与此同时, 碘又是重要的无机化工原料之一, 属于稀缺资源。碘及碘的化合物在农业、医药科学和工业生产中有着广泛应用[7]。许多盐湖中碘资源丰富, 大量的前期研究表明, 卤水中碘的浓度远远高于海水中碘的浓度, 极具开采价值[8]。在富集碘的各种技术中, 基于固体吸附剂的固定床方法以其简单和成本相对较低而具有明显的优越性[9,10,11]。Pei等[12]制备的两种多孔有机骨架材料(POFs)在298 K/40 Pa的条件下, 对碘的吸附容量分别为1.86及1.44 g·g-1。Sigen等[13]制备的金属-卟啉共轭微孔聚合物, 用于吸附碘蒸气, 吸附率达到202wt%, 同时在有机溶剂中最高吸附量为326 mg·g-1。Li等[14]合成的多孔偶氮桥联卟啉-酞菁网络(AzoPPN)对碘蒸气的吸附性能优异, 吸附率可达到290wt%。Janeta等[15]制备了一种用于可逆碘捕获的高效气凝胶, 即多孔硅倍半氧嘧啶骨架(PSIF), 其对碘的吸附率高达485wt%, 是目前报道的最高水平。另外, Wang等[16]使用带有吡啶基团的MOFs材料在环己烷溶液中吸附碘, 最大吸附容量可以达到1250 mg·g-1。但是由于碘的吸附剂一般具有强极性, 在水中稳定性较差以及碘在水溶液中含量难以准确测定等缺点, 已有的研究几乎都是从有机溶剂中或者以固体吸附的方式吸附碘, 从水环境中有效捕获碘仍然面临巨大的挑战。
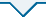
本工作首先建立测定水溶液中碘浓度的一般方法, 然后制备ZIF-8及ZIF-67两种沸石咪唑骨架材料, 研究其在水中对碘的吸附情况。
1 实验方法
1.1 试剂与仪器
试剂: 六水合硝酸钴(Co(NO3)2·6H2O, AR)、六水合硝酸锌(Zn(NO3)2·6H2O, AR)、2-甲基咪唑(C4H6N2, AR)、碘(I2)、甲醇(CH3OH)、无水乙醇(C2H5OH)、环己烷(C6H12)。
仪器: 控温摇床(IKA/KS4000, 德国IKA仪器设备有限公司)、双光束紫外-可见分光光度计(TU-1901, 北京普析通用仪器有限公司)、扫描电子显微镜(SEM)(KYKY-EM3200, 中科科仪)、同步热分析仪(TGA/DSC)(TGA/DSC1, 瑞士梅特勒-托利多)、X射线粉末衍射仪(XRD)(XRD-6000, 岛津公司)、N2吸脱附测试仪 (Autosorb-iQ, 美国康塔仪器公司)。
1.2 材料制备
ZIF-8的制备: 参照文献[17], 首先将1.5 g Zn(NO3)2·6H2O和3.32 g 2-甲基咪唑, 分别溶解在70 mL无水甲醇中; 然后将含2-甲基咪唑的水溶液加入到Zn(NO3)2·6H2O溶液中搅拌, 在25 ℃下剧烈搅拌24 h, 对所得乳浊液进行离心处理, 用无水甲醇洗涤固体三次, 在70 ℃下真空干燥24 h, 得到样品ZIF-8。
ZIF-67的制备: 参照文献[18], 将328.0 mg 2-甲基咪唑和249.0 mg Co(NO3)2·6H2O分别溶解在25 mL去离子水中, 超声处理, 将含2-甲基咪唑的水溶液加入到Co(NO3)2·6H2O溶液中, 搅拌10 min后静置20 h, 收集紫色固体, 用无水乙醇和去离子水分别清洗三次, 在60 ℃下真空干燥24 h, 得到样品ZIF-67。
1.3 吸附实验
实验中所有碘溶液均用纯度为99.8%的碘作为碘源。用去离子水制备溶液, 用1 mol·L-1盐酸调整溶液pH为5。
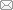
建立标准曲线: 配制一系列浓度梯度碘水溶液, 分别取5 mL碘水溶液置于50 mL的分液漏斗中, 分三次用环己烷进行萃取, 每次加入5 mL, 将三次萃取的萃取液混合, 通过紫外分光光度计测量其吸光度, 建立碘-环己烷标准曲线(R2 = 0.9990) (图1)。
图1
图1
用环己烷从水中萃取碘后的碘-环己烷标准曲线
Fig. 1
Standard curve of iodine-cyclohexane after extraction of iodine from water with cyclohexane
吸附实验结果测定: 进行吸附实验, 吸附达到平衡后, 取吸附完成的溶液若干, 过滤后取5 mL滤液置于50 mL的分液漏斗中, 分三次用环己烷进行萃取, 每次加入5 mL, 将三次萃取的萃取液混合, 用紫外分光光度计测定碘的浓度。理论计算表明, 经三次萃取, 萃取率可达99%以上。在每组实验中, 我们都建立空白对照组, 以消除碘升华对吸附结果的影响。所有数据均为三次重复实验的平均值。
1.4 数据分析
上述各方程中, Qe/(mg·g-1)是吸附达到平衡时的平衡吸附量, C0/(mg·L-1)是初始溶液中I2浓度, Ce/(mg·L-1)是吸附达到平衡时溶液中I2浓度, V/mL是I2溶液的体积, ω/mg是加入的吸附剂的质量; Qm/(mg·g-1)是吸附剂对I2的最大理论吸附量, kL/(L·mg-1)是Langmuir模型常数, kF/(mg·g-1)是Freundlich 模型常数, n是线性常数; Qt/(mg·g-1)是时间t时的吸附量, k1/(L·mg-1)和k2/(g·min-1·mg-1)是一级、二级动力学模型的速率常数。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 材料表征
图2
图2
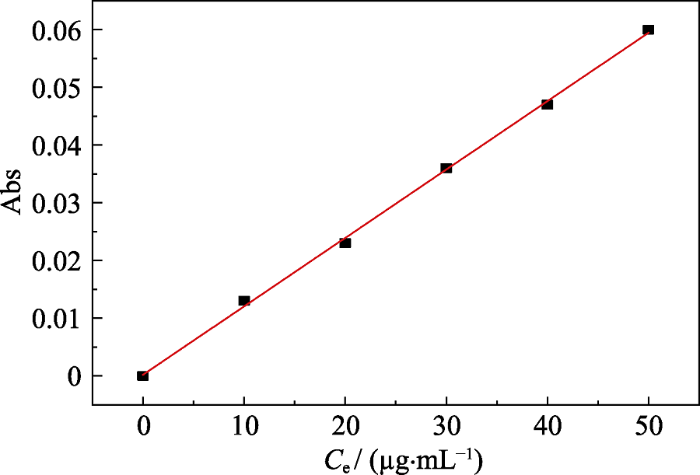
ZIF-8和ZIF-67的模拟及实验XRD图谱
Fig. 2
Simulated and experimental XRD patterns of ZIF-8 and ZIF-67
图3
图3
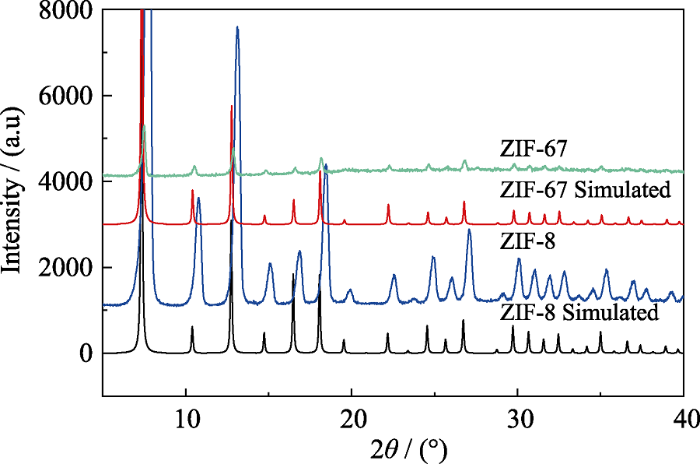
ZIF-8及ZIF-67吸附碘前后扫描电镜照片
Fig. 3
SEM images of ZIF-8 and ZIF-67 before and after iodine adsorption
(a) ZIF-8 before adsorption, (b) ZIF-8 after adsorption, (c) ZIF-67 before adsorption, (d) ZIF-67 after adsorption
