

高频低损耗的Fe/亚微米FeNi软磁复合材料
收稿日期: 2023-12-29
修回日期: 2024-03-20
网络出版日期: 2024-04-15
基金资助
新型电子元器件关键材料与工艺国家重点实验室开放基金(Fenghua-2024-0064)
Fe/Submicron FeNi Soft Magnetic Composites with High Working Frequency and Low Loss
Received date: 2023-12-29
Revised date: 2024-03-20
Online published: 2024-04-15
Supported by
Open Fund of State Key Laboratory of Key Materials and Technologies for New Electronic Components(Fenghua-2024-0064)
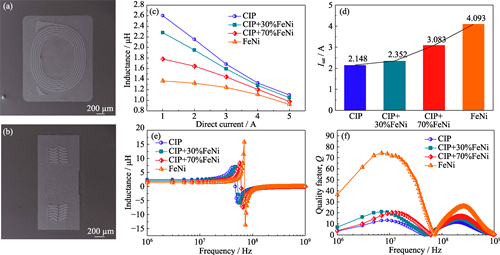
高功率电力电子设备的应用对功率电感的高频电感性能和能量效率提出了更高的要求,迫切需要开发高频低损耗的软磁材料。为降低软磁复合材料的涡流损耗, 获得高频低损耗、大功率的一体成型电感, 通过等离子体炬制备了高纯度亚微米FeNi颗粒, 并采用简化的有限元模型探讨了亚微米FeNi颗粒对软磁复合材料涡流损耗的影响。本工作制备了含不同质量分数亚微米FeNi颗粒的Fe/亚微米FeNi软磁复合材料, 重点讨论了亚微米FeNi颗粒对软磁复合材料及一体成型电感性能的影响。结果表明: 与纯羰基铁粉制备的软磁复合材料相比, 当亚微米FeNi颗粒质量分数为30%时, 环形磁芯代表损耗的磁导率虚部µ″由1.57降至1.36, 降低了13.4%; 一体成型电感在10 MHz条件下的品质因数Q由13升至20, 提高了53.8%, 并且自谐振频率提高了12.7%, 饱和电流由2.148 A升至2.352 A。通过提高材料内阻和减小涡流流动区域的尺寸, 亚微米FeNi颗粒能有效降低涡流损耗, 提高软磁复合材料的高频磁导率稳定性。复合亚微米FeNi颗粒有望低成本、大规模地获得高频低损耗、综合性能良好的一体成型电感。
何思哲 , 王俊舟 , 张勇 , 费嘉维 , 吴爱民 , 陈意峰 , 李强 , 周晟 , 黄昊 . 高频低损耗的Fe/亚微米FeNi软磁复合材料[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024 , 39(8) : 871 -878 . DOI: 10.15541/jim20230599
Application of high-power electronic equipment requires inductors with greater high-frequency performance and higher energy efficiency than ever, and thus it is urgent to develop new soft magnetic composites to meet these requirements. To reduce the eddy current loss of soft magnetic composites and obtain molded inductors with high working frequency, low loss and high power, high purity submicron FeNi particles were prepared by plasma torch, and effect of these particles on eddy current loss of soft magnetic composites was examined by simplified finite element model. Soft magnetic composites and molded inductors were prepared by mixing carbonyl iron powder and submicron FeNi particles with different mass fractions. The influence of submicron FeNi particles on the properties of soft magnetic composites and molded inductors is analyzed emphatically. With 30% of mass fraction of submicron FeNi particles, the imaginary part of permeability (μ") of the ring core decreases from 1.57 to 1.36 (reduced by 13.4%), compared with that of the soft magnetic composite made by only pure carbonyl iron powder. The quality factor Q of the molded inductors at 10 MHz increases from 13 to 20 (increased by 53.8%), while the self-resonance frequency increases by 12.7% and the saturation current increases from 2.148 A to 2.352 A. Submicron FeNi particles can effectively reduce eddy current loss and improve stability of the high frequency permeability of soft magnetic composites by increasing the internal resistance of materials and reducing the size of eddy current flow region. Therefore, this study demonstrates that compounding submicron FeNi particles is a promising method to obtain molded inductors with high frequency, low loss, and good comprehensive performance at low cost on a large scale.

| [1] | SHOKROLLAHI H, JANGHORBAN K. Soft magnetic composite materials (SMCs). Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2007, 189(1/2/3): 1. |
| [2] | PéRIGO E A, WEIDENFELLER B, KOLLáR P, et al. Past, present, and future of soft magnetic composites. Applied Physics Reviews, 2018, 5(3): 031301. |
| [3] | SILVEYRA J M, FERRARA E, HUBER D L, et al. Soft magnetic materials for a sustainable and electrified world. Science, 2018, 362(6413): eaao0195. |
| [4] | LEARY A M, OHODNICKI P R, MCHENRY M E. Soft magnetic materials in high-frequency, high-power conversion applications. JOM, 2012, 64(7): 772. |
| [5] | 吴深, 李杰超, 管英杰, 等. 软磁复合材料制备工艺的研究进展. 电子元件与材料, 2022, 41(3): 221. |
| [6] | ZHAO R L, HUANG J J, YANG Y, et al. The influence of FeNi nanoparticles on the microstructures and soft magnetic properties of FeSi soft magnetic composites. Advanced Powder Technology, 2022, 33(8): 103663. |
| [7] | LIU J Q, DONG Y N, WANG P, et al. Improved high-frequency magnetic properties of FeSiBCCr amorphous soft magnetic composites by adding carbonyl iron powders. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2023, 605: 122166. |
| [8] | 池强, 谢磊, 常良, 等. 羰基铁粉/FeSiBCCr复合非晶磁粉芯的性能. 材料导报, 2021, 35(10): 10023. |
| [9] | ZHANG Y, CHI Q, CHANG L, et al. Novel Fe-based amorphous compound powder cores with enhanced DC bias performance by adding FeCo alloy powder. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2020, 507: 166840. |
| [10] | 汪洋. 大功率新型一体成型电感器设计及应用前景分析. 电子元器件与信息技术, 2020, 4(1): 1. |
| [11] | 黄家毅, 唐建伟, 龚志良, 等. 大功率金属粉芯模压电感设计与验证. 电子元器件与信息技术, 2022, 6(11): 43. |
| [12] | SUGIMURA K, MIYAJIMA Y, SONEHARA M, et al. Formation of high electrical-resistivity thin surface layer on carbonyl-iron powder (CIP) and thermal stability of nanocrystalline structure and vortex magnetic structure of CIP. AIP Advances, 2016, 6(5): 055932. |
| [13] | JIN X W, LI T, JIA Z L, et al. Over 100 MHz cut-off frequency mechanism of Fe-Si soft magnetic composites. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2022, 556: 169366. |
| [14] | YIN L F, WEI D H, LEI N, et al. Magnetocrystalline anisotropy in permalloy revisited. Physical Review Letters, 2006, 97(6): 067203. |
| [15] | ZHANG H, WANG K, HUANG Y D, et al. The excess loss analysis of an easy-plane FeSiAl@SiO2 soft magnetic composite with high permeability. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2023, 588: 171471. |
| [16] | KOLLáR P, BIR?áKOVá Z, FüZER J, et al. Power loss separation in Fe-based composite materials. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2013, 327: 146. |
| [17] | GANGOPADHYAY S, HADJIPANAYIS G C, DALE B, et al. Magnetic properties of ultrafine iron particles. Physical Review B, 1992, 45(17): 9778. |
| [18] | LIU D H, LIU X, WANG J, et al. The influence of Fe nanoparticles on microstructure and magnetic properties of Fe-6.5wt%Si soft magnetic composites. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 835: 155215. |
| [19] | REN X T, CORCOLLE R, DANIEL L. A 2D finite element study on the role of material properties on eddy current losses in soft magnetic composites. The European Physical Journal Applied Physics, 2016, 73(2): 20902. |
| [20] | KIM E S, HAFTLANG F, AHN S Y, et al. Effects of processing parameters and heat treatment on the microstructure and magnetic properties of the in-situ synthesized Fe-Ni permalloy produced using direct energy deposition. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 907: 164415. |
| [21] | WU L Z, DING J, JIANG H B, et al. High frequency complex permeability of iron particles in a nonmagnetic matrix. Journal of Applied Physics, 2006, 99(8): 83905. |
| [22] | ANHALT M. Systematic investigation of particle size dependence of magnetic properties in soft magnetic composites. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2008, 320(14): e366. |
| [23] | BERTOTTI G. General properties of power losses in soft ferromagnetic materials. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 1988, 24(1): 621. |
| [24] | WANG J H, SONG S Q, SUN H B, et al. Insulation layer design for soft magnetic composites by synthetically comparing their magnetic properties and coating process parameters. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2021, 519: 167496. |
| [25] | HUAN L, TANG X L, SU H, et al. Effects of SnO2 on DC-bias superposition characteristic of the low-temperature-fired NiCuZn ferrites. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2014, 50(11): 2006104. |
| [26] | 龚志良, 黄家毅, 舒恺, 等. 各类高频电感电气参数及其电路应用的论述和探讨. 电子元器件与信息技术, 2022, 6(8): 69. |
| [27] | HE J, YUAN H, NIE M, et al. Soft magnetic materials for power inductors: state of art and future development. Materials Today Electronics, 2023, 6: 100066. |
| [28] | LI T, WANG Y, SHI H G, et al. Impact of skin effect on permeability of permalloy films. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2022, 545: 168750. |
| [29] | BARTOLI M, REATTI A, KAZIMIERCZUK M K. Modelling Iron-powder Inductors at High Frequencies. Denver:Proceedings of 1994 IEEE Industry Applications Society Annual Meeting, 1994. |
| [30] | HUANG Y D, ZHANG H, SHANG R X, et al. Improved magnetic properties in amorphous FeSiBCr soft magnetic composites with easy-plane anisotropy for high-frequency applications. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2023, 56(6): 065004. |
| [31] | HSU Y, FONTANA R, WILLIAMS M, et al. High frequency high field permeability of patterned Ni80Fe20 and Ni45Fe55 thin films. Journal of Applied Physics, 2001, 89(11): 6808. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |