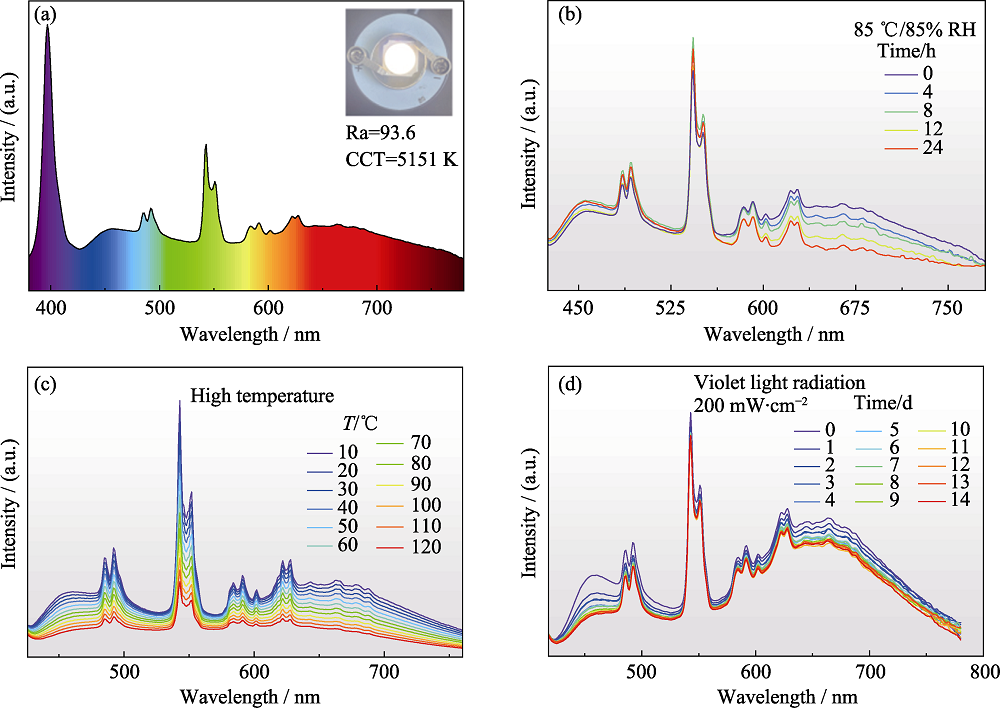
图5 白光LED的耐候性能
Fig. 5 Environmental stability of white LED (a) EL spectrum of white LED device; (b) EL spectra of white LED device when kept in 85 ℃/85% RH condition for different duration time; (c) Temperature-dependent EL spectra of white LED device; (d) EL spectra of white LED device when radiated under 200 mW·cm-2 of violet light for different duration time. Colorful figures are available on website
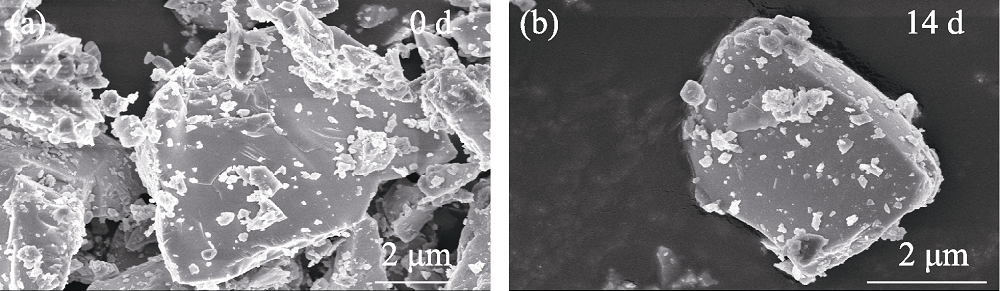
图S6 Ca2YHf2Al3O12:Ce3+,Tb3+荧光粉在水中浸泡14 d前(a)后(b)的SEM照片
Fig. S6 SEM images of Ca2YHf2Al3O12:Ce3+,Tb3+ phosphor before (a) and after (b) soaking in water for 14 d
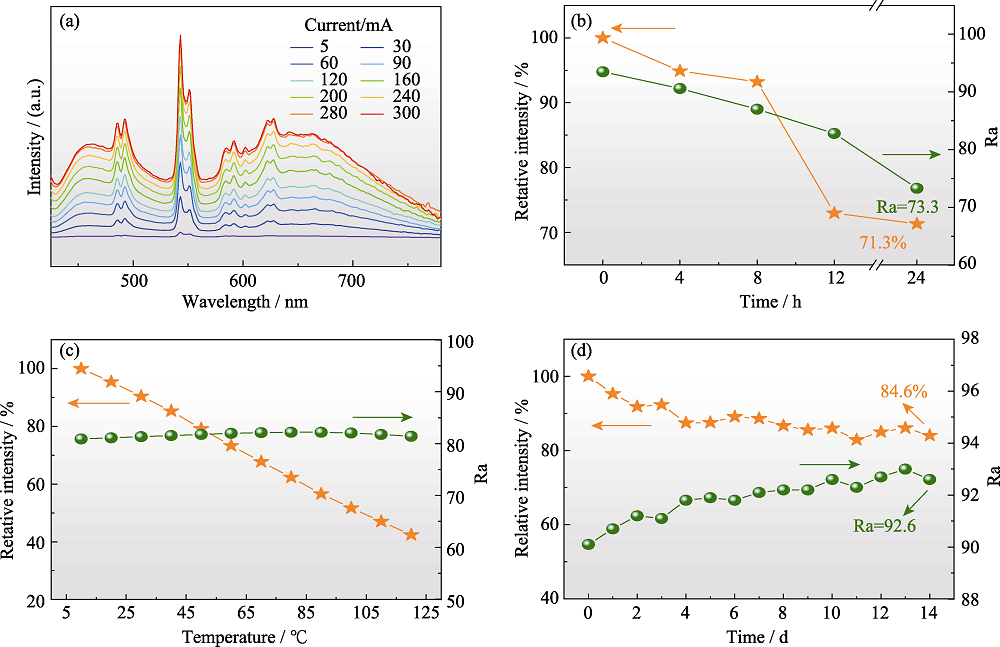
图S9 白光LED的耐候性能
Fig. S9 Environmental stability data of white LED (a) EL spectra of the white LED device under different input current; (b) Relative intensity and rendering index (Ra) of white LED device when kept in 85 ℃/85% RH condition with different duration time; (c) Relative intensity and Ra of white LED device under different temperature; (d) Relative intensity and Ra of white LED device when radiated under 200 mW·cm-2 of violet light with different duration time
| Component | PLQY | Thermal stability (150 ℃) | High temperature and high humidity stability (85 ℃/85% RH) | Water resistance | Light irradiation stability (200 mW·cm-2) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K2Ca(PO4)F:Eu2+ | 75% (407 nm) | 85% | - | - | - | [20] |
| K2Ca(PO4)F:Eu2+ | 94.5% (390 nm) | 82% | - | - | - | [S1] |
| Rb0.5K1.5Ca(PO4)F:Eu2+ | 87% (395 nm) | 85.5% | - | - | - | [S2] |
| Na2Ca0.995PO4F:Eu2+ | 84% (400 nm) | ~70% | - | - | - | [S3] |
| K2Ca(PO4)F:Eu2+ | 95.33% (380 nm) | 82.2% | 34.7%, 14 d | - | 87.9%, 14 d | This Work |
| K1.6Al11O17+δ:Eu2+ | 92% (400 nm) | >100% | - | - | - | [21] |
| K0.84Sr0.06Al11O17+δ:Eu2+ | 92.4% (360 nm) | >100% | - | - | - | [44] |
| K0.6Ba0.1Eu0.1Al11O17:Eu2+ | 91.2% (345 nm) | ~100% | - | - | - | [S4] |
| K1.3Al11O17+δ:Eu2+ | 74.29% (400 nm) | 81.8% | 92.2%, 14 d | ~100%,14 d | 57.6%, 14 d | This Work |
| Ca2YHf2Al3O12:Ce3+,Tb3+ | 78.5% (408 nm) | 43.3% | - | - | - | [22] |
| Ca2YHf2Al3O12:Ce3+ | 68.5% (400 nm) | 76.6% | - | - | - | [S5] |
| Ca2GdHf2Al3O12:Ce3+,Tb3+ | 82.7% (408 nm) | 48% | - | - | - | [S6] |
| Ca2YHf2Al3O12:Ce3+,Tb3+ | 95.72% (410 nm) | 59.8% | 84.6%, 14 d | ~100%,14 d | 95.5%, 14 d | This Work |
表S1 荧光粉发光性能及耐候性对比
Table S1 Comparison of phosphors in optical performance and environmental stability
| Component | PLQY | Thermal stability (150 ℃) | High temperature and high humidity stability (85 ℃/85% RH) | Water resistance | Light irradiation stability (200 mW·cm-2) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K2Ca(PO4)F:Eu2+ | 75% (407 nm) | 85% | - | - | - | [20] |
| K2Ca(PO4)F:Eu2+ | 94.5% (390 nm) | 82% | - | - | - | [S1] |
| Rb0.5K1.5Ca(PO4)F:Eu2+ | 87% (395 nm) | 85.5% | - | - | - | [S2] |
| Na2Ca0.995PO4F:Eu2+ | 84% (400 nm) | ~70% | - | - | - | [S3] |
| K2Ca(PO4)F:Eu2+ | 95.33% (380 nm) | 82.2% | 34.7%, 14 d | - | 87.9%, 14 d | This Work |
| K1.6Al11O17+δ:Eu2+ | 92% (400 nm) | >100% | - | - | - | [21] |
| K0.84Sr0.06Al11O17+δ:Eu2+ | 92.4% (360 nm) | >100% | - | - | - | [44] |
| K0.6Ba0.1Eu0.1Al11O17:Eu2+ | 91.2% (345 nm) | ~100% | - | - | - | [S4] |
| K1.3Al11O17+δ:Eu2+ | 74.29% (400 nm) | 81.8% | 92.2%, 14 d | ~100%,14 d | 57.6%, 14 d | This Work |
| Ca2YHf2Al3O12:Ce3+,Tb3+ | 78.5% (408 nm) | 43.3% | - | - | - | [22] |
| Ca2YHf2Al3O12:Ce3+ | 68.5% (400 nm) | 76.6% | - | - | - | [S5] |
| Ca2GdHf2Al3O12:Ce3+,Tb3+ | 82.7% (408 nm) | 48% | - | - | - | [S6] |
| Ca2YHf2Al3O12:Ce3+,Tb3+ | 95.72% (410 nm) | 59.8% | 84.6%, 14 d | ~100%,14 d | 95.5%, 14 d | This Work |
| [1] | WANG S, SONG Z, LIU Q. Recent progress in Ce3+/Eu2+-activated LEDs and persistent phosphors: focusing on the local structure and the electronic structure. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2023, 11(1): 48. |
| [2] | FANG M H, BAO Z, HUANG W T, et al. Evolutionary generation of phosphor materials and their progress in future applications for light-emitting diodes. Chemical Reviews, 2022, 122(13): 11474. |
| [3] | NAIR G B, SWART H C, DHOBLE S J. A review on the advancements in phosphor-converted light emitting diodes (pc-LEDs): phosphor synthesis, device fabrication and characterization. Progress in Materials Science, 2020, 109: 100622. |
| [4] | WANG L, XIE R J, SUEHIRO T, et al. Down-conversion nitride materials for solid state lighting: recent advances and perspectives. Chemical Reviews, 2018, 118(4): 1951. |
| [5] | XIA Z, LIU Q. Progress in discovery and structural design of color conversion phosphors for LEDs. Progress in Materials Science, 2016, 84: 59. |
| [6] | LI S, ZHU Q, TANG D, et al. Al2O3-YAG:Ce composite phosphor ceramic: a thermally robust and efficient color converter for solid state laser lighting. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2016, 4(37): 8648. |
| [7] | YAO Q, HU P, SUN P, et al. YAG:Ce3+ transparent ceramic phosphors brighten the next-generation laser-driven lighting. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(19): 1907888. |
| [8] | LI Y, FANG S, ZHU Q, et al. Breaking through the luminescence stability bottleneck of oxyfluoride phosphor for sun-like led lighting. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2024, 18(5): 2300915. |
| [9] | BAI Y, JIA Z, GAO J, et al. A novel red-emitting phosphor K2MgGeO4:Eu3+ for WLEDs: zero-thermal quenching induced by heterovalent substitution. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2022, 10(42): 15957. |
| [10] | LENG Z, BAI H, QING Q, et al. A zero-thermal-quenching blue phosphor for sustainable and human-centric WLED lighting. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2022, 10(33): 10966. |
| [11] | LIAO M, WU F, WANG J, et al. Accurately controlling the occupation of Eu2+ in Cs(K, Na)3(Li3SiO4)4 to achieve narrow-band green emission for wide color gamut displays. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(42): 47892. |
| [12] | KIM K B, KIM Y I, CHUN H G, et al. Structural and optical properties of BaMgAl10O17:Eu2+ phosphor. Chemistry of Materials, 2002, 14(12): 5045. |
| [13] | SONG Y, YOU H, YANG M, et al. Facile synthesis and luminescence of Sr5(PO4)3Cl:Eu2+ nanorod bundles via a hydrothermal route. Inorganic Chemistry, 2010, 49(4): 1674. |
| [14] | SHAO Q, LIN H, DONG Y, et al. Temperature-dependent photoluminescence properties of (Ba,Sr)2SiO4:Eu2+ phosphors for white LEDs applications. Journal of Luminescence, 2014, 151: 165. |
| [15] | LI P, YANG Z, WANG Z, et al. Preparation and luminescence characteristics of Sr3SiO5:Eu2+ phosphor for white LED. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2008, 53(7): 974. |
| [16] | XIE R J, HIROSAKI N, SUEHIRO T, et al. A simple, efficient synthetic route to Sr2Si5N8:Eu2+-based red phosphors for white light-emitting diodes. Chemistry of Materials, 2006, 18(23): 5578. |
| [17] | PIAO X, MACHIDA K I, HORIKAWA T, et al. Preparation of CaAlSiN3:Eu2+ phosphors by the self-propagating high-temperature synthesis and their luminescent properties. Chemistry of Materials, 2007, 19(18): 4592. |
| [18] | DENAULT K A, BRGOCH J, GAULTOIS M W, et al. Consequences of optimal bond valence on structural rigidity and improved luminescence properties in SrxBa2-xSiO4:Eu2+ orthosilicate phosphors. Chemistry of Materials, 2014, 26(7): 2275. |
| [19] | LIN L, NING L, ZHOU R, et al. Site occupation of Eu2+ in Ba2-xSrxSiO4 (x=0-1.9) and origin of improved luminescence thermal stability in the intermediate composition. Inorganic Chemistry, 2018, 57(12): 7090. |
| [20] | DAICHO H, SHINOMIYA Y, ENOMOTO K, et al. A novel red-emitting K2Ca(PO4)F:Eu2+ phosphor with a large Stokes shift. Chemical Communications, 2018, 54(8): 884. |
| [21] | WU X, SHI R, ZHANG J, et al. Highly efficient and zero-thermal- quenching blue-emitting Eu2+-activated K-beta-alumina phosphors. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 429: 132225. |
| [22] | WANG S, DEVAKUMAR B, SUN Q, et al. Highly efficient near-UV-excitable Ca2YHf2Al3O12:Ce3+,Tb3+ green-emitting garnet phosphors with potential application in high color rendering warm- white LEDs. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2020, 8(13): 4408. |
| [23] | DING X, WANG Y. Novel orange light emitting phosphor Sr9(Li, Na, K)Mg(PO4)7: Eu2+ excited by NUV light for white LEDs. Acta Materialia, 2016, 120: 281. |
| [24] | LI G, TIAN Y, ZHAO Y, et al. Recent progress in luminescence tuning of Ce3+ and Eu2+-activated phosphors for pc-WLEDs. Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(23): 8688. |
| [25] | WANG B, WANG Z, LIU Y, et al. Valent control and spectral tuning by cation site engineering strategy in Eu doped Sr1-xBaxAl2Si2O8 phosphor. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 806: 529. |
| [26] | LIU Y, ZHANG C, CHENG Z, et al. Origin and luminescence of anomalous red-emitting center in rhombohedral Ba9Lu2Si6O24:Eu2+ blue phosphor. Inorganic Chemistry, 2016, 55(17): 8628. |
| [27] | LIU Y, ZHANG J, ZHANG C, et al. Ba9Lu2Si6O24:Ce3+: an efficient green phosphor with high thermal and radiation stability for solid-state lighting. Advanced Optical Materials, 2015, 3(8): 1096. |
| [28] | WEI Y, GAO Z, LIU S, et al. Highly efficient green-to-yellowish- orange emitting Eu2+-doped pyrophosphate phosphors with superior thermal quenching resistance for w-LEDs. Advanced Optical Materials, 2020, 8(6): 1901859. |
| [29] | LIAO M, WU F, ZHU D, et al. Towards single broadband white emission in Rb0.5K1.5CaPO4(F, Cl): Eu2+ via selective site occupancy engineering for solid-state lighting applications. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 449: 137801. |
| [30] | LIU Y X, HU J X, JU L C, et al. Hydrophobic surface modification toward highly stable K2SiF6:Mn4+ phosphor for white light-emitting diodes. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(7): 8811. |
| [31] | HUANG D, ZHU H, DENG Z, et al. Moisture-resistant Mn4+- doped core-shell-structured fluoride red phosphor exhibiting high luminous efficacy for warm white light-emitting diodes. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(12): 3843. |
| [32] | QIAO J, NING L, MOLOKEEV M S, et al. Eu2+ site preferences in the mixed cation K2BaCa(PO4)2 and thermally stable luminescence. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2018, 140(30): 9730. |
| [33] | YANG H J, XU H R, ZHU G S, et al. Facile preparation of Y2.9Ce0.1Al5O12 nano-phosphors without photobleaching behavior. Materials Letters, 2013, 92: 161. |
| [34] | CHEN J, ZHANG N, GUO C, et al. Site-dependent luminescence and thermal stability of Eu2+ doped fluorophosphate toward white LEDs for plant growth. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(32): 20856. |
| [35] | DENG D, QIANG J, WANG T, et al. Surface passivation to improve the water resistance and fluorescent thermal stability of K2SiF6:Mn4+ by using Na2S2O4 as a passivator. Journal of Luminescence, 2022, 252: 119429. |
| [36] | SHAO Q, LIN H, DONG Y, et al. Thermostability and photostability of Sr3SiO5:Eu2+ phosphors for white LED applications. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2015, 225: 72. |
| [37] | WEI Y, HUANG Q, YU S, et al. Reconstructing the surface of K2SiF6:Mn4+ phosphors toward enhanced moisture resistance for white LED applications. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2024, 16(41): 55792. |
| [38] | LIU Y, YING Y, XIE Q, et al. Bifunctional ligand passivation enables stable blue mixed-halide CsPb(Br/Cl)3 perovskite quantum dots toward light-emitting diodes. Inorganic Chemistry, 2024, 63(35): 16167. |
| [39] | ZHOU Z, ZHU H, HUANG X, et al. Anti-thermal-quenching, color-tunable and ultra-narrow-band cyan green-emitting phosphor for w-LEDs with enhanced color rendering. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 433: 134079. |
| [40] | HARIYANI S, BRGOCH J. Advancing human-centric led lighting using Na2MgPO4F:Eu2+. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(14): 16669. |
| [41] | SUN Y, WANG Y, CHEN W, et al. Rapid synthesis of phosphor- glass composites in seconds based on particle self-stabilization. Nature Communications, 2024, 15(1): 1033. |
| [42] | LI X, YANG C, QIU L, et al. NaAlSiO4: Eu2+ glass ceramics: self-reduced in situ growth and high-power LED/LD lighting. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2022, 16(1): 2100346. |
| [43] | LI X, FENG W, YOU F, et al. In situ glass crystallization enables narrowband blue luminescence for full-spectrum lighting and transparent display. Advanced Optical Materials, 2024, 12(14): 2302823. |
| [44] | KUANG Y, LI Y, CHEN B, et al. Regulating anti-thermal quenching to zero thermal quenching for highly efficient blue-emitting Eu2+-doped K-beta-alumina phosphors. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2023, 11(17): 5874. |
| [1] | 瞿牡静, 张淑兰, 朱梦梦, 丁浩杰, 段嘉欣, 代恒龙, 周国红, 李会利. CsPbBr3@MIL-53纳米复合荧光粉的合成、性能及其白光LEDs应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(9): 1035-1043. |
| [2] | 陆晨辉, 葛万银, 宋盼盼, 张盼锋, 徐美美, 张伟. 用于白光LED稀土Eu掺杂SiAlON基荧光粉的发光性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(1): 97-104. |
| [3] | 王兆武, 姬海鹏, 王飞翔, 侯星慧, 易莎莎, 周颖, 陈德良. 调控Al2O3晶型控制MgAl2O4:Mn4+荧光粉中Mn价态研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(5): 513-520. |
| [4] | 姬海鹏, 张宗涛, XU Jian, TANABE Setsuhisa, 陈德良, 解荣军. Mn4+激活氧氟化物红光荧光粉的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(8): 847-856. |
| [5] | 董宇辉, 曾书玉, 韩博宁, 薛洁, 宋继中, 曾海波. BN/CsPbX3复合纳米晶的制备及其白光LED应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(1): 72-78. |
| [6] | 邵秀晨, 周圣明, 唐燕如, 易学专, 郝德明, 陈杰. Ce:YAG荧光陶瓷掺杂Gd对白光LED发光性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(10): 1119-1123. |
| [7] | 张 瑞, 王伯阳, 王 海. 白光LED用Phosphor-in-Glass荧光材料的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(4): 337-345. |
| [8] | 张 延, 刘 升, 许虹杰, 王连军, 江 莞. LED用荧光玻璃的制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(6): 588-592. |
| [9] | 向卫东, 赵斌宇, 梁晓娟, 陈兆平, 谢翠萍, 骆 乐, 张志敏, 张景峰, 钟家松. 白光LED用Ce:YAG单晶光学性能及封装工艺的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(6): 614-620. |
| [10] | 张守超, 阮永丰, 贾国治, 冯志辉, 刘枝朋, 裴利斌. 紫外光激发Ce3+掺YVO4蓝光发射性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(10): 1067-1072. |
| [11] | 李梦娜, 雷 芳, 陈昊鸿, 施 鹰, 赵景泰. Li、Eu掺杂NaY(WO4)2荧光粉的合成与红色发光[J]. 无机材料学报, 2013, 28(12): 1281-1285. |
| [12] | 王志军, 李 妍, 王 颖, 李盼来, 郭庆林, 杨志平. Eu2+在KNaCa2(PO4)2中的发光及晶体学格位[J]. 无机材料学报, 2011, 26(7): 731-734. |
| [13] | 王志军, 李盼来, 杨志平, 郭庆林. KBaPO4,Tb3+材料制备及其发光特性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2011, 26(5): 503-507. |
| [14] | 王志军,李盼来,杨志平,郭庆林. Dy3+激活的LiCaBO3材料发光特性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2009, 24(5): 1069-1072. |
| [15] | 罗勇悦,彭蕾蕾,淡宜,张立,赵昆. 硅铝二元膜包覆稀土发光材料的结构及耐水性能的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2007, 22(3): 499-503. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||