

钛网表面含hBMP-2的复合涂层制备及hBMP-2的释放研究
收稿日期: 2019-03-25
修回日期: 2019-05-04
网络出版日期: 2019-05-29
基金资助
国家自然科学基金(51572228);四川省教育厅自然科学基金(16ZB0546);雅安职业技术学院自然科学基金(2016yzk15)
hBMP-2 Contained Composite Coatings on Titanium Mesh Surface: Preparation and hBMP-2 Release
Received date: 2019-03-25
Revised date: 2019-05-04
Online published: 2019-05-29
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(51572228);Natural Science Foundation Project of Sichuan Provincial Education Department(16ZB0546);Natural Science Foundation Project of Ya' an Polytechnic College(2016yzk15)
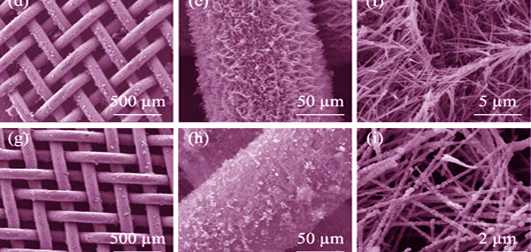
为提高骨接合钛网的骨整合性和生物活性, 本研究采用碱热处理法在钛网表面构建出具有多孔结构的钛酸盐纳米纤维, 利用电化学沉积技术在钛酸盐纳米纤维表面制备磷酸钙涂层, 并采用不同方法将人骨形态发生蛋白(hBMP-2)引入涂层, 制备了三种含hBMP-2分子的复合涂层(TmhB、TmHedhB和TmHhBed)。实验对各复合涂层的表面形貌、化学成分、相组成和hBMP-2的含量与释放性能进行了表征。研究发现: 各涂层都具有多孔纤维结构, TmHedhB和TmHhBed中的磷酸钙相为羟基磷灰石(HA), 呈“串珠”状包裹在钛酸盐纳米纤维表面, “串珠”状HA的引入促进了复合涂层对hBMP-2的吸附。电化学共沉积技术在钛酸盐纳米纤维表面制备的HA/hBMP-2复合涂层中hBMP-2的含量最大, 达886 ng/mg, 在6~48 h内具有明显的hBMP-2缓释性能。
付亚康 , 翁杰 , 刘耀文 , 张科宏 . 钛网表面含hBMP-2的复合涂层制备及hBMP-2的释放研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020 , 35(2) : 173 -178 . DOI: 10.15541/jim20190127
Titanate nanofibers were prepared on titanium mesh by alkali-heat treatment, and calcium phosphate coating was fabricated on the porous titanate nanofibers by electrochemical deposition technology. Then hBMP-2 was introduced into the coating by different methods to improve its osteointegration and bioactivity. Three kinds of composite coatings modified by hBMP-2 were prepared (TmhB, TmHedhB and TmHhBed). Surface morphology, chemical composition, phase composition and hBMP-2 amounts and hBMP-2 release performance of the composite coatings were characterized by SEM, ATR-FTIR, XRD, and hBMP-2 ELISA kit, respectively. Results showed that all of the coatings display porous fiber structure, calcium phosphate phase in TmHedhB and TmHhBed samples was hydroxyapatite (HA), and bead-like HA particles formed on the surface of titanate nanofibers. Protein adsorption experiments showed that introduction of bead-like HA phase increased the hBMP-2 adsorption on the composite coatings, and composite coatings prepared by electrochemical co-deposition technique further enhanced hBMP-2 adsorption up to 886 ng/mg, which were supported hBMP-2 sustained release within 6-48 h.

| [1] | BUSER D, SCHENK R K, STEINEMANN S , et al. Influence of surface characteristics on bone integration of titanium implants. a histomorphometric study in miniature pigs. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research, 1991,25(7):889-902. |
| [2] | DABROWSKI B, SWIESZKOWSKI W, GODLINSKI D , et al. Highly porous titanium scaffolds for orthopaedic applications. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B Applied Biomaterials, 2010,95B(1):53-61. |
| [3] | CARINE V, YANN C, DIDIER L O , et al. Surface modification of titanium with phosphonic acid to improve bone bonding: characterization by XPS and ToF-SIMS. Langmuir, 2002,18(7):2582-2589. |
| [4] | WANG X H, LI J S, HU R , et al. Mechanical properties and bioactive surface modification via alkali-heat treatment of porous titanium for biomedical applications. Advanced Materials Research, 2013,647:511-517. |
| [5] | DAS K, BALLA V K, BANDYOPADHYAY A , et al. Surface modification of laser-processed porous titanium for load-bearing implants. Scripta Materialia, 2008,59(8):822-825. |
| [6] | RAKHMATIA Y D, AYUKAWA Y, FURUHASHI A , et al. Current barrier membranes: titanium mesh and other membranes for guided bone regeneration in dental applications. J. Prosthodont. Res., 2013,57(1):3-14. |
| [7] | MARBACHER S, ANDRES R H, FATHI A R , et al. Primary reconstruction of open depressed skull fractures with titanium mesh. Journal of Craniofacial Surgery, 2008,19(2):490-495. |
| [8] | SCH N R, METZGER M C, ZIZELMANN C , et al. Individually preformed titanium mesh implants for a true-to-original repair of orbital fractures. International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, 2006,35(11):990-995. |
| [9] | NAKASE H, PARK Y S, KIMURA H , et al. Complications and long-term follow-up results in titanium mesh cage reconstruction after cervical corpectomy. Journal of Spinal Disorders & Techniques, 2006,19(19):353-357. |
| [10] | MARTIN M P, OLSON S . Post-operative complications with titanium mesh. Journal of Clinical Neuroscience, 2009,16(8):1080-1081. |
| [11] | CARRAD A . Development of bioactive hydroxyapatite coatings on titanium alloys. Key Engineering Materials, 2012,533:183-193. |
| [12] | LANGELIER B, WANG X, GRANDFIELD K . Atomic scale chemical tomography of human bone. Scientific Reports, 2017,7:39958. |
| [13] | KANE R, MA P X . Mimicking the nanostructure of bone matrix to regenerate bone. Materials Today, 2013,16(11):418-423. |
| [14] | HABIBOVIC P, YUAN H, VAN D D M , et al. Relevance of osteoinductive biomaterials in critical-sized orthotopic defect. Journal of Orthopaedic Research, 2010,24(5):867-876. |
| [15] | LI C, VEPARI C, JIN H J , et al. Electrospun silk-BMP-2 scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials, 2006,27(16):3115-3124. |
| [16] | MURPHY C M, SCHINDELER A, GLEESON J P , et al. A collagen- hydroxyapatite scaffold allows for binding and co-delivery of recombinant bone morphogenetic proteins and bisphosphonates. Acta Biomaterialia, 2014,10(5):2250-2258. |
| [17] | GUO X, PARK H, YOUNG S , et al. Repair of osteochondral defects with biodegradable hydrogel composites encapsulating marrow mesenchymal stem cells in a rabbit model. Acta Biomaterialia, 2010,6(1):39-47. |
| [18] | CHEN P C, XU Z K . Mineral-coated polymer membranes with superhydrophilicity and underwater superoleophobicity for effective oil/water separation. Sci. Rep., 2013,3(6153):2776. |
| [19] | USINSKAS P, STANKEVICIUTE Z, BEGANSKIENE A , et al. Sol-Gel derived porous and hydrophilic calcium hydroxyapatite coating on modified titanium substrate. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2016,307:935-940. |
| [20] | CHA C, LIECHTY W B, KHADEMHOSSEINI A , et al. Designing biomaterials to direct stem cell fate. ACS Nano, 2012,6(11):9353-9358. |
| [21] | LUTOLF M P, GILBERT P M, BLAU H M . Designing materials to direct stem-cell fate. Nature, 2009,462(7272):433-441. |
| [22] | DOM NGUEZ-TRUJILLO C, PE N E, CHICARDI E , et al. Sol-Gel deposition of hydroxyapatite coatings on porous titanium for biomedical applications. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2017,333(15):158-162. |
| [23] | PENG H, USAS A, OLSHANSKI A , et al. VEGF improves, whereas sFlt1 inhibits, BMP2-induced bone formation and bone healing through modulation of angiogenesis. Journal of Bone & Mineral Research, 2010,20(11):2017-2027. |
| [24] | CHEN L, JIANG W, HUANG J , et al. Insulin-like growth factor 2(IGF-2) potentiates BMP-9-induced osteogenic differentiation and bone formation. Journal of Bone & Mineral Research, 2010,47(11):S432-S433. |
| [25] | BOSE S, TARAFDER S . Calcium phosphate ceramic systems in growth factor and drug delivery for bone tissue engineering: a review. Acta Biomaterialia, 2012,8(4):1401-1421. |
| [26] | KHAN S N, BOSTROM M P, LANE J M . Bone growth factors. Orthopedic Clinics of North America, 2000,31(3):375-387. |
| [27] | WANG Z, CHEN L, XU J , et al. Bioadhesive microporous architectures by self-assembling polydopamine microcapsules for biomedical applications. Chemistry of Materials, 2015,27(3):848-856. |
| [28] | ZHANG C D, XIAO D Q, FU Y K , et al. Fabrication of nanostructured hierarchical coatings composed of calcium phosphate/ titanate on titanium substrate. Key Engineering Materials, 2014, 575-576:253-258. |
| [29] | ZHAO H, DONG W, ZHENG Y , et al. The structural and biological properties of hydroxyapatite-modified titanate nanowire scaffolds. Biomaterials, 2011,32(25):5837-5846. |
| [30] | KOUTSOPOULOS S . Synthesis and characterization of hydroxyapatite crystals: a review study on the analytical methods. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A, 2002,62(4):600-612. |
| [31] | PALAZZO B, IAFISCO M, LAFORGIA M , et al. Biomimetic hydroxyapatite-drug nanocrystals as potential bone substitutes with antitumor drug delivery properties. Advanced Functional Materials, 2010,17(13):2180-2188. |
| [32] | CAI L, LIN D, CHAI Y , et al. MBG scaffold containing chitosan microspheres as binary delivery system of IL-8 and BMP-2 for bone regeneration. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2018,6(27):4453-4465. |
| [33] | LU X, WANG Y B, LIU Y R , et al. Preparation of HA/chitosan composite coatings on alkali treated titanium surfaces through Sol-Gel techniques. Materials Letters, 2007,61(18):3970-3973. |
| [34] | PANG D, HE L, WEI L , et al. Preparation of a beta-tricalcium phosphate nanocoating and its protein adsorption behaviour by quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation technique. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 2018,162:1-7. |
| [35] | DONG X, WANG Q, WU T , et al. Understanding adsorption- desorption dynamics of BMP-2 on hydroxyapatite(001) surface. Biophysical journal, 2007,93(3):750-759. |
| [36] | WALLWORK M L, KIRKHAM J, ZHANG J , et al. Binding of matrix proteins to developing enamel crystals: an atomic force microscopy study. Langmuir, 2001,17(8):2508-2513. |
| [37] | ZHU X, FAN H, LI D , et al. Protein adsorption and zeta potentials of a biphasic calcium phosphate ceramic under various conditions. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B App.l Biomater., 2007,82(1):65-73. |
| [38] | ZHOU H, WU T, DONG X , et al. Adsorption mechanism of BMP-7 on hydroxyapatite(001) surfaces. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2007,361(1):91-96. |
| [39] | KANDORI K, FUDO A, ISHIKAWA T . Study on the particle texture dependence of protein adsorption by using synthetic micrometer- sized calcium hydroxyapatite particles. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 2002,24(2):145-153. |
| [40] | BOIX T, GOMEZ-MORALES J, TORRENT-BURGUES J , et al. Adsorption of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein rhBMP-2m onto hydroxyapatite. Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry, 2005,99(5):1043-1050. |
| [41] | FU Y K, ZHOU X, XIAO D Q , et al. Influence of micro-nano structure of haydroxyapatite particles on protein adsorption. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015,30(5):523-528. |
| [42] | FU Y K, LI X Z, XIA X , et al. Effect of zeta potential of hydroxyapatite on protein adsorption. Progress in Modern Biomedicine, 2016,16(19):3610-3613. |
| [43] | IMAMURA T, KAITO T . Homeostasis and disorder of musculoskeletal system.BMP and TGF signaling and locomotive tissues. Clinical Calcium, 2018,28(3):313. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |