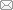
氮化硼(Boron nitride, BN)是由等数量硼原子和氮原子构成的一种性能优异、极具发展前景的宽带隙材料[1], 其晶体类型主要包括三种: sp2杂化的六方氮化硼(h-BN)[2], sp3杂化的立方氮化硼(c-BN)和纤锌矿型氮化硼(w-BN)[3,4]。其中六方氮化硼(h-BN)与石墨具有相似的层状结构和晶格参数, 并且在室温下呈象牙白色, 故也被称作“白石墨”[5], 其层内是由交替排列的N原子和B原子以sp2杂化轨道形成的六角型蜂巢结构二维网络, 层间由微弱的范德华力结合, 相邻层的六元环属于AA’堆积, 并且B原子与N原子延C轴依次交替排列(如图1)[6]。六方氮化硼(h-BN)与石墨互为等电子体[7], 因此二者具有相似的性质, 如高热导率、低摩擦系数、低热膨胀系数、良好的热力学和化学稳定性等[8,9,10]。近年来, 鉴于石墨烯(Graphene, G)材料优异的性能及其潜在的应用价值, 其研究与应用开发持续升温。作为石墨烯的类似体, BN纳米材料也逐渐得到研究者的青睐, 在能源、催化、传感、生物医学等领域已取得了一系列重要进展[11,12,13]。
气凝胶材料是一类以固体为骨架、气体为分散介质的具有三维多孔网络结构的新型纳米材料, 凭借自身低热导(0.01~0.04 W·m-1·K-1)、低密度(0.003~ 0.3 g·cm3)、高孔隙率(80%~99.8%)、高比表面积(500~1300 m2·g-1)等独特性能, 已经广泛应用在建筑、输热管道、航空航天等领域[14,15,16]。由于化学键的差异(B-N键与C=C键), BN气凝胶表现出不同于石墨烯气凝胶(Graphene aerogel, GA)的独特性能。例如, 相比于GA, BN气凝胶具有更强的抗氧化性和化学惰性, 在空气中的抗氧化温度(~900 ℃)远高于GA(~450 ℃), 并且与酸、碱和熔融金属不易发生化学反应[17]; 另外, 由于N原子的电负性小于B原子, 电子云向N原子偏移并被束缚, 因此共轭的π电子不能完全离域形成大π键[18], 这决定了BN气凝胶是一种宽带隙的绝缘体(5.9 eV), 使其在诸多领域具有更显著的优势及应用价值。本文从近年来国内外BN气凝胶的研究进展出发, 系统介绍了BN气凝胶的制备方法及其在气体吸附、催化、污水净化及导热/隔热等领域的应用, 并对其未来发展方向进行了展望。
1 BN气凝胶的制备方法
随着BN气凝胶得到不同领域研究者的高度关注, 针对BN气凝胶制备方法的研究也方兴未艾, 现主要发展成模板法、低维BN组装法、无模板法等合成策略。就模板法而言, 根据模板的不同, 具体又分为以活性炭、GA、沸石等多孔材料为模板的硬模板法和以阳离子表面活性剂、嵌段共聚物等高分子为模板的软模板法[19,20]。模板法是一种发展较为成熟的制备方法, 但采用硬模板法制备的BN气凝胶的比表面积大多在100~1100 m2·g-1范围内, 而采用无模板法制备出的BN气凝胶比表面积可高达1900 m2·g-1[21]。相比于其他制备方法, 低维BN组装法更适用于大规模制备BN气凝胶。根据理论计算, 稳定的BN多孔结构的比表面积最大可达4800 m2·g-1[22,23], 这表明高比表面积BN气凝胶的制备仍有很大的发展潜力。
图1
1.1 硬模板法
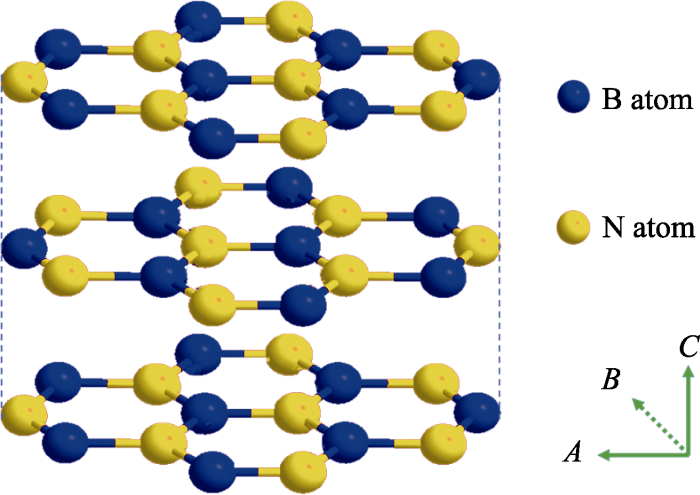
硬模板法是指以多孔无机非金属或金属材料为模板, 采用化学方法在其上生长BN, 再采用化学刻蚀法去除模板后得到与模板具有相似微观形貌的BN气凝胶。2004年, Han等[24]首次报道了以活性炭为模板, 以B2O3和N2为硼源和氮源, 在高温下合成出多孔BN气凝胶的方法。虽然BN气凝胶继承了活性炭模板的多孔结构, 但制备出的BN气凝胶比表面积只有167.8 m2·g-1, 远低于活性炭模板的比表面积(779 m2·g-1)(如图2), 这是由于活性炭的孔径分布不均, 先驱体在多孔模板中填充不充分导致的。研究表明, 这种比表面积大幅下降的现象在硬模板法中普遍存在, 为了克服这一问题, 人们将孔径分布均匀的多孔材料应用到硬模板法中。Mokaya等[25]在SBA-15介孔分子筛模板中渗入BH3NH3先驱体制备出比表面积为327 m2·g-1的BN气凝胶, 但较小的比表面积仍制约着BN气凝胶性能的发挥。
图2
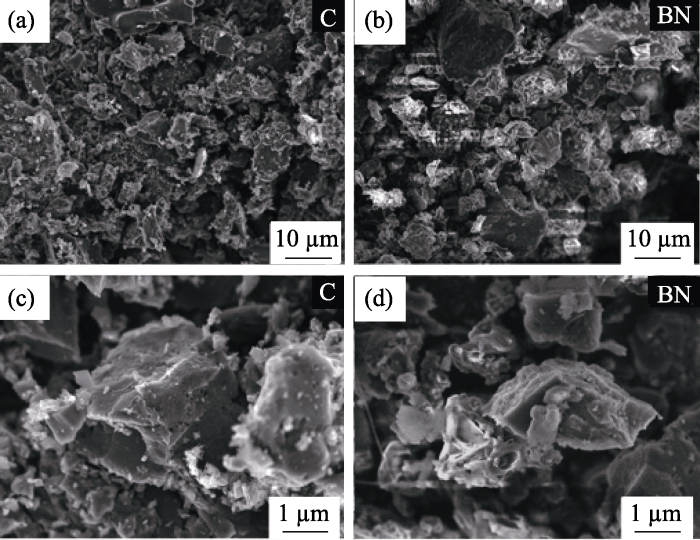
近期, Xu等[26,27]采用冷冻干燥法首先制备出具有负泊松比和负热膨胀系数的双曲线型多孔GA模板, 然后在此基础上采用CVD法在其上沉积BN, 经热刻蚀后得到比表面积为1080 m2·g-1的BN气凝胶(如图3(a))。该气凝胶密度仅为0.1 mg·cm-3, 是目前为止所报道的最轻的固体材料(如图3(b))。此外, 负泊松比使BN气凝胶具有良好的机械性能和超弹性, 其相对高度和杨氏模量在100次压缩循环后, 仍可以保留90%以上(如图3(c, d))。除了作为生长模板, 无机非金属模板在高温下还可被B原子和N原子取代, 进而得到BN气凝胶或杂化BN气凝胶。Kutty等[28]以掺杂碳纳米管的氧化石墨烯(GO)为模板, 在1600 ℃下通入N2和B2O3后发生原子取代反应, 成功制得比表面积为716.56 m2·g-1的BN气凝胶。另外, 通过改变实验温度等条件, 可以实现原子不完全取代, 制备出含B、N、C三种元素的气凝胶材料。
