
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2019, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (12): 1316-1324.DOI: 10.15541/jim20190903
Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Yi-Qing,LIU Li,ZHANG Shu-Juan,WAN Zheng-Rui,LIU Hong-Ying,ZHOU Li-Qun( )
)
Received:2019-03-01
Revised:2019-03-28
Published:2019-12-20
Online:2019-12-02
Supported by:CLC Number:
ZHANG Yi-Qing, LIU Li, ZHANG Shu-Juan, WAN Zheng-Rui, LIU Hong-Ying, ZHOU Li-Qun. Preparation and Dehydrogenation Property of NH2-UIO-66 Supported RuCuMo Nanocatalyst[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(12): 1316-1324.
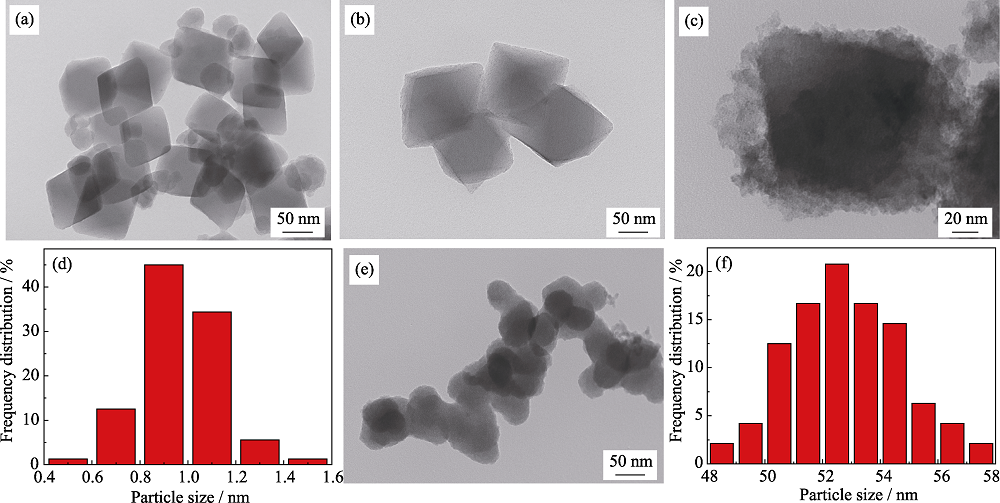
Fig. 2 TEM images of (a, b) NH2-UIO-66, (c) Ru1Cu2Mo0.5@NH2-UIO-66, (e) RuCuMo NPs, (d, f) particle size distributions of (d) Ru1Cu2Mo0.5@NH2-UIO-66 and (f) RuCuMo NPs
| Catalyst | Initial ratio of Ru : Cu : Mo | Actual ratio of Ru : Cu : Mo | Actual Ru loading/wt% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ru1Cu2Mo0.25@NH2-UIO-66 | 1.00 : 2.00 : 0.25 | 1.00 : 2.20 : 0.04 | 4.89 |
| Ru1Cu2Mo0.5@NH2-UIO-66 | 1.00 : 2.00 : 0.50 | 1.00 : 1.82 : 0.09 | 5.48 |
| Ru1Cu2Mo1.0@NH2-UIO-66 | 1.00 : 2.00 : 1.00 | 1.00 : 2.04 : 0.19 | 5.16 |
Table 1 ICP-AES analyses of RuCuMo@NH2-UIO-66 catalysts with different molar ratios
| Catalyst | Initial ratio of Ru : Cu : Mo | Actual ratio of Ru : Cu : Mo | Actual Ru loading/wt% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ru1Cu2Mo0.25@NH2-UIO-66 | 1.00 : 2.00 : 0.25 | 1.00 : 2.20 : 0.04 | 4.89 |
| Ru1Cu2Mo0.5@NH2-UIO-66 | 1.00 : 2.00 : 0.50 | 1.00 : 1.82 : 0.09 | 5.48 |
| Ru1Cu2Mo1.0@NH2-UIO-66 | 1.00 : 2.00 : 1.00 | 1.00 : 2.04 : 0.19 | 5.16 |
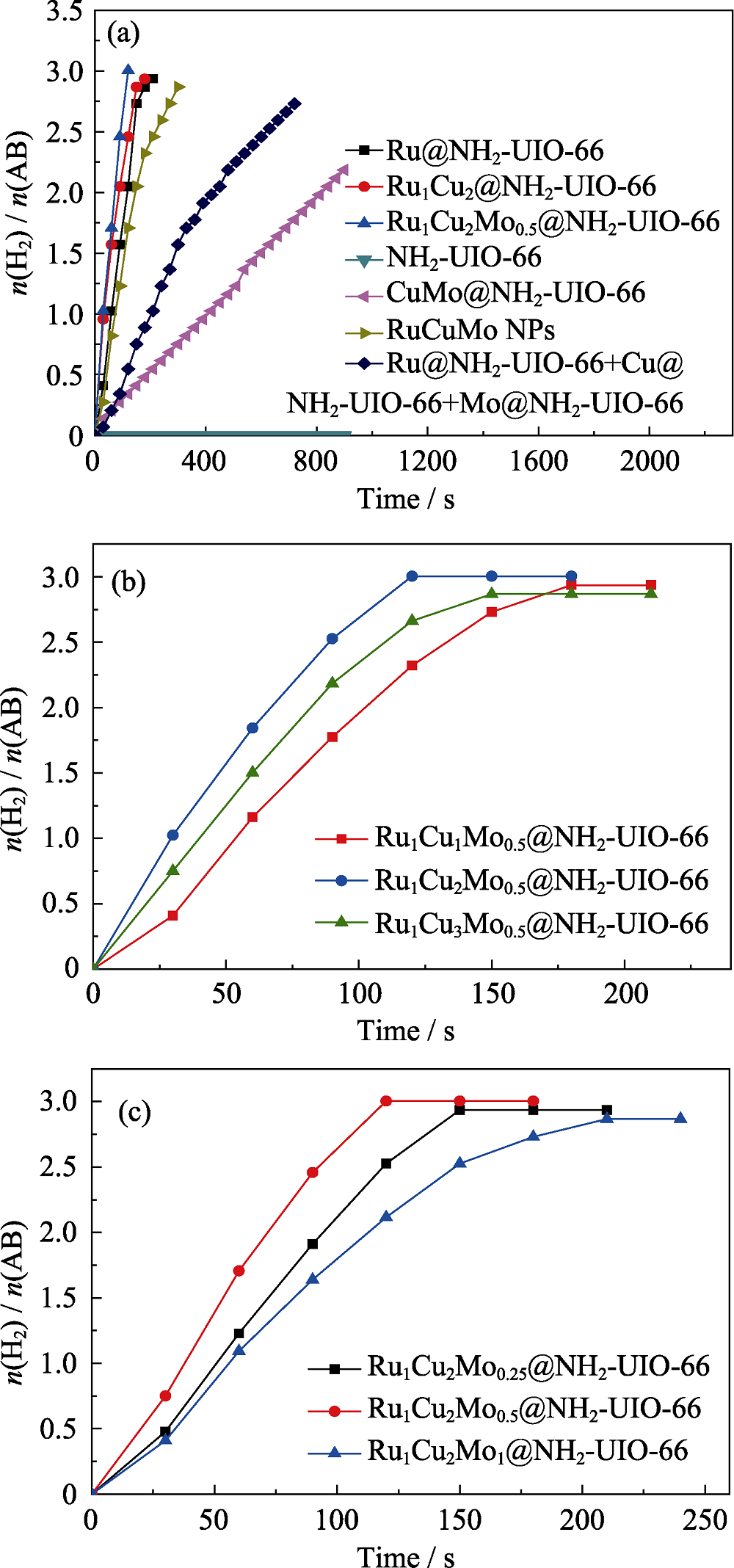
Fig. 6 Plots of time vs. n(H2)/n(NH3BH3) from the hydrolysis of AB (18.5 mg): (a) RuCuMo NPs, Ru@NH2-UIO-66+Cu@NH2-UIO-66+Mo@NH2-UIO-66, Ru@NH2-UIO-66, Ru1Cu2 @NH2-UIO-66, CuMo@NH2-UIO-66, Ru1Cu2Mo0.5@NH2-UIO-66, NH2-UIO-66; (b) Ru1CuxMo0.5@NH2-UIO-66, and (c) Ru1Cu2Moy@NH2-UIO-66
| Catalyst | TOF/($\text{mo}{{\text{l}}_{{{\text{H}}_{2}}}}\cdot \text{mol}_{\text{Ru}}^{-1}\cdot {{\min }^{-1}}$) | Ea/(kJ?mol-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ru NPs | 26.70 | 66.50 | [34] |
| RuCu(1:1)/γ-Al2O3 | 16.40 | 52.00 | [35] |
| RuCo(1:1)/γ-Al2O3 | 32.90 | 47.00 | [35] |
| Ru(0)/TiO2 | 241.00 | 70.00 | [36] |
| RuCo@MIL-53 | 87.24 | 34.32 | [16] |
| Ru@g-C3N4 | 313.00 | 37.40 | [37] |
| RuCu/graphene | 135.00 | 30.60 | [38] |
| RuCuMo@NH2-UIO-66 | 180.83 | 30.10 | This study |
Table 2 Catalytic activities of different Ru-based catalysts used for the hydrolytic dehydrogenation of AB
| Catalyst | TOF/($\text{mo}{{\text{l}}_{{{\text{H}}_{2}}}}\cdot \text{mol}_{\text{Ru}}^{-1}\cdot {{\min }^{-1}}$) | Ea/(kJ?mol-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ru NPs | 26.70 | 66.50 | [34] |
| RuCu(1:1)/γ-Al2O3 | 16.40 | 52.00 | [35] |
| RuCo(1:1)/γ-Al2O3 | 32.90 | 47.00 | [35] |
| Ru(0)/TiO2 | 241.00 | 70.00 | [36] |
| RuCo@MIL-53 | 87.24 | 34.32 | [16] |
| Ru@g-C3N4 | 313.00 | 37.40 | [37] |
| RuCu/graphene | 135.00 | 30.60 | [38] |
| RuCuMo@NH2-UIO-66 | 180.83 | 30.10 | This study |
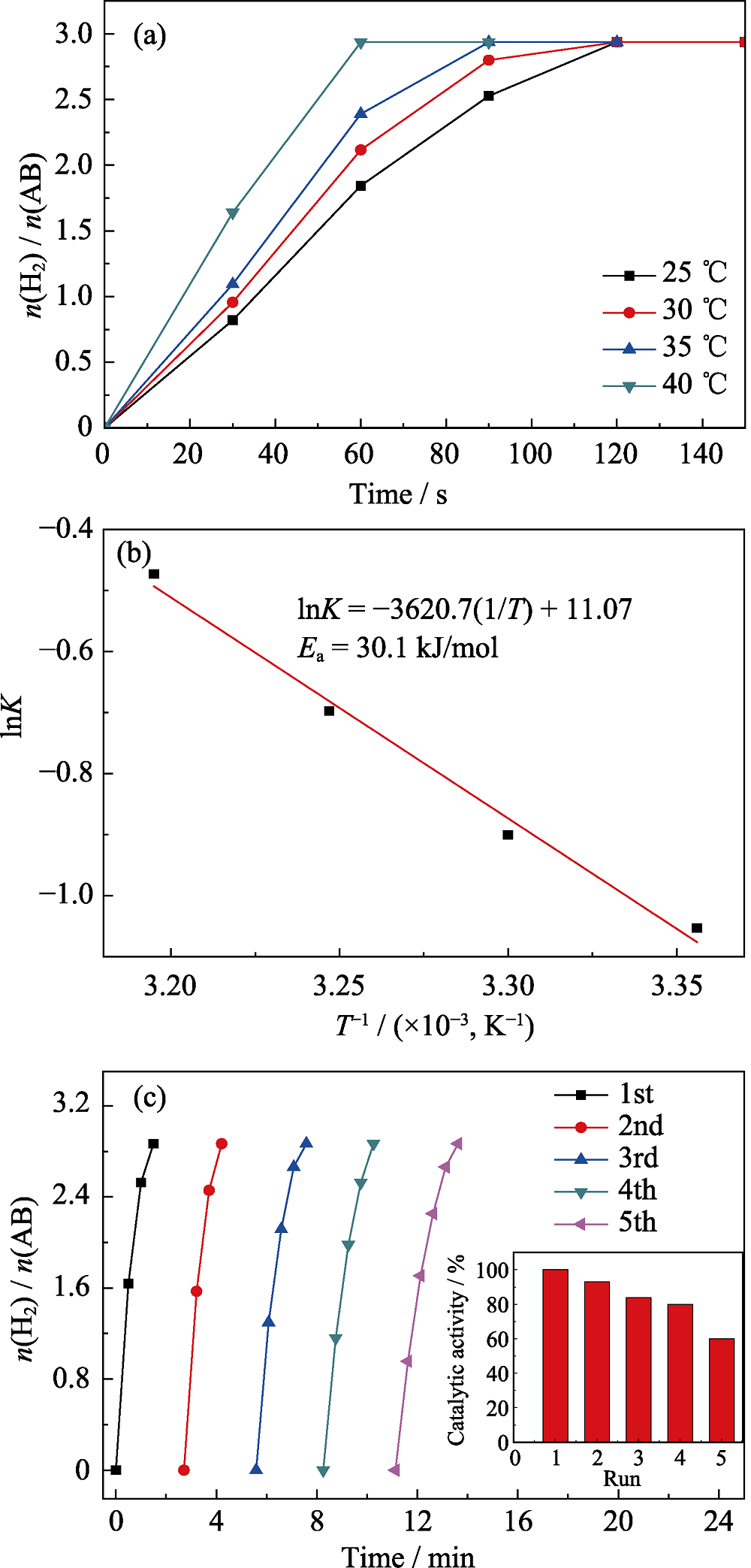
Fig. 7 Plots of time vs. n(H2)/n(NH3BH3) for the hydrolysis of AB (18.5 mg) aqueous solution catalyzed by Ru1Cu2Mo0.5@NH2-UIO-66 at different temperatures(a), and the corresponding Arrhenius plot (b), and reusability test for the Ru1Cu2Mo0.5@NH2-UIO-66 within five cycles(c)
| [1] | LONG J, WANG S, DING Z , et al. A mine-functionalized zirconium metal-organic framework as efficient visible-light photocatalyst for aerobic organic transformations. Chemical Communications, 2012,48(95):11656-11658. |
| [2] | GUO Z, XIAO C, MALIGALGANESH R V , et al. Pt nanoclusters confined within metal-organic framework cavities for chemoselective cinnamaldehyde hydrogenation. ACS Catalysis, 2014,4(5):1340-1348. |
| [3] | SUN D, FU Y, LIU W , et al. Studies on photocatalytic CO2 reduction over NH2-UIO-66 (Zr) and its derivatives: towards a better understanding of photocatalysis on metal-organic frameworks. Chemistry - A European Journal, 2013,19(42):14279-14285. |
| [4] | PETERSON G W, DECOSTE J B, FATOLLAHI-FARD F , et al. Engineering UiO-66-NH2 for toxic gas removal. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2013,53(2):701-707. |
| [5] | XU X Y, YAN B . Eu (Ⅲ) functionalized Zr-based metal-organic framework as excellent fluorescent probe for Cd2+, detection in aqueous environment . Sensors & Actuators B Chemical, 2016,222:347-353. |
| [6] | CHANDRA M, XU Q . A high-performance hydrogen generation system: transition metal-catalyzed dissociation and hydrolysis of ammonia-borane. Journal of Power Sources, 2006,156(2):190-194. |
| [7] | FAN Y, LI X, HE X , et al. Effective hydrolysis of ammonia borane catalyzed by ruthenium nanoparticles immobilized on graphic carbon nitride. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014,39(35):19982-19989. |
| [8] | DAI H, SU J, KAI H , et al. Pd nanoparticles supported on MIL-101 as high-performance catalysts for catalytic hydrolysis of ammonia borane. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014,39(10):4947-4953. |
| [9] | ZHANG X B, YAN J M, HAN S , et al. Magnetically recyclable Fe@Pt core-shell nanoparticles and their use as electrocatalysts for ammonia borane oxidation: the role of crystallinity of the core. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2009,131(8):2778-2779. |
| [10] | YAN J M, ZHANG X B, SHIOYAMA H , et al. Room temperature hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane catalyzed by Co nanoparticles. Journal of Power Sources, 2010,195(4):1091-1094. |
| [11] | ZAHMAKIRAN M, DURAP F, ÖZKAR S . Zeolite confined copper (0) nanoclusters as cost-effective and reusable catalyst in hydrogen generation from the hydrolysis of ammonia-borane. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2010,35(1):187-197. |
| [12] | YANG K, YAO Q, HUANG W , et al. Enhanced catalytic activity of NiM (M=Cr, Mo, W) nanoparticles for hydrogen evolution from ammonia borane and hydrazine borane. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017,42(10):6840-6850. |
| [13] | YAO Q, LU Z H, HUANG W , et al. High Pt-like activity of the Ni-Mo/graphene catalyst for hydrogen evolution from hydrolysis of ammonia borane. Journal of Materials Chemical A, 2016,4(22):8579-8583. |
| [14] | ZHANG L, ZHOU L, YANG K , et al. Pd, Ni nanoparticles supported on MIL-101 as high-performance catalysts for hydrogen generation from ammonia borane. Journal of Alloys & Compounds, 2016,677:87-95. |
| [15] | WANG Q, XU C, MING M , et al. In situ formation of AgCo stabilized on graphitic carbon nitride and concomitant hydrolysis of ammonia borane to hydrogen. Nanomaterials, 2018,8(5):280-289. |
| [16] | CHEN M, ZHOU L, LU D , et al. RuCo bimetallic alloy nanoparticles immobilized on multi-porous MIL-53 (Al) as a highly efficient catalyst for the hydrolytic reaction of ammonia borane. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018,43(3):1439-1450. |
| [17] | XIONG X, ZHOU L, YU G , et al. Synthesis and catalytic performance of a novel RuCuNi/CNTs nanocomposite in hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2015,40(45):15521-15528. |
| [18] | YANG K, ZHOU L, XIONG X , et al. RuCuCo nanoparticles supported on MIL-101 as a novel highly efficient catalysts for the hydrolysis of ammonia borane. Microporous & Mesoporous Materials, 2016,225:1-8. |