图4
图4
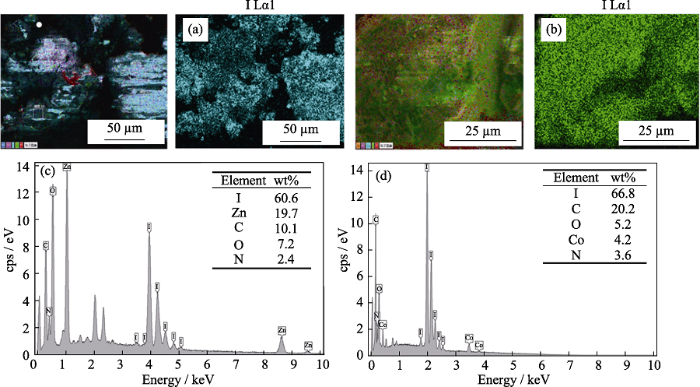
ZIF-8和ZIF-67吸附碘后的Mapping图像及EDS图谱
Fig. 4
Mapping images and EDS patterns of ZIF-8 and ZIF-67
(a) Mapping image of ZIF-8 after adsorption iodine; (b) Mapping image of ZIF-67 after adsorption iodine; (c) EDS pattern of ZIF-8 after adsorption iodine; (d) EDS pattern of ZIF-67 after adsorption iodine
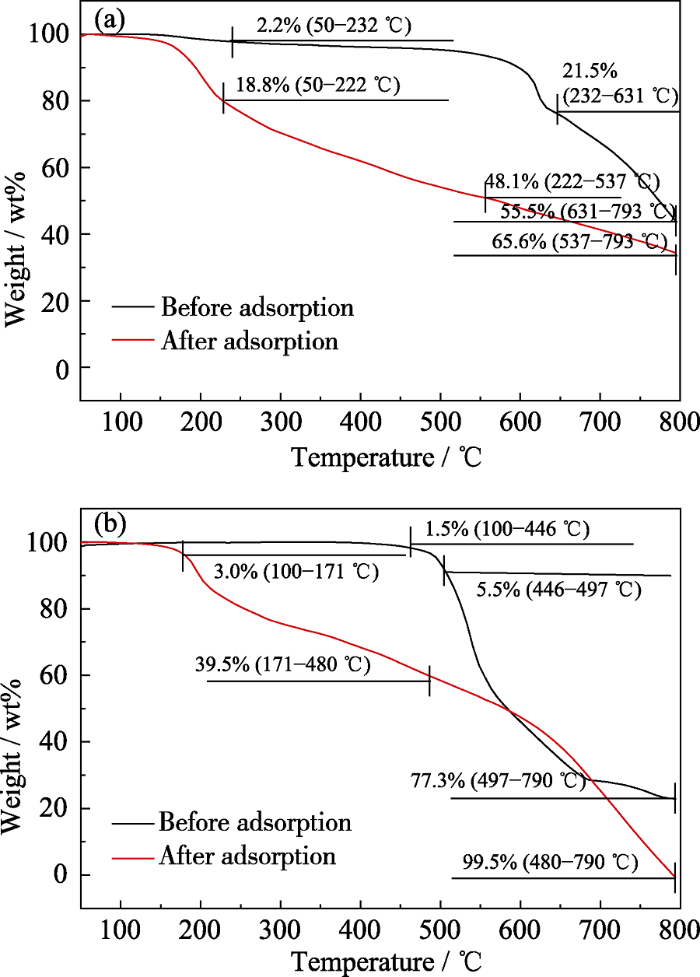
利用热重分析仪测定ZIF-8及ZIF-67材料的热稳定性, 设置温度为50~800 ℃, 升温速率为10 ℃/min。由图5(a)可知, 未吸附碘时, ZIF-8材料从50 ℃升温至232 ℃时, 样品损失了2.23wt%, 可能是残存的水从材料中脱除造成的; 当温度升高到631 ℃时, 样品损失了21.47wt%, 可能是有机配体脱除导致的; 当温度升高到793 ℃时, 样品损失了55.53wt%, 这可能是材料框架结构坍塌, 晶体不再完整造成的。从以上分析可以看出, ZIF-8具有较好的热稳定性, 热稳定温度为631 ℃。吸附碘后, 从50 ℃升温至573 ℃, 样品损失了66.94wt%, 可能是由于碘分子从材料上脱除造成的。由图5(b)可知, ZIF-67未吸附碘时, 在100 ℃左右出现缓慢失重; 升温至 446 ℃左右时, 损失的质量约为1.5wt%, 主要归因于水分子的挥发, 之后质量趋于稳定; 升温至497 ℃时, 质量开始急剧损失, 原材料ZIF-67开始分解; 升温至790 ℃, 分解基本结束。而ZIF-67吸附碘后, 质量从171 ℃开始急剧损失, 损失的质量约39.5wt%, 可能是碘从样品上脱除导致的。这一结果证明制备的样品确实能大量吸附碘。
图5
图6
图6
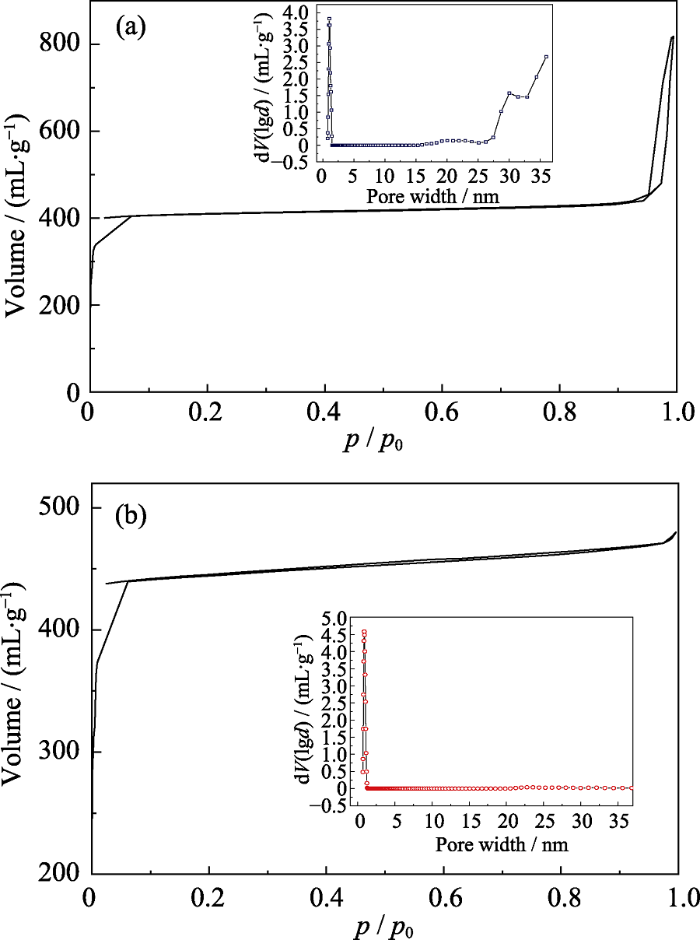
ZIF-8(a)及ZIF-67 (b)的氮气吸脱附曲线
Fig. 6
Nitrogen adsorption and desorption curves of ZIF-8 (a) and ZIF-67 (b)
2.2 吸附实验
2.2.1 溶液初始浓度对MOFs材料吸附碘的影响
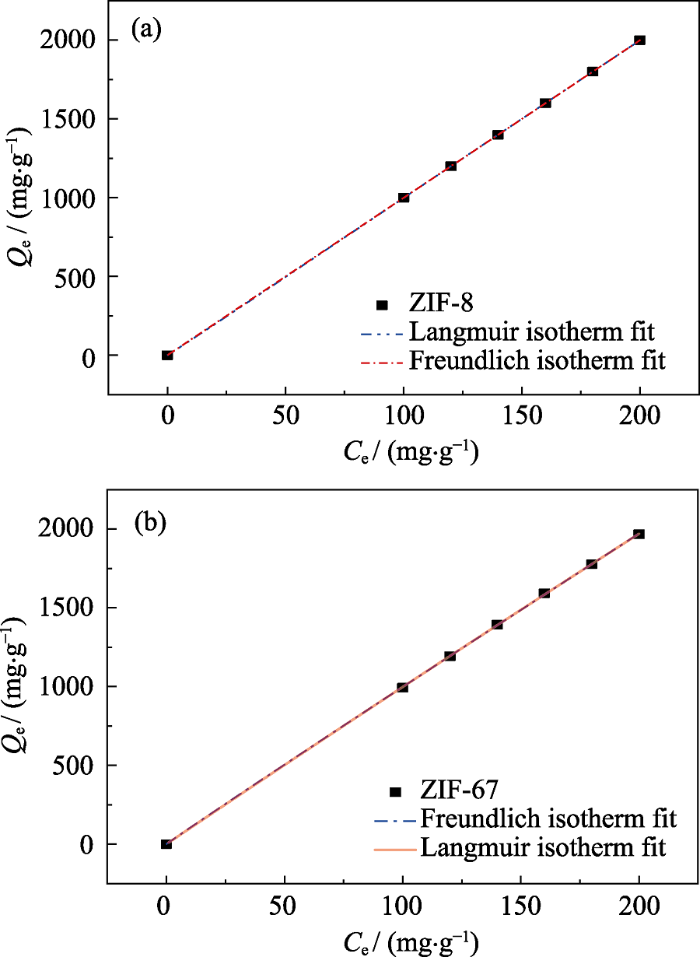
图7
图7
ZIF-8(a)及ZIF-67(b)的吸附量随溶液初始浓度变化曲线图
Fig. 7
ZIF-8 (a) and ZIF-67 (b) adsorption capacity dependences of the initial concentration of the solution