图3
图3
(a)双壁双曲线型BN气凝胶的制备流程示意图, (b)BN气凝胶与其他材料的密度对比, (c)BN气凝胶的相对高度、最大压力和杨氏模量与循环次数的关系曲线, (d)BN气凝胶在不同压力下的光学照片和SEM照片[26]
Fig. 3
(a) Schematic illustration of the metastructure design of BN aerogels; (b) The lightest hBN aerogels sample compared with other ultralight materials; (c) The ultimate stress, Young’s modulus, and relative height for 100 compression cycles; (d) Optical and SEM images of BN aerogels under different pressures[26]
1.2 软模板法
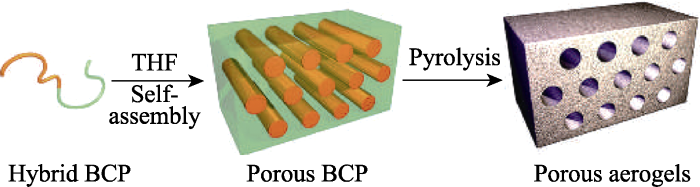
软模板通常是由表面活性剂分子聚集而成, 主要包括两亲分子形成的各种有序聚合物, 如囊泡、胶团、微乳液、自组装膜、生物分子和高分子的自组织结构等[31,32,33,34]。软模版法是通过分子间的弱相互作用力引导和调控游离前驱体的规律性组装, 进而形成具有特异结构纳米材料的方法。Meile等[35]将表面活性剂十六烷基三甲基溴化铵(CATB)和三甲基环硼氮烷(MAB)混合后在120 ℃长时间热处理, 去除溶剂后制备出比表面积为800 m2·g-1的BN气凝胶(孔径约为6 nm)。Malenfant等[36]利用有机-无机杂化的嵌段共聚物聚降冰片烯-癸硼烷(polynorbornene- decaborane), 在四氢呋喃(THF)中自组装制备出多孔BN气凝胶(图4, 比表面积为950 m2·g-1)。软模版法难以控制产物的尺寸和形貌, 效率较低, 但软模板法具有形态多样、模板易去除、成本低廉等优势。
图4
1.3 低维BN组装法
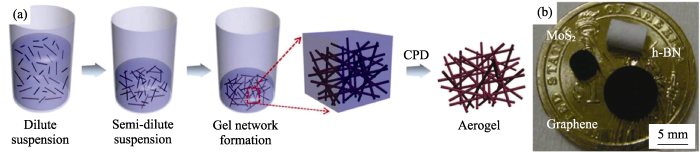
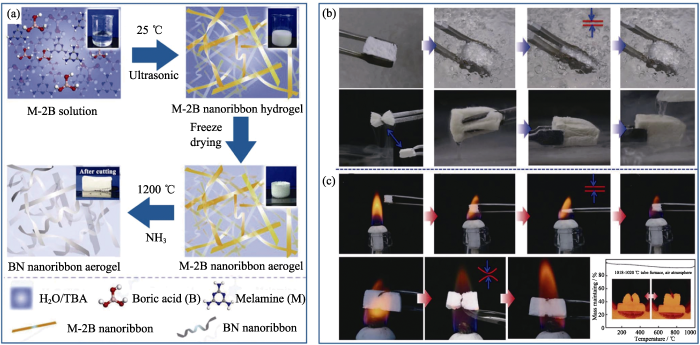
低维BN组装法是指利用纳米管、纳米带、纳米片等低维BN纳米材料通过分子桥接、静电相互作用、范德华力等共价键或非共价键作用, 聚集组装成具有三维多孔结构BN气凝胶的方法[37,38,39]。低维组装法反应条件较为温和, 并且可以保留低维BN纳米材料的原有特性, 以制备具有特殊功能的BN气凝胶。2012年, Jung等[40]发现低维BN纳米材料(包括纳米线、纳米管和纳米片)在胆酸钠中分散后, 经低温蒸发溶剂、溶剂置换和超临界干燥可组装成具有三维网络结构的BN气凝胶(图5(a))。该课题组后续又采用类似方法以MnO2纳米线、碳纳米管、MoS2和石墨烯纳米片为原料制备出多种气凝胶(图5(b)), 表明这是一种较为通用的制备气凝胶的方法。近期, Li等[41]采用氨化三聚氰胺二硼酸的方法制备出由纳米带相互缠绕而成的BN气凝胶(图6(a))。该气凝胶在-196~1000 ℃范围内仍能够很好地保持压缩-回弹性能(图6(b,c)), 在极端环境中有广阔的应用前景。
图5
图6
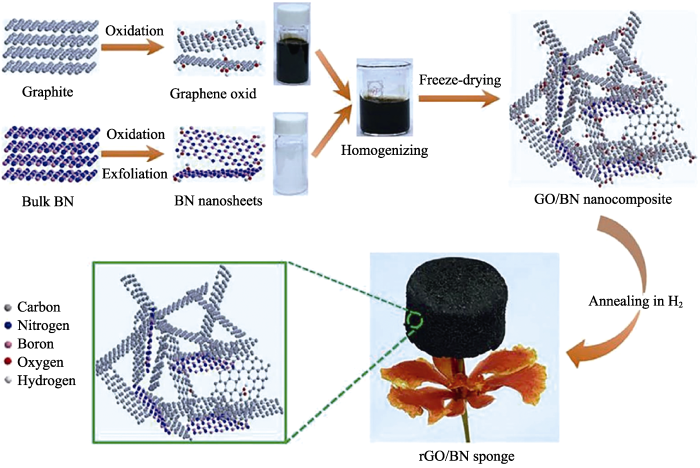
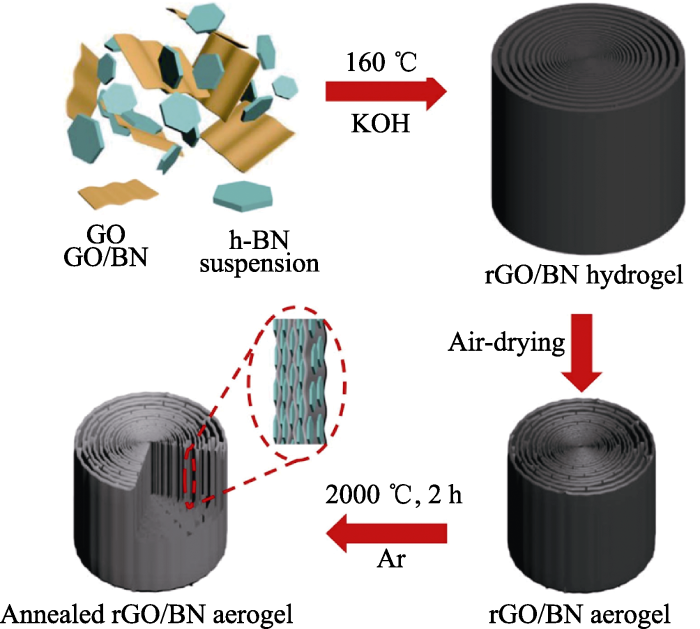
随着“绿色化学”的兴起, 研究者们致力于利 用化学技术在化学反应中减少催化剂、产物及副产物的使用与产生。范德华固体是指二维材料通过范德华力直接进行堆叠组装, 从而避免了交联剂的使用。2012年, GAO等[42]通过液相剥离方法制备h-BN层和G的分散体, 通过混合后得到h-BN/G块体。这些范德华堆叠的混合固体材料显示出与其起始母体层明显不同的电学、机械和光学性质, 但是这种材料由于孔隙率太低, 仍不属于气凝胶范畴。2017年, Li等[43]首次报道了无化学交联剂法制备还原氧化石墨烯(rGO)/BN复合气凝胶(图7)。研究人员直接对混合均匀的rGO纳米片和BN纳米片进行冷冻干燥, 在300 ℃下氢气还原得到密度仅为3.6 mg·cm-3的复合气凝胶。均匀分布的BN纳米片既阻止了rGO的团聚, 也促使其形成网状结构, 使气凝胶在制备过程中没有明显的体积收缩。无交联剂自组装法制备过程简单, 并且可得到任意尺寸和形状的气凝胶, 有望用于大规模制备气凝胶。
图7
1.4 无模板法
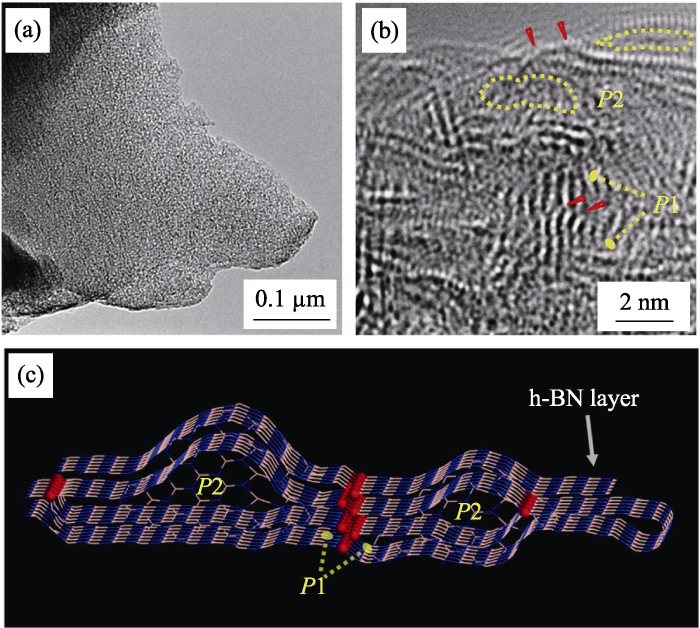
无模板法是在不借助外界模板的情况下, 通过B源和N源直接发生化学反应制备多孔气凝胶的方法。2010年, Rao课题组以硼酸和尿素为原料, 直接通过二者反应制备出BN气凝胶, 经通过调整原料的比例和优化反应条件, 得到比表面积为927 m2·g-1 的多孔气凝胶[44]。研究者也尝试过用其他方法制备BN气凝胶, 如高压蒸汽法、热聚合BH3NH3法等[45,46,47], 但是所得气凝胶的比表面积和孔体积都不尽人意。近几年, 随着研究的深入, 无模板法制备BN气凝胶取得了突破性进展。Weng等[21]以硼酸和双氰胺为先驱体, 制备出比表面积高达1900 m2·g-1的BN气凝胶。有趣的是, 在透射扫描电镜下并不能观察到孔的存在(图8(a)), 通过高分辨透射电镜进一步观察, 可以发现晶格存在错位(图8(b,c)), 这是因为气凝胶的孔径仅有1 nm, 并且仅存在于BN层间的“褶皱”中(如P1、P2所示)。类似的, Lei等[48]利用硼酸-盐酸胍为先驱体合成出了比表面积为1425 m2·g-1的BN气凝胶。总之, 相比于模板法, 无模板法不受模板的空间和形态限制, 是制备高比表面积BN气凝胶的有效方法。
图8
2 BN气凝胶的应用
2.1 气体吸附
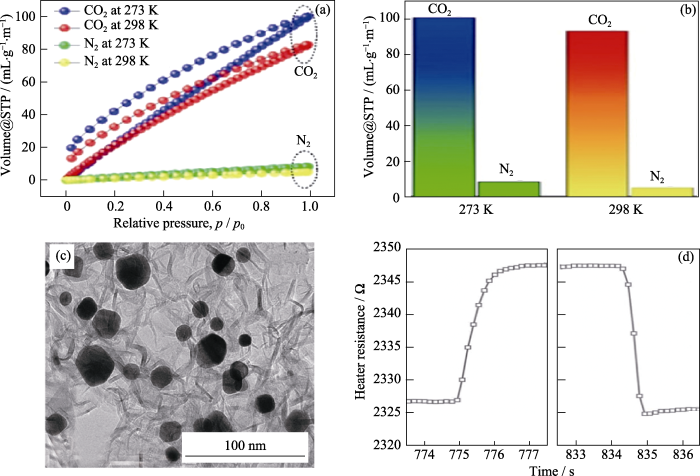
氢能作为一种储量丰富、来源广泛、能量密度高的绿色能源, 引起了人们的高度重视, 而氢能的储运则是氢能应用的关键。研究表明, H2分子在BN表面的结合能比在碳上的结合能高40%, 因此BN气凝胶有望用作储氢材料[51]。上文提到, Weng等[21]采用无模板法合成出孔隙率为1.07 cm3·g-1的高比表面积BN气凝胶(1900 m2·g-1), 这种气凝胶在 -196 ℃、1 MPa的条件下, 对氢气的吸收能力高达2.57%。多孔BN气凝胶不仅可以储氢, 而且对二氧化碳、丙烷等气体展现出良好的吸附能力。近期, Kutty等[28]利用原子取代法制备的BN气凝胶对二氧化碳气体表现出较高的选择性, 无论在室温(298 K)和低温(273 K)条件下, 对二氧化碳的吸收量都远高于氮气(如图9(a,b))。相似的, Anna等[52]通过在BN气凝胶上负载Pt纳米晶制备出高性能丙烷气体传感器(图9(c))。该传感器不仅在500 ℃下有良好的稳定性, 而且具有较快的响应/恢复速率(1.35 s和0.6 s)(图9(d)), 这是因为BN的高热导率可以有效防止热点堆积和纳米粒子的烧结。
图9
图9
(a)在273和298 K下, BN气凝胶对CO2和N2的吸收量及(b)相应的柱状图[28], (c)Pt纳米晶/BN气凝胶的SEM照片, (d)Pt纳米晶/BN气凝胶对丙烷的响应/恢复曲线[52]
Fig. 9
(a) The absorption of CO2 and N2 at 273 and 298 K by BN aerogel and (b) corresponding histograms[28]; (c) SEM image of Pt nanocrystals/BN aerogel; (d) Response/recovery curve of Pt nanocrystal/BN aerogel towards propane[52]
2.2 催化
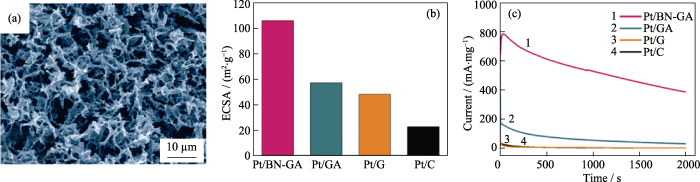
BN良好的化学稳定性和抗氧化性使其在高温和氧化条件下表现出优于传统催化剂载体的性能。此外, BN气凝胶的多孔网状结构有利于反应物的扩散, 超高的比表面积可以最大程度地负载金属活性组分, 进而提高催化性能[53,54]。虽然甲醇燃料电池被认为是很有前途的“绿色”便携式发电机, 但它们的进一步发展很大程度上受限于目前Pt基阳极催化剂的高成本和低催化活性。近期, Li等[55]提出了一种“自下而上”的大规模制造超细Pt纳米颗粒/ BN-石墨烯掺杂气凝胶(Pt/BN-GA)的方法。Pt/BN- GA催化剂具有的三维交联多孔网络, 高比表面积(369.2 m2·g-1), 众多B和N活性位点, 均匀分散的Pt纳米颗粒和良好的导电性, 构成了甲醇燃料电池理想的阳极催化体系(图10(a))。因此, 相比于传统的Pt/炭黑(Pt/C)、Pt/G和Pt/GA催化剂, Pt/BN-GA催化剂的催化活性、耐久性和强抗毒性得到显著提高。实验表明, Pt/BN-GA催化剂的电化学活性面积(ECSA)高达106.0 m2·g-1, 分别是Pt/GA、Pt/G和Pt/C催化剂的1.9、2.2和4.7倍(图10(b))。经测试, Pt/BN-GA催化剂的初始电流在2×103 s内仅下降了39%(图10(c)), 远低于Pt/GA(~78%)、Pt/G(~93%)和Pt/C(95%)。
图10
另外, 人们普遍认为宽带隙和化学惰性的h-BN不适合用于光催化和光伏转换材料。然而, Weng等[56]通过结构设计使BN气凝胶羟基功能化的(002)晶面充分暴露, 在紫外和可见光范围内表现出广谱吸收, 与锐钛矿型TiO2纳米粒子杂交后, 制备的TiO2/BN气凝胶在4420 nm可见光下对乙酸和染料(结晶紫)降解有较强的光催化作用, 是有机化合物氧化降解的有效光催化剂。值得注意的是, BN气凝胶自身也可以作为催化剂。Chen等[57]制备出BN/石墨烯杂化气凝胶(BN/GA), 可用作高效的双效氧电催化剂。BN/GA不仅表现出与商业Pt/C相似的氧化还原反应活性, 而且与商用Pt/C相比, 还具有更优异的稳定性和甲醇耐受性。同时, BN/GA表现出的析氧反应活性使其有望作为锌-空气电池装置的阴极。
2.3 污水净化
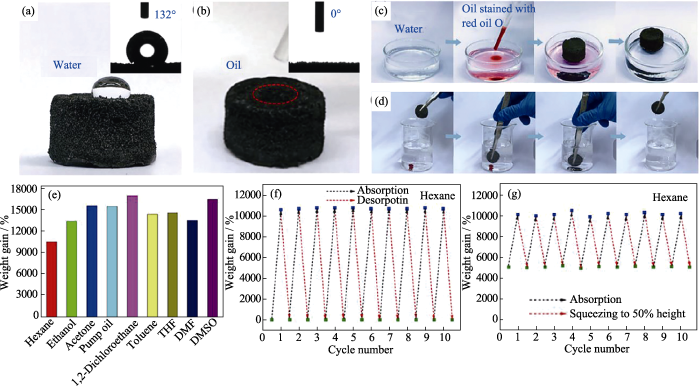
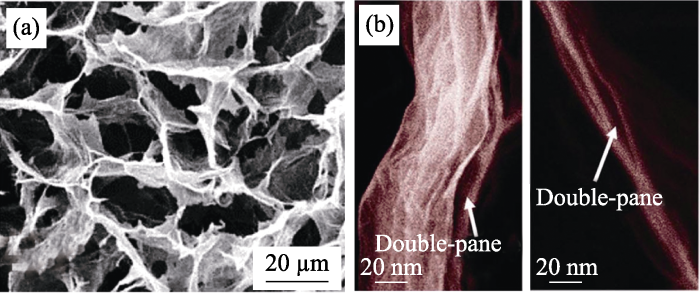
研究表明, 吸附效率与吸附剂的孔径尺寸、孔隙率和比表面积密切相关[58]。BN气凝胶中微小而均匀分布的孔隙不仅赋予BN气凝胶超高的比表面积, 使吸附位点充分暴露, 而且有效减小了被吸附物由气凝胶表面进入内部的阻力, 更有利于吸附过程的持续进行。此外, BN气凝胶良好的疏水亲油性保证了吸附水中有机溶剂的能力, 并呈现出经济和高效的特点。Li等[59]制备的rGO/BN气凝胶不仅具有卓越的机械性能还具有优异的疏水吸油能力, 吸油量达到自身重量的170倍, 是用于污水净化的良好材料(图11)。Zhao等[60]和Pham等[61]制备的BN气凝胶也表现出优异的吸油能力, 分别可吸附自身重量的150倍和190倍的有机污染物。更重要的是, BN气凝胶具有良好的热稳定性和机械性能, 吸附了油污的BN气凝胶可以通过简单挤压和燃烧的 方式除去污染物, 从而实现低成本循环利用。Song等[62]采用CVD法制备出的BN气凝胶可在5 s之内吸收自身重量160倍的油, 饱和的BN气凝胶在空气中灼烧后可循环使用, 并且没有明显的性能下降。除此之外, BN气凝胶还可用于吸附污水中的重金属离子, Xue等[63]制备的气凝胶在水中对Cd2+的吸附能力达到561 mg·g-1。
图11
图11
(a~d) rGO/BN气凝胶的润湿行为和吸油能力, (e) rGO/BN气凝胶吸收不同有机液体的能力, (f) rGO/BN气凝胶反复吸收己烷并在热处理(85℃)下释放其蒸汽的循环曲线, (g) rGO/BN气凝胶在反复吸收-挤压下吸收己烷的循环曲线[59]
Fig. 11
(a-d) The Wetting behaviour and oil absorption capacity of rGO/BN sponge; (e) The ability of rGO/BN sponge to absorb different organic liquids; (f) The rGO/BN sponge repetitively absorbed hexane and released its vapour under heat treatment (85 ℃); (g) Recyclability of the rGO/BN sponge for absorption of hexane under absorption-squeezing cycles[59]
2.4 导热与隔热
BN与其他材料复合后, 由于自身的高热导率, 可大幅度提高复合材料的导热性能; 另外, 通过结构设计, BN气凝胶因独特的纳米多孔网络结构而具有高孔隙率、高比表面积、低密度及低热导率等性质, 也是一种理想的隔热材料。石墨烯气凝胶是一种很有潜力的导热材料, 但其高孔隙率、低密度和各向同性的结构阻碍了其热导率的进一步提高。An等[64]通过水热处理GO和BN纳米片的悬浮液, 制备出具有长程有序结构和中等密度的高度各向异性rGO/BN混合气凝胶(图12)。所得复合材料具有11.01 W·m-1·K-1的超高平面导热率, 相比于纯石墨烯气凝胶, 导热率提高了277%。另一方面, Xu等[26]采用多尺度结构化设计和石墨烯气凝胶模板, 合成了兼具良好机械和低热导率的层状双壁结构BN气凝胶(图13)。层状双壁结构将气凝胶分成微小的单元, 有效降低了空气对流, 小尺寸的晶粒和中空的双壁结构减少了固体传导, 大幅抑制了声子散射, 从而实现低于空气的超低热导率(0.02 W·m-1·K-1)。在高温热振测试中, 这类材料表现出优异的热稳定性, 机械强度损失不到1%。因此, 这种材料在航空航天隔热领域有广阔的发展前景。
图12
凭借自身优异的性能, BN气凝胶在其他重要领域也有很多潜在的应用。例如, 新兴的化学功能化方法为BN气凝胶未来的界面改性提供了良好的机会。可以将其他组分化学键合到BN气凝胶表面, 从而开发高效耐用的纳米催化剂或用于调整复合材料的带结构以改善光生空穴和电子分离。此外, 研究表明, BN纳米结构比碳材料具有更好的生物相容性和更低的细胞毒性[65,66]。Weng等[67]报道了一种简单的热取代方法, 制造出高羟基化水溶性BN气凝胶。这些羟基化的BN气凝胶具有生物相容性, 并且可以有效地加载抗癌药物(例如多柔比星, DOX)直至超过其自身重量三倍。加载在这种BN载体上相同或甚至更少的药物可表现出比游离药物更强的抑制LNCaP癌细胞活力的效力, 是一种良好的药物载体。
图13
3 结束语
BN气凝胶具有低密度、孔隙率高、高比表面积、良好的抗氧化性和化学稳定性等优异性能, 在气体吸附、催化、污水净化、导热/隔热等领域极具应用前景。但是相比于碳材料, 其在相关领域的研究还不够充分, 因此拓宽其应用领域是值得重视的课题。一个可能的方案就是通过化学修饰或掺杂改变BN的组分, 进而调控其性质, 但BN的高化学惰性阻碍了对其进行后处理和改性。迄今为止, 已经建立了各种用于BN功能化的后合成方法, 然而, 这些策略的范围和效率仍然很少令人满意。另外, 如何精准控制BN气凝胶的孔结构, 包括孔径尺寸和孔隙率, 仍然是一个挑战。除了发展合成方法, 设计精确的分析技术表征BN纳米结构也是至关重要的。例如, 尖端的高分辨率透射电子显微镜是一种在空间和化学上解析单个原子的有力工具, 这项技术会为BN功能化研究提供有价值的信息, 比如精确测定BN表面的功能化位置, 形成的键的几何形状和性质等。然而, 这个技术仍然具有挑战性, 因为B、C和N原子通常在显微成像下显示出接近的原子尺寸和对比度, 难以直接分辨。