| [19] | GU Y, WU Y N, LI L , et al. Controllable modular growth of hierarchical MOF-on-MOF architectures. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2017,56(49):15658-15662. |
| [20] | YANG K, ZHOU L, YU G , et al. Ru nanoparticles supported on MIL-53 (Cr, Al) as efficient catalysts for hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of ammonia borane. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2016,41(15):6300-6309. |
| [21] | YURDERI M, BULUT A, ZAHMAKIRAN M , et al. Ruthenium (0) nanoparticles stabilized by metal-organic framework (ZIF-8): highly efficient catalyst for the dehydrogenation of dimethyla mine-borane and transfer hydrogenation of unsaturated hydrocarbons using dimethyla mine-borane as hydrogen source. Applied Catalysis B Environmental, 2014, 160-161(1):534-541. |
| [22] | CAO N, SU J, LUO W , et al. Ni-Pt nanoparticles supported on MIL-101 as highly efficient catalysts for hydrogen generation from aqueous alkaline solution of hydrazine for chemical hydrogen storage. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014,39(18):9726-9734. |
| [23] | RAKAP M . PVP-stabilized Ru-Rh nanoparticles as highly efficient catalysts for hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of ammonia borane. Journal of Alloys & Compounds, 2015,649:1025-1030. |
| [24] | CHUSUEI C C, BROOKSHIER M A, GOODMAN D W . Correlation of relative X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy shake-up intensity with CuO particle size. Langmuir, 1999,15(8):2806-2808. |
| [25] | GUCZI L, BAZIN D . Structure and selectivity of metal catalysts: revisiting bimetallic zeolite systems. Applied Catalysis A General, 1999,188(1/2):163-174. |
| [26] | GU Z, XIONG Z, REN F , et al. Flower-like PdCu catalyst with high electrocatalytic properties for ethylene glycol oxidation. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2018,83:32-39. |
| [27] | WANG P, QI J, CHEN X , et al. New insights into high-valence state Mo in molybdenum carbide nanobelts for hydrogen evolution reaction. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017,42(16):10880-10890. |
| [28] | LOC LUU C, THI T V N, NGUYEN T , et al. Synthesis, characterization and adsorption ability of UiO-66-NH2. Advances in Natural Sciences Nanoscience & Nanotechnology, 2015,6(2):025004-025009. |
| [29] | LOISEAU T, SERRE C, HUGUENARD C , et al. A rationale for the large breathing of the porous aluminum terephthalate (MIL-53) upon hydration. Chemistry-A European Journal, 2004,10(6):1373-1382. |
| [30] | LI J, ZHU Q L, XU Q . Non-noble bimetallic CuCo nanoparticles encapsulated in the pores of metal-organic frameworks: synergetic catalysis in the hydrolysis of ammonia borane for hydrogen generation. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2014,5(1):525-530. |
| [31] | NING H, LU D, ZHOU L . Bimetallic RuM (M=Co, Ni) alloy NPs supported on MIL-110(Al): synergetic catalysis in hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane. Chinese Journal of Chemical Physics, 2018,31(1):99-109. |
| [32] | WANG X, CHEN W, ZHANG L , et al. Uncoordinated a mine groups of MOFs to anchor single Ru sites as chemoselective catalysts towards the hydrogenation of quinolone. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2017,139(28):9419-9422. |
| [33] | CAO N, LIU T, SU J , et al. Ruthenium supported on MIL-101 as an efficient catalyst for hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of a mine boranes. New Journal of Chemistry, 2014,38(9):4032. |
| [34] | ZHOU Q, YANG H, XU C . Nanoporous Ru as highly efficient catalyst for hydrolysis of ammonia borane. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2016,41(30):12714-12721. |
| [35] | RACHIERO G, DEMIRCI U, MIELE P . Bimetallic RuCo and RuCu catalysts supported on γ-Al2O3. A comparative study of their activity in hydrolysis of ammonia-borane. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2011,36(12):7051-7065. |
| [36] | AKBAYRAK S, TANYILDIZI S, MORKAN I , et al. Ruthenium (0) nanoparticles supported on nanotitania as highly active and reusable catalyst in hydrogen generation from the hydrolysis of ammonia borane. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014,39(18):9628-9637. |
| [37] | YAN R, LI X, HE X , et al. Effective hydrolysis of ammonia borane catalyzed by ruthenium nanoparticles immobilized on graphic carbon nitride. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014,39(35):19982-19989. |
| [38] | CAO N, HU K, LUO W , et al. RuCu nanoparticles supported on graphene: a highly efficient catalyst for hydrolysis of ammonia borane. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2014,590:241-246. |
| [1] | ZHANG Yiqing,ZHANG Shujuan,WAN Zhengrui,MO Han,WANG Niangui,ZHOU Liqun. RuFe Nanoparticles Modified Sheet-like BiVO4 : High-efficient Synergistic Catalyst for Ammonia Borane Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(7): 809-816. |
| [2] | SUI Li-Li, WANG Run, ZHAO Dan, SHEN Shu-Chang, SUN Li, XU Ying-Ming, CHENG Xiao-Li, HUO Li-Hua. Construction of Hierarchical α-MoO3 Hollow Microspheres and Its High Adsorption Performance towards Organic Dyes [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(2): 193-200. |
| [3] | WU Xuan-Rong, YANG Qiao-Zhen, ZHAO Yong-Xiang, LU Yan-Luo. Hydrothermal/Solvothermal Synthesis and Photocatalytic Performance of ZnS Microspheres [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(5): 473-478. |
| [4] | LI Bin, LI Ying-Lian, MO Shu-Yi, CHEN Ming-Guang, WANG Dong-Sheng, LONG Fei. Synthesis of Core-shell Structure In2Se3/Cuse Micro/Nano-powders Followed by Coated-rapid Heating Treatment Method for Preparing CuInSe2 Thin Films [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(10): 1135-1140. |
| [5] | LU Qing, HUA Luo-Guang, CHEN Yi-Lin, GAO Bi-Fen, LIN Bi-Zhou. Preparation and Property of Oxygen-deficient Bi2WO6-x Photocatalyst Active in Visible Light [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(4): 413-419. |
| [6] | ZHOU Chao, FENG Qing, GAO Yan-Min. Synthesis and Characterization of Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS) Powders by Solvothermal Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(5): 487-492. |
| [7] | CAO Tie-Ping, LI Yue-Jun, WANG Chang-Hua. Preparation and Photocatalytic Property of NiO/ZnO Heterostructured Nanofibers [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(3): 295-300. |
| [8] | LI Yue-Jun, CAO Tie-Ping, SHAO Chang-Lu, WANG Chang-Hua. Preparation and Photocatalytic Properties of γ-Bi2O3/TiO2 Composite Fibers [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(7): 687-692. |
| [9] | ZHU Zhen-Feng, WANG Xiao-Feng, LIU Hui, LIU Dian-Guang. Synthesis of Quasi-monodispersed SnO2 Microspheres via Microwave Solvothermal Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(3): 311-316. |
| [10] | LI Tian-Bao, LIANG Jian, XU Bing-She, WANG Jin. Preparation and Characteristic of One-dimensional Magnesium Borate Nanomaterials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2010, 25(9): 947-951. |
| [11] | ZHU Kong-Jun, SU Li-Kui, JI Hong-Li, QIU Jin-Hao, BAI Lin, YANAGISAWA Kazumichi, KAJIYOSHI Koji. Hydrothermal Solvothermal Synthesis of (K, Na)NbO3 Lead-free Piezoelectric Ceramics and Its Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2010, 25(11): 1159-1163. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||