表1 ZIF-8及ZIF-67吸附碘的Langmuir及Freundlich方程参数值
Table 1
| ZIF-8 | ZIF-67 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir equation | Qm/(mg·g-1) | 64416.71 | 77747.64 |
| kL/(L·mg-1) | 1.59×10-4 | 1.30×10-4 | |
| R2 | 0.99 | 0.99 | |
| Freundlich equation | kF/(mg·g-1) | 10.00 | 10.84 |
| n | 1.00 | 0.98 | |
| R2 | 1.00 | 0.99 |
对于ZIF-8材料, Langmuir 等温模型中kL= 1.59×10-4 L·mg-1, 0<C0<200, RL约等于1, 即表示吸附等温线呈线性; Freundlich 吸附模型中n=1.00, 1/n=1, 即表示吸附是线性吸附。
对于ZIF-67材料, Langmuir等温模型中kL= 1.30×10-4, 0<C0<200, RL约等于1, 即表示吸附等温线呈线性; Freundlich 吸附模型中n=0.98, 1/n=1.02, 约等于1, 即表示吸附是线性吸附。
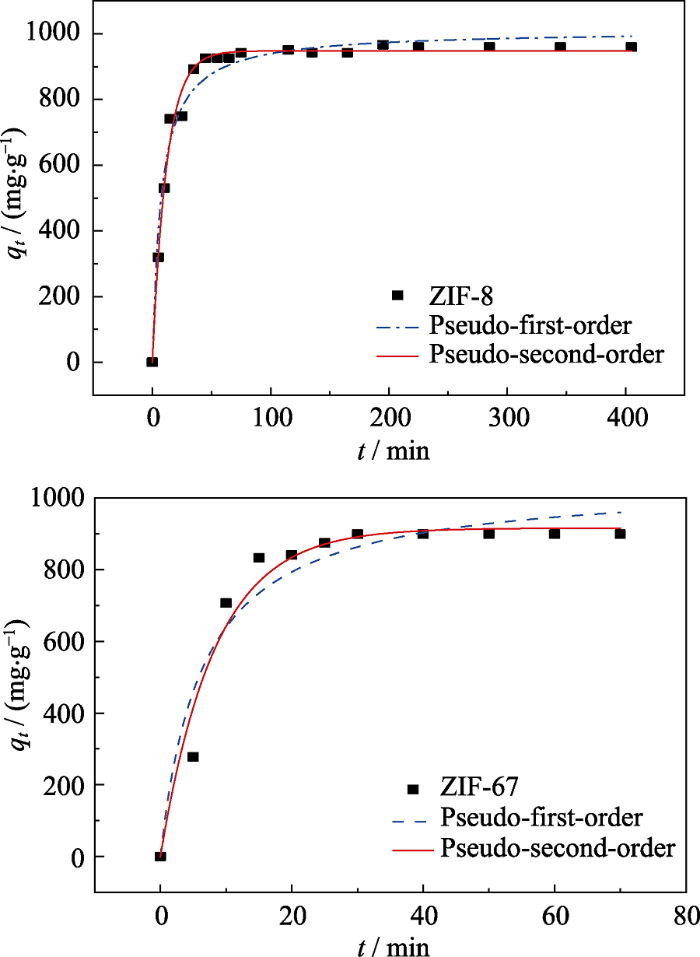
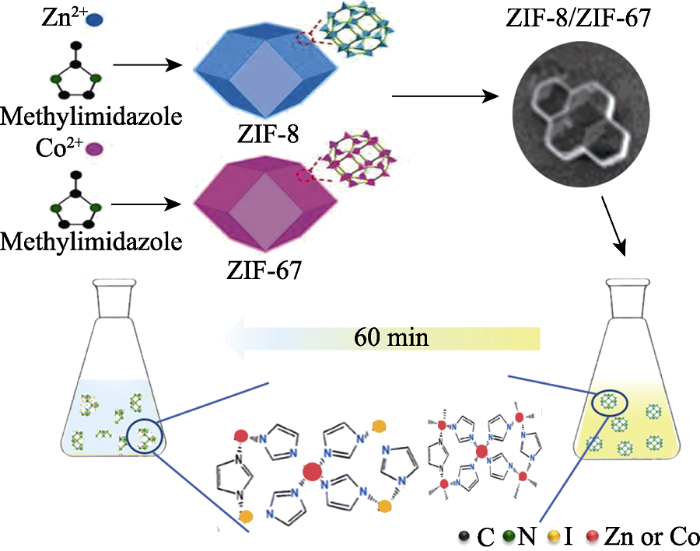
2.2.2 吸附时间对MOFs材料吸附碘的影响
图8
图8
ZIF-8及ZIF-67对碘的吸附量随时间的变化曲线
Fig. 8
Iodine adsorption capacity dependence of the adsorption time by ZIF-8 and ZIF-67
表2 ZIF-8及ZIF-67吸附I2的准一级及准二级方程参数值
Table 2
| ZIF-8 | ZIF-67 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Psedo-first-order kinetics equation | Qe/(mg·g-1) | 1010.54 | 1047.37 |
| k1/(L·mg-1) | 1.30×10-4 | 1.49×10-4 | |
| R2 | 0.97 | 0.93 | |
| Psedo-second-order kinetics equation | Qe/(mg·g-1) | 947.61 | 916.08 |
| k2/(g·min-1·mg-1) | 0.08 | 0.12 | |
| R2 | 0.99 | 0.96 |
2.2.3 机理讨论
图9
图9
ZIF-8及ZIF-67对碘的吸附机理示意图
Fig. 9
Adsorption mechanism of iodine on ZIF-8 and ZIF-67
3 结论
本研究建立了从水溶液中测定碘的一般方法, 并成功制备了两种ZIF材料ZIF-8和ZIF-67, 它们具有完整均匀的晶体结构, 较大的比表面积和良好的热稳定性。通过EDS和热重分析, 以及静态吸附实验, 证明ZIF-8和ZIF-67对水溶液中的碘具有超高效吸附能力, 在初始浓度为200 mg·L-1的条件下, 吸附量可以达到2000 mg·g-1。
参考文献
Assessment of the actual sustainability of nuclear fission power
Acceptance of nuclear power: the Fukushima effect
Risk communication about radionuclide contamination of food after the Fukushima nuclear power plant accident
Removal of radioactive iodine and cesium in water purification
Midterm report on removal of radioactive iodine and cesium from rainwater contaminated by Fukushima daiichi nuclear accident
Radionuclides in environmental samples and sample concentration of land in the analysis in the method of direct
Recent developments in the chemistry of polyvalent iodine compounds
Inorganic iodine speciation in tropical Atlantic aerosol
Adsorption of iodine on silver wire
Iodine adsorption in metal organic frameworks in the presence of humidity
Enhanced removal of iodide from aqueous solution by ozonation and subsequent adsorption on Ag-Ag2O modified on carbon spheres
Ultrahigh iodine adsorption in porous organic frameworks
Highly efficient and reversible iodine capture using a metalloporphyrin-based conjugated microporous polymer
Porous azo-bridged porphyrin- phthalocyanine network with high iodine capture capability
Porous silsesquioxane-imine frameworks as highly efficient adsorbents for cooperative iodine capture
The water-based synthesis of chemically stable Zr-based MOFs using pyridine-containing ligands and their exceptionally high adsorption capacity for iodine
In situ high pressure study of ZIF-8 by FTIR spectroscopy
Hierarchically structured layered-double- hydroxides derived by ZIF-67 for uranium recovery from simulated seawater
Removal of uranium (VI) from aqueous solutions by manganese oxide coated zeolite: discussion of adsorption isotherms and pH effect
Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems
Study on biosorption kinetics and thermodynamics of uranium by Citrobacter freudii
Preparation and characterization of surface imprinted polymer for selective sorption of uranium (VI)
Hollow Zn/Co ZIF particles derived from core-shell ZIF-67@ZIF-8 as selective catalyst for the semi-hydrogenation of acetylene
Synthesis of ZIF-8 and ZIF-67 using mixed-base and their dye adsorption
High-throughput synthesis and characterization of nanocrystalline porphyrinic zirconium metal-organic frameworks
Adsorption-desorption studies of indigocarmine from industrial effluents by using deoiled mustard and its comparison with charcoal
Adsorption isotherm, kinetic modeling and mechanism of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol on coconut husk-based activated carbon