考虑到上述限制, 研究人员应该着力于开发更有效和经济的BN气凝胶合成和功能化策略, 使其满足未来高性能生物、热防护、电化学等装置的应用需求。我们相信, 随着研究的深入, BN气凝胶将呈现出更为广阔的应用前景。
参考文献
Progress in preparation and application of boron nitride nanosheets
Summarization about the peculiarities of cBN
Synthesis and structure transformation of wBN under HPHT
The Morphology, synthesis, properties, and applications of graphene-like two-dimensional h-BN nanomaterials
Nano boron nitride flatland
Advances in 2D boron nitride nanostructures: nanosheets, nanoribbons, nanosheets, and hybrids with graphene
The recent surge in graphene research has stimulated interest in the investigation of various 2-dimensional (2D) nanomaterials. Among these materials, the 2D boron nitride (BN) nanostructures are in a unique position. This is because they are the isoelectric analogs to graphene structures and share very similar structural characteristics and many physical properties except for the large band gap. The main forms of the 2D BN nanostructures include nanosheets (BNNSs), nanoribbons (BNNRs), and nanomeshes (BNNMs). BNNRs are essentially BNNSs with narrow widths in which the edge effects become significant; BNNMs are also variations of BNNSs, which are supported on certain metal substrates where strong interactions and the lattice mismatch between the substrate and the nanosheet result in periodic shallow regions on the nanosheet surface. Recently, the hybrids of 2D BN nanostructures with graphene, in the form of either in-plane hybrids or inter-plane heterolayers, have also drawn much attention. In particular, the BNNS-graphene heterolayer architectures are finding important electronic applications as BNNSs may serve as excellent dielectric substrates or separation layers for graphene electronic devices. In this article, we first discuss the structural basics, spectroscopic signatures, and physical properties of the 2D BN nanostructures. Then, various top-down and bottom-up preparation methodologies are reviewed in detail. Several sections are dedicated to the preparation of BNNRs, BNNMs, and BNNS-graphene hybrids, respectively. Following some more discussions on the applications of these unique materials, the article is concluded with a summary and perspectives of this exciting new field.
Large-scale fabrication of boron nitride nanosheets and their utilization in polymeric composites with improved thermal and mechanical properties.
Oxidation of a two-dimensional hexagonal boron nitride monolayer: a first-principles study.
Two-dimensional (2D) hexagonal boron-nitride oxide (h-BNO) is a structural analogue of graphene oxide. Motivated by recent experimental studies of graphene oxide, we have investigated the chemical oxidation of 2D h-BN sheet and the associated electronic properties of h-BNO. Particular emphasis has been placed on the most favorable site(s) for chemisorption of atomic oxygen, and on the migration barrier for an oxygen atom hopping to the top, bridge, or hollow site on the h-BN surface, as well as the most likely pathway for the dissociation of an oxygen molecule on the h-BN surface. We find that when an oxygen atom migrates on the h-BN surface, it is most likely to be over an N atom, but confined by three neighbor B atoms (forming a triangle ring). In general, chemisorption of an oxygen atom will stretch the B-N bond, and under certain conditions may even break the B-N bond. Depending on the initial location of the first chemisorbed O atom, subsequent oxidation tends to form an O domain or O chain on the h-BN sheet. The latter may lead to a synthetic strategy for the unzipping of the h-BN sheet along a zigzag direction. A better understanding of the oxidation of h-BN sheet has important implications for tailoring the properties of the h-BN sheet for applications.
Direct-bandgap properties and evidence for ultraviolet lasing of hexagonal boron nitride single crystal
The demand for compact ultraviolet laser devices is increasing, as they are essential in applications such as optical storage, photocatalysis, sterilization, ophthalmic surgery and nanosurgery. Many researchers are devoting considerable effort to finding materials with larger bandgaps than that of GaN. Here we show that hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) is a promising material for such laser devices because it has a direct bandgap in the ultraviolet region. We obtained a pure hBN single crystal under high-pressure and high-temperature conditions, which shows a dominant luminescence peak and a series of s-like exciton absorption bands around 215 nm, proving it to be a direct-bandgap material. Evidence for room-temperature ultraviolet lasing at 215 nm by accelerated electron excitation is provided by the enhancement and narrowing of the longitudinal mode, threshold behaviour of the excitation current dependence of the emission intensity, and a far-field pattern of the transverse mode.
Atomically thin boron nitride: unique properties and applications
Research and application progress of hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) based composite ceramics
Recent progress on fabrications and applications of boron nitride nanomaterials: a review
Aerogels-airy materials: chemistry, structure, and properties
Research progress of polyurethane based aerogel insulation materials
Direct-bandgap properties and evidence for ultraviolet lasing of hexagonal boron nitride single crystal
The demand for compact ultraviolet laser devices is increasing, as they are essential in applications such as optical storage, photocatalysis, sterilization, ophthalmic surgery and nanosurgery. Many researchers are devoting considerable effort to finding materials with larger bandgaps than that of GaN. Here we show that hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) is a promising material for such laser devices because it has a direct bandgap in the ultraviolet region. We obtained a pure hBN single crystal under high-pressure and high-temperature conditions, which shows a dominant luminescence peak and a series of s-like exciton absorption bands around 215 nm, proving it to be a direct-bandgap material. Evidence for room-temperature ultraviolet lasing at 215 nm by accelerated electron excitation is provided by the enhancement and narrowing of the longitudinal mode, threshold behaviour of the excitation current dependence of the emission intensity, and a far-field pattern of the transverse mode.
Progress in catalysis of hexagonal boron nitride and boron nitride nanosheets
Preparation of nanomaterials employing template method
The progress of nanomaterials prepared in the presence of soft template
One-step template-free synthesis of highly porous boron nitride microsponges for hydrogen storage
Unusual metallic microporous boron nitride networks
Two metallic zeolite-like microporous BN crystals with all-sp(2) bonding networks are predicted from an unbiased structure search based on the particle-swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm in combination with first-principles density functional theory (DFT) calculations. The stabilities of both microporous structures are confirmed via the phonon spectrum analysis and Born-Oppenheimer molecular dynamics simulations with temperature control at 1000 K. The unusual metallicity for the microporous BN allotropes stems from the delocalized p electrons along the axial direction of the micropores. Both microporous BN structures entail large surface areas, ranging from 3200 to 3400 m(2)/g. Moreover, the microporous BN structures show a preference toward organic molecule adsorption (e.g., the computed adsorption energy for CH3CH2OH is much more negative than that of H2O). This preferential adsorption can be exploited for water cleaning, as demonstrated recently using porous boron BN nanosheets (Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1777).
Porous boron nitride with tunable pore size
On the basis of a global structural search and first-principles calculations, we predict two types of porous boron-nitride (BN) networks that can be built up with zigzag BN nanoribbons (BNNRs). The BNNRs are either directly connected with puckered B (N) atoms at the edge (type I) or connected with sp(3)-bonded BN chains (type II). Besides mechanical stability, these materials are predicted to be thermally stable at 1000 K. The porous BN materials entail large surface areas, ranging from 2800 to 4800 m(2)/g. In particular, type-II BN material with relatively large pores is highly favorable for hydrogen storage because the computed hydrogen adsorption energy (-0.18 eV) is very close to the optimal adsorption energy (-0.15 eV) suggested for reversible hydrogen storage at room temperature. Moreover, the type-II materials are semiconductors with width-dependent direct bandgaps, rendering the type-II BN materials promising not only for hydrogen storage but also for optoelectronic and photonic applications.
Activated boron nitride derived from activated carbon
Mesoporous boron nitride and boron- nitride-carbon materials from mesoporous silica templates
Double-negative-index ceramic aerogels for thermal superinsulation
Ceramic aerogels are attractive for thermal insulation but plagued by poor mechanical stability and degradation under thermal shock. In this study, we designed and synthesized hyperbolic architectured ceramic aerogels with nanolayered double-pane walls with a negative Poisson's ratio (-0.25) and a negative linear thermal expansion coefficient (-1.8 x 10(-6) per degrees C). Our aerogels display robust mechanical and thermal stability and feature ultralow densities down to ~0.1 milligram per cubic centimeter, superelasticity up to 95%, and near-zero strength loss after sharp thermal shocks (275 degrees C per second) or intense thermal stress at 1400 degrees C, as well as ultralow thermal conductivity in vacuum [~2.4 milliwatts per meter-kelvin (mW/m.K)] and in air (~20 mW/m.K). This robust material system is ideal for thermal superinsulation under extreme conditions, such as those encountered by spacecraft.
Hyperbolically patterned 3D graphene metamaterial with negative poisson ratio and superelasticity
.A hyperbolically patterned 3D graphene metamaterial (GM) with negative Poisson's ratio and superelasticity is highlighted. It is synthesized by a modified hydrothermal approach and subsequent oriented freeze-casting strategy. GM presents a tunable Poisson's ratio by adjusting the structural porosity, macroscopic aspect ratio (L/D), and freeze-casting conditions. Such a GM suggests promising applications as soft actuators, sensors, robust shock absorbers, and environmental remediation.
A topologically substituted boron nitride hybrid aerogel for highly selective CO2 uptake
Ultralight three-dimensional boron nitride foam with ultralow perm ittivity and superelasticity
Dielectrics with ultralow permittivity within 2 times that of air, excellent mechanical performance, and high thermal stability are highly attractive to many applications. However, since the finding of silica aerogels in the 1930s, no alternative ultralight porous dielectric with density below 10 mg/cm(3) has been developed. Here we present three-dimensional hierarchical boron nitride foam with permittivity of 1.03 times that of air, density of 1.6 mg/cm(3), and thermal stability up to 1200 degrees C obtained by chemical vapor deposition on a nickel foam template. This BN foam exhibits complete recovery after cyclic compression exceeding 70% with permittivity within 1.12 times that of air. Gathering all these exceptional characters, the BN foam should create a breakthrough development of flexible ultralow-permittivity dielectrics and ultralight materials.
Novel monolith-type boron nitride hierarchical foams obtained through integrative chemistry
A novel class of monolith-type boron nitride hierarchical foams has been prepared through an integrative chemistry-based synthetic path. These materials contain interconnected pores in the nanometre to the micrometre range with high porosity (similar to 75 vol%), a specific surface area up to 300 m(2) g(-1) and a resistance toward mechanical stress making them suitable for innovative applications.
Preparation of graphene aerogels with soft templates and their oil adsorption mechanism from water
Rational design of mesoporous metals and related nanomaterials by a soft-template approach
Facile sodium alginate assisted assembly of Ni/Al layered double hydroxide nanostructures
The progress of nanomaterials prepared in the presence of soft template
Nanostructured and architectured boron nitride from boron, nitrogen and hydrogen-containing molecular and polymeric precursors
The controlled synthesis of boron nitride at the nanoscale with predefined and uniform nanostructures and architectures is in general a big challenge, and making full use of these materials in applications still requires great effort. In this article, recent progress on the synthesis of nanostructured and architectured boron nitride involving molecular and polymeric precursors which contain only boron, nitrogen and hydrogen are reviewed. The potential applications of these materials with controlled porosity and/or dimensions controlled at the nanoscale as zero, one, two and three dimensional materials are discussed. Finally, future prospects for boron nitride in terms of synthesis and applications are considered.
Self-assembly of an organic-inorganic block copolymer for nano-ordered ceramics
Self-assembly low dimensional inorganic/organic heterojunction nanomaterials
Supramolecular materials via block copolymer self-assembly
Assembling nano and macrostructures and the supramolecular liquid crystal
A facile route for 3D aerogels from nanostructured 1D and 2D materials
Boron nitride aerogels with super-flexibility ranging from liquid nitrogen temperature to 1000 ℃
Artificially stacked atomic layers: toward new van der waals solids
Strong in-plane bonding and weak van der Waals interplanar interactions characterize a large number of layered materials, as epitomized by graphite. The advent of graphene (G), individual layers from graphite, and atomic layers isolated from a few other van der Waals bonded layered compounds has enabled the ability to pick, place, and stack atomic layers of arbitrary compositions and build unique layered materials, which would be otherwise impossible to synthesize via other known techniques. Here we demonstrate this concept for solids consisting of randomly stacked layers of graphene and hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN). Dispersions of exfoliated h-BN layers and graphene have been prepared by liquid phase exfoliation methods and mixed, in various concentrations, to create artificially stacked h-BN/G solids. These van der Waals stacked hybrid solid materials show interesting electrical, mechanical, and optical properties distinctly different from their starting parent layers. From extensive first principle calculations we identify (i) a novel approach to control the dipole at the h-BN/G interface by properly sandwiching or sliding layers of h-BN and graphene, and (ii) a way to inject carriers in graphene upon UV excitations of the Frenkell-like excitons of the h-BN layer(s). Our combined approach could be used to create artificial materials, made predominantly from inter planar van der Waals stacking of robust bond saturated atomic layers of different solids with vastly different properties.
Multifunctional and highly compressive cross-linker-free sponge based on reduced graphene oxide and boron nitride nanosheets
Graphene analogues of BN: novel synthesis and properties
Enthused by the fascinating properties of graphene, we have prepared graphene analogues of BN by a chemical method with a control on the number of layers. The method involves the reaction of boric acid with urea, wherein the relative proportions of the two have been varied over a wide range. Synthesis with a high proportion of urea yields a product with a majority of 1-4 layers. The surface area of BN increases progressively with the decreasing number of layers, and the high surface area BN exhibits high CO(2) adsorption, but negligible H(2) adsorption. Few-layer BN has been solubilized by interaction with Lewis bases. We have used first-principles simulations to determine structure, phonon dispersion, and elastic properties of BN with planar honeycomb lattice-based n-layer forms. We find that the mechanical stability of BN with respect to out-of-plane deformation is quite different from that of graphene, as evident in the dispersion of their flexural modes. BN is softer than graphene and exhibits signatures of long-range ionic interactions in its optical phonons. Finally, structures with different stacking sequences of BN have comparable energies, suggesting relative abundance of slip faults, stacking faults, and structural inhomogeneities in multilayer BN.
Low-temperature synthesis of meshy boron nitride with a large surface area
Simple synthesis of mesoporous boron nitride with strong cathodoluminescence emission
Mesoporous BN was prepared at 550 degrees C for 10 h or so via a simple reaction between NaBH4 and CO(NH2)(2). X-ray diffraction demonstrates the formation of t-BN with lattice constants a=2.46 and c=6.67 angstrom. High-resolution transmission electron microscopy displays a lot of porous films in the product, which possesses a high surface area of 219 m(2) g(-1) and a pore size primarily around 3.8 nm tested by nitrogen adsorption-desorption method. The mesoporous BN exhibits a strong luminescence emission around 3.41 eV in the cathodoluminescence spectra, a high stability in both morphology and structure, and good oxidation resistance up to 800 degrees C. The byproducts generated during the reaction are responsible for the formation of the mesoporous BN. (C) 2011 Elsevier Inc.
High yield synthesis of novel boron nitride submicro-boxes and their photocatalytic application under visible light irradiation
Porous boron nitride nanosheets for effective water cleaning
Mechanically robust honeycomb graphene aerogel multifunctional polymer composites
Mussel-inspired, ultralight, multifunctional 3D nitrogen-doped graphene aerogel
Hydrogen adsorption on boron nitride nanotubes: a path to room temperature hydrogen storage
Gas sensors: platinum nanoparticle loading of boron nitride aerogel and its use as a novel material for low-power catalytic gas sensing
Synthesis and characterization of boron nitride sponges as a noveI support for metal nanoparticles
Micrometric BN powders used as catalyst support: influence of the precursor on the properties of the BN ceramic
Three-dimensional boron- and nitrogen-codoped graphene aerogel supported pt nanoparticles as highly active electrocatalysts for methanol oxidation reaction
Design of BN porous sheets with richly exposed (002) plane edges and their application as TiO2 visible light sensitizer
Three-dimensional boron- and nitrogen-codoped graphene aerogel supported Pt nanoparticles as highly active electrocatalysts for methanol oxidation reaction
Template-free synthesis of functional 3D BN architecture for removal of dyes from water
Three-dimensional (3D) architectures are of interest in applications in electronics, catalysis devices, sensors and adsorption materials. However, it is still a challenge to fabricate 3D BN architectures by a simple method. Here, we report the direct synthesis of 3D BN architectures by a simple thermal treatment process. A 3D BN architecture consists of an interconnected flexible network of nanosheets. The typical nitrogen adsorption/desorption results demonstrate that the specific surface area for the as-prepared samples is up to 1156 m(2) g(-1), and the total pore volume is about 1.17 cm(3) g(-1). The 3D BN architecture displays very high adsorption rates and large capacities for organic dyes in water without any other additives due to its low densities, high resistance to oxidation, good chemical inertness and high surface area. Importantly, 88% of the starting adsorption capacity is maintained after 15 cycles. These results indicate that the 3D BN architecture is potential environmental materials for water purification and treatment.
Multifunctional and highly compressive cross-linker-free sponge based on reduced graphene oxide and boron nitride nanosheets
3D graphene foam scavengers: vesicant-assisted foaming boosts the gram-level yield and forms hierarchical pores for super-strong pollutant removal applications
Nanoscale structure and superhydrophobicity of sp 2-bonded boron nitride aerogels
Aerogels have much potential in both research and industrial applications due to their high surface area, low density, and fine pore size distribution. Here we report a thorough structural study of three-dimensional aerogels composed of highly crystalline sp(2)-bonded boron nitride (BN) layers synthesized by a carbothermic reduction process. The structure, crystallinity and bonding of the as-prepared BN aerogels are elucidated by X-ray diffraction, (11)B nuclear magnetic resonance, transmission electron microscopy, and resonant soft X-ray scattering. The macroscopic roughness of the aerogel's surface causes it to be superhydrophobic with a contact angle of approximately 155 degrees and exhibit high oil uptake capacity (up to 1500 wt%). The oil can be removed from the BN aerogel by oxidizing in air without damaging the crystalline porous structure of the aerogel or diminishing its oil absorption capacity.
Ultralight boron nitride aerogels via template-assisted chemical vapor deposition
Boron nitride (BN) aerogels are porous materials with a continuous three-dimensional network structure. They are attracting increasing attention for a wide range of applications. Here, we report the template-assisted synthesis of BN aerogels by catalyst-free, low-pressure chemical vapor deposition on graphene-carbon nanotube composite aerogels using borazine as the B and N sources with a relatively low temperature of 900 ( degrees )C. The three-dimensional structure of the BN aerogels was achieved through the structural design of carbon aerogel templates. The BN aerogels have an ultrahigh specific surface area, ultralow density, excellent oil absorbing ability, and high temperature oxidation resistance. The specific surface area of BN aerogels can reach up to 1051 m(2) g(-1), 2-3 times larger than the reported BN aerogels. The mass density can be as low as 0.6 mg cm(-3), much lower than that of air. The BN aerogels exhibit high hydrophobic properties and can absorb up to 160 times their weight in oil. This is much higher than porous BN nanosheets reported previously. The BN aerogels can be restored for reuse after oil absorption simply by burning them in air. This is because of their high temperature oxidation resistance and suggests broad utility as water treatment tools.
Template-free synthesis of boron nitride foam-like porous monoliths and their high-end applications in water purification
Highly anisotropic graphene/boron nitride hybrid aerogels with long-range ordered architecture and moderate density for highly thermally conductive composites
Preparation of ultrathin hexagonal boron nitride nanoplates for cancer cell imaging and neurotransmitter sensing
A facile and convenient process was optimized for preparing water-soluble hydroxyl-functionalized hexagonal boron nitride (hBN-OH) from hBN. The hBN-OH (2-3 nm thickness) contains approximately 40% oxygen and exhibits blue emission with a quantum yield of approximately 36%. The hBN-OH could be used for imaging cells and for the in vitro detection of biomolecules through electrochemical analysis.
Hexagonal boron nitride nanomaterials: advances towards bio-applications
Hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) nanotubes and nanosheets are isoelectronic and structural analogues to graphitic carbon nanoforms. These h-BN nanomaterials possess ultimate physical, chemical and mechanical properties, which enable them to be promising in diverse applications. This article presents an overview of recent advances in the manipulation of h-BN nanomaterials, including their representative production techniques and significant functionalization schemes with various organic molecules and biospecies. Furthermore, the demonstrative in vitro applications of h-BN nanomaterials in biosubstance delivery, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) agents, biosensor and tissue engineering as well as their biocompatibility issues are also discussed.