

多功能MXene油墨:面向印刷能源及电子器件的新视角
收稿日期: 2023-09-24
修回日期: 2023-10-15
网络出版日期: 2023-11-10
基金资助
国家自然科学基金(22209118);国家自然科学基金(00301054A1073);国家自然科学基金(20826044D3083);国家自然科学基金(20822041G4080);国家自然科学基金(1082204112A26)
MXene Multifunctional Inks: a New Perspective toward Printable Energy-related Electronic Devices
Received date: 2023-09-24
Revised date: 2023-10-15
Online published: 2023-11-10
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(22209118);National Natural Science Foundation of China(00301054A1073);National Natural Science Foundation of China(20826044D3083);National Natural Science Foundation of China(20822041G4080);National Natural Science Foundation of China(1082204112A26)
基于功能油墨的先进印刷技术(打印、涂布), 能够突破传统制造手段的瓶颈, 实现具有复杂结构和特定功能的个性化薄膜及电子器件的快速成型, 在可穿戴智能识别、能源存储、电磁屏蔽及吸波、触摸显示等领域展现出巨大的应用前景。印刷先进能源及电子器件的关键在于, 开发先进功能油墨材料和与之相匹配的先进印刷技术。2011年发现的MXene材料, 是一类由过渡金属碳化物、氮化物或碳氮化物所组成的二维大家族的总称, 因其卓越的物理和化学性质(如高电导率、出色的亲水性和丰富的表面化学)而受到广泛关注, 特别适合作为印刷电子器件的油墨材料。探索MXene油墨的印刷行为特征并厘清MXene油墨在印刷关键环节中的机理, 不仅有助于获得高精度的MXene油墨印刷图案, 而且可以为印刷多尺度、多材料的多功能薄膜和电子器件打下了坚实基础。本文首先介绍了MXene的制备及其片层胶体的化学稳定性, 并对其流变学特性、可打印油墨的形成、油墨印刷行为以及与之适配的打印方法进行了讨论, 着眼于MXene油墨在能源、健康监测和传感应用方面的最新进展, 分析了该领域面临的挑战和未来的发展方向, 为该领域的研究者提供新的视角和启示。
邓顺桂 , 张传芳 . 多功能MXene油墨:面向印刷能源及电子器件的新视角[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024 , 39(2) : 195 -203 . DOI: 10.15541/jim20230437
Advanced ink printing techniques, such as printing and coating, have overcome the limitations of traditional manufacturing methods, allowing for rapid prototyping of films and electronic devices with sophisticated structures and specific functions. These techniques hold enormous potential in wearable smart identification, energy storage, electromagnetic shielding and absorption, touch display, and so on. The key to printing advanced energy and electronic devices lies in the development of cutting-edge functional inks and their corresponding printing technologies. MXene, a family of two-dimensional compounds composed of transition metal carbides, nitrides, or carbonitrides, was discovered in 2011. MXene exhibits remarkable physical and chemical properties, including high conductivity, pronounced hydrophilicity, and diverse surface chemistry, which has garnered significant attention within the research community and made it particularly suitable as inks in printing applications. Conducting research on the printing behavior and mechanisms of MXene inks is crucial not only for achieving high-precision patterns but also for establishing a solid foundation for manufacturing techniques that can precisely create multiscale, multimaterial and multifunctional films, and electronic devices. This article begins with a brief discussion of MXene flakes’ synthesis and colloidal stability, followed by a detailed examination of its rheological characteristics, printable ink formulation, and printing methods. Additional, special attention is given to the latest advances of MXene ink in energy, health, and sensing applications. The perspective concludes with a summary of current research challenges and future directions in this area, offering new perspectives and insights for researchers.

Key words: printing; functional ink; MXene; additive manufacturing; health monitoring; perspective
| [1] | LI N, PENG J H, ONG W J, et al. Mxenes: an emerging platform for wearable electronics and looking beyond. Matter, 2021, 4(2): 377. |
| [2] | ABDOLHOSSEINZADEH S, ZHANG C F, SCHNEIDER R, et al. A universal approach for room-temperature printing and coating of 2d materials. Advanced Materials, 2022, 34(4): 2103660. |
| [3] | CAI X K, LUO Y T, LIU B, et al. Preparation of 2d material dispersions and their applications. Chemical Society Reviews, 2018, 47(16): 6224. |
| [4] | TORRISI F, HASAN T, WU W P, et al. Inkjet-printed graphene electronics. ACS Nano, 2012, 6 (4): 2992. |
| [5] | ZHANG Y Z, WANG Y, CHENG T, et al. Printed supercapacitors: Materials, printing and applications. Chemical Society Reviews, 2019, 48(12): 3229. |
| [6] | SECOR E B, AHN B Y, GAO T Z, et al. Rapid and versatile photonic annealing of graphene inks for flexible printed electronics. Advanced Materials, 2015, 27(42): 6683. |
| [7] | LI J T, NAIINI M M, VAZIRI S, et al. Inkjet printing of MoS2. Advanced Functional Materials, 2014, 24(41): 6524. |
| [8] | JUN H Y, RYU S O, KIM S H, et al. Inkjet printing of few-layer enriched black phosphorus nanosheets for electronic devices. Advanced Electronic Materials, 2021, 7(10): 2100577. |
| [9] | UZUN S, SCHELLING M, HANTANASIRISAKUL K, et al. Additive-free aqueous mxene inks for thermal inkjet printing on textiles. Small, 2021, 17(1): 2006376. |
| [10] | WANG Z, LIANG X W, ZHAO T, et al. Facile synthesis of monodisperse silver nanoparticles for screen printing conductive inks. Journal of Materials Science-Materials in Electronics, 2017, 28(22): 16939. |
| [11] | LIU F X, QIU X B, XU J F, et al. High conductivity and transparency of graphene-based conductive ink: prepared from a multi-component synergistic stabilization method. Progress in Organic Coatings, 2019, 133: 125. |
| [12] | LI X K, LI M J, ZONG L, et al. Liquid metal droplets wrapped with polysaccharide microgel as biocompatible aqueous ink for flexible conductive devices. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018, 28(39): 1804197. |
| [13] | ZHAO L H, HONG C Y, WANG C H, et al. Enhancement of the adhesion strength of water-based ink binder based on waterborne polyurethane. Progress in Organic Coatings, 2023, 183: 107765. |
| [14] | AGHAYAR Z, MALAKI M, ZHANG Y Z. MXene-based ink design for printed applications. Nanomaterials, 2022, 12 (23): 4346. |
| [15] | ZHANG C F. Interfacial assembly of two-dimensional MXenes. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2021, 60: 417. |
| [16] | NAGUIB M, MASHTALIR O, CARLE J, et al. Two-dimensional transition metal carbides. ACS Nano, 2012, 6(2): 1322. |
| [17] | COME J, NAGUIB M, ROZIER P, et al. A non-aqueous asymmetric cell with a Ti2C-based two-dimensional negative electrode. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2012, 159(8): 1368. |
| [18] | ZHANG C, MA Y L, ZHANG X T, et al. Two-dimensional transition metal carbides and nitrides (MXenes): synthesis, properties, and electrochemical energy storage applications. Energy & Environmental Materials, 2020, 3(1): 29. |
| [19] | ABDOLHOSSEINZADEH S, JIANG X T, ZHANG H, et al. Perspectives on solution processing of two-dimensional MXenes. Materials Today, 2021, 48: 214. |
| [20] | ZHANG Y Z, WANG Y, JIANG Q, et al. Mxene printing and patterned coating for device applications. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(21): 1908486. |
| [21] | ALHABEB M, MALESKI K, ANASORI B, et al. Guidelines for synthesis and processing of two-dimensional titanium carbide (Ti3C2Tx MXene). Chemistry of Materials, 2017, 29(18): 7633. |
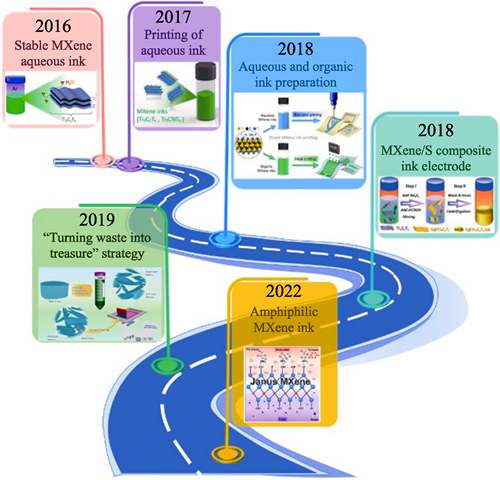
| [22] | ABDOLHOSSEINZADEH S, HEIER J, ZHANG C F. Printing and coating mxenes for electrochemical energy storage devices. Journal of Physics-Energy, 2020, 2(3): 031004. |
| [23] | SREENILAYAM S P, UL AHAD I, NICOLOSI V, et al. MXene materials based printed flexible devices for healthcare, biomedical and energy storage applications. Materials Today, 2021, 43: 99. |
| [24] | NAGUIB M, KURTOGLU M, PRESSER V, et al. Two- dimensional nanocrystals produced by exfoliation of Ti3AlC2. Advanced Materials, 2011, 23(37): 4248. |
| [25] | GHIDIU M, LUKATSKAYA M R, ZHAO M Q, et al. Conductive two-dimensional titanium carbide 'clay' with high volumetric capacitance. Nature, 2014, 516(7529): 78. |
| [26] | URBANKOWSKI P, ANASORI B, MAKARYAN T, et al. Synthesis of two-dimensional titanium nitride Ti4N3 (MXene). Nanoscale, 2016, 8(22): 11385. |
| [27] | LI T F, YAO L L, LIU Q L, et al. Fluorine-free synthesis of high- purity Ti3C2Tx (T=OH, O) via alkali treatment. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(21): 6115. |
| [28] | SHEN M, JIANG W Y, LIANG K, et al. One-pot green process to synthesize MXene with controllable surface terminations using molten salts. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(52): 27013. |
| [29] | ZHANG C F J, PINILLA S, MCEYOY N, et al. Oxidation stability of colloidal two-dimensional titanium carbides (MXenes). Chemistry of Materials, 2017, 29(11): 4848. |
| [30] | NATU V, HART J L, SOKOL M, et al. Edge capping of 2D-MXene sheets with polyanionic salts to mitigate oxidation in aqueous colloidal suspensions. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(36): 12655. |
| [31] | ZHAO X F, VASHISTH A, PREHN E, et al. Antioxidants unlock shelf-stable Ti3C2Tx (MXene) nanosheet dispersions. Matter, 2019, 1(2): 513. |
| [32] | FAN Z M, HE H Y, YU J X, et al. Binder-free Ti3C2Tx MXene doughs with high redispersibility. ACS Materials Letters, 2020, 2(12): 1598. |
| [33] | DENG S G, GUO T Z, NUEESCH F, et al. Stable MXene dough with ultrahigh solid fraction and excellent redispersibility toward efficient solution processing and industrialization. Advanced Science, 2023, 10(19): 2300660. |
| [34] | AKUZUM B, MALESKI K, ANASORI B, et al. Rheological characteristics of 2D titanium carbide (MXene) dispersions: a guide for processing mxenes. ACS Nano, 2018, 12 (3): 2685. |
| [35] | GLASSER A, CLOUTET é, HADZIIOANNOU G, et al. Tuning the rheology of conducting polymer inks for various deposition processes. Chemistry of Materials, 2019, 31(17): 6936. |
| [36] | LI H P, LIANG J J. Recent development of printed micro- supercapacitors: printable materials, printing technologies, and perspectives. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(3): 1805864. |
| [37] | ABDOLHOSSEINZADEH S, SCHNEIDER R, VERMA A, et al. Turning trash into treasure: additive free MXene sediment inks for screen-printed micro-supercapacitors. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(17): 2000716. |
| [38] | ZHANG C F, MCKEON L, KREMER M P, et al. Additive-free MXene inks and direct printing of micro-supercapacitors. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 1795. |
| [39] | ZHANG C F, KREMER M P, SERAL-ASCASO A, et al. Stamping of flexible, coplanar micro-supercapacitors using MXene inks. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018, 28(9): 1705506. |
| [40] | YANG W J, YANG J, BYUN J J, et al. 3D printing of freestanding MXene architectures for current-collector-free supercapacitors. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(37): 1902725. |
| [41] | WU Z Y, LIU S R, HAO Z J, et al. MXene contact engineering for printed electronics. Advanced Science, 2023, 10(19): 2207174. |
| [42] | LUOMA E, VALIMAKI M, OLLILA J, et al. Bio-based polymeric substrates for printed hybrid electronics. Polymers, 2022, 14(9): 1863. |
| [43] | LINGHU C H, ZHANG S, WANG C J, et al. Transfer printing techniques for flexible and stretchable inorganic electronics. npj Flexible Electronics, 2018, 2: 26. |
| [44] | CAREY T, CACOVICH S, DIVITINI G, et al. Fully inkjet-printed two-dimensional material field-effect heterojunctions for wearable and textile electronics. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 1202. |
| [45] | MA J X, ZHENG S H, CAO Y X, et al. Aqueous MXene/ph1000 hybrid inks for inkjet-printing micro-supercapacitors with unprecedented volumetric capacitance and modular self-powered microelectronics. Advanced Energy Materials, 2021, 11(23): 2100746. |
| [46] | HU G H, KANG J, NG L W T, et al. Functional inks and printing of two-dimensional materials. Chemical Society Reviews, 2018, 47(9): 3265. |
| [47] | SAADI M, MAGUIRE A, POTTACKAL N T, et al. Direct ink writing: a 3D printing technology for diverse materials. Advanced Materials, 2022, 34(28): 2108855. |
| [48] | AZADMANJIRI J, REDDY T N, KHEZRI B, et al. Prospective advances in MXene inks: screen printable sediments for flexible micro-supercapacitor applications. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2022, 10(9): 4533. |
| [49] | ZHANG C F, PARK S N, SERAL-ASCASO A, et al. High capacity silicon anodes enabled by MXene viscous aqueous ink. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 849. |
| [50] | TANG H, LI W L, PAN L M, et al. A robust, freestanding MXene-sulfur conductive paper for long-lifetime Li-S batteries. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(30): 1901907. |
| [51] | TANG H, LI W L, PAN L M, et al. In situ formed protective barrier enabled by sulfur@titanium carbide MXene ink for achieving high-capacity, long lifetime Li-S batteries. Advanced Science, 2018, 5(9): 1800502. |
| [52] | CHEN M J, LI L L, DENG Z M, et al. Two-dimensional janus MXene inks for versatile functional coatings on arbitrary substrates. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2023, 15(3): 4591. |
| [53] | SHAO Y Z, WEI L S, WU X Y, et al. Room-temperature high-precision printing of flexible wireless electronics based on MXene inks. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 3223 |
| [54] | SONG Y, TAY R Y, LI J, et al. 3D-printed epifluidic electronic skin for machine learning-powered multimodal health surveillance. Science Advances, 2023, 9(37): 6492. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |