

Cu掺杂ZnSe高效量子点的合成及其光学特性研究
收稿日期: 2012-03-22
修回日期: 2012-06-01
网络出版日期: 2013-01-23
基金资助
国家自然科学基金(61106066);浙江省杰出青年基金(R4100242);宁波市自然科学基金(2011A610094) National Natural Science Foundation of China (61106066);Zhejiang Provincial Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars (R4100242);Ningbo Municipal Natural Science Foundation of China (2011A610094)
Synthesis of Effective and Qualified Cu-doped ZnSe Quantum Dots and Their Optical Properties
Received date: 2012-03-22
Revised date: 2012-06-01
Online published: 2013-01-23
郑金桔 , 曹盛 , 高凤梅 , 尉国栋 , 贾龙 , 杨为佑 . Cu掺杂ZnSe高效量子点的合成及其光学特性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2013 , 28(2) : 159 -164 . DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1077.2013.12184
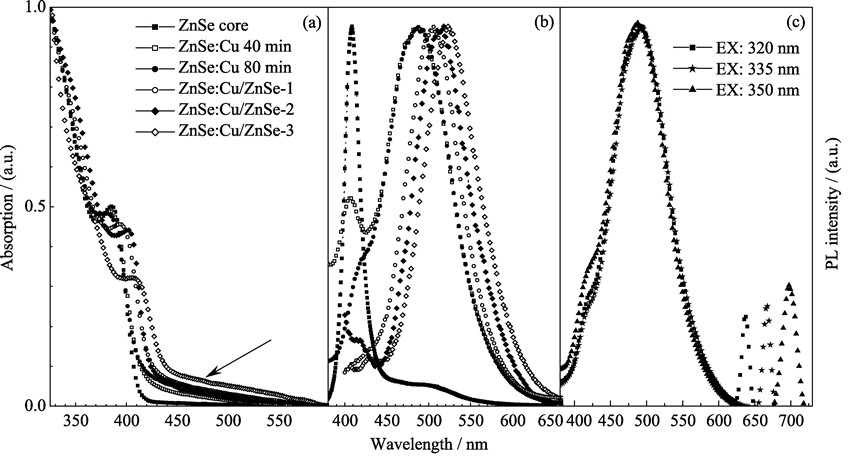
Effective Cu-doped ZnSe quantum dots (ZnSe:Cu d-dots) with high qualities were synthesized by a growth-doping strategy. The effect of the ratios of Zn to Se precursor within the raw materials on the quality of the ZnSe cores and ZnSe:Cu d-dots was studied. The photoluminescence (PL) properties of ZnSe:Cu d-dots in Cu doping process were investigated systematically. The results suggested that the optical performance and stability of the d-dots could be remarkably improved by further coated with a homogeneous ZnSe shell on the fabricated surface-doped ZnSe:Cu d-dots. In addition, the obtained ZnSe:Cu d-dots could be changed to be water-soluble by ligand exchange. It implied that these novel d-dots could be a promising candidate to substitute for the conventional quantum dots containing Cd elements, suggesting their potentially environment-friendly applications in the fields of solid state lighting and diagnostics.
Key words: ZnSe; quantum dots; growth-doping strategy; photoluminescence
| [1] | Acharya S, Pradhan N. Insertion/ejection of dopant ions in composition tunable semiconductor nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2011, 115(40): 19513-19519. |
| [2] | Erwin S C, Zu L, Haftel M I, et al. Doping semiconductor nanocrystals. Nature, 2005, 436(7047): 91-94. |
| [3] | Nag A, Chakraborty S, Sarma D. To dope Mn2+ in a semiconducting nanocrystal. J. Am. Chem. Soc, 2008, 130(32): 10605-10611. |
| [4] | Norris D, Yao N, harnock F, et al. High-quality manganese-doped ZnSe nanocrystals. Nano Lett., 2001, 1(1): 3-7. |
| [5] | Zheng J J, Yuan X Y, Ikezawa M Y, et al. Efficient photoluminescence of Mn2+ ions in MnS/ZnS Core/Shell quantum dots. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, 113(39): 16969-16974. |
| [6] | Zheng J, Ji W, Wang X.et al. Improved photoluminescence of MnS / ZnS core / shell nanocrystals by controlling diffusion of Mn ions into the ZnS shell. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2010, 114(36): 15331-15336. |
| [7] | Xie R G, Peng X G. Synthesis of Cu-doped InP nanocrystals (d-dots) with ZnSe diffusion barrier as efficient and color-tunable NIR emitters. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131(30): 10645-10651. |
| [8] | Pradhan N, Battaglia D M, Liu Y, et al. Efficient, stable, small, and water-soluble doped ZnSe nanocrystal emitters as non-cadmium biomedical labels. Nano Lett., 2007, 7(2): 312-317. |
| [9] | Sarkar S, Bose R, Jana S, et al. Doped semiconductor nanocrystals and organic dyes: an efficient and greener FRET system. J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2010, 1(3): 636-640. |
| [10] | Chen J, Zheng A, Gao Y, et al. Functionalized CdS quantum dots-based luminescence probe for detection of heavy and transition metal ions in aqueous solution. Spectrochim Acta Part A: Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc., 2008, 69(3): 1044-1052. |
| [11] | Pradhan N, Goorskey D, Thessing J, et al. An alternative of CdSe nanocrystal emitters: pure and tunable impurity emissions in ZnSe nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127(50): 17586-17587. |
| [12] | Soo Y L, Ming Z H, Huang S W, et al. Local structures around Mn luminescent centers in Mn-doped nanocrystals of ZnS. Phys. Rev. B, 1994, 50(11): 7602-7607. |
| [13] | Nag A, Sapra S, Nagamani C, et al. A study of Mn2+ doping in CdS nanocrystals. Chem. Mater., 2007, 19(13): 3252-3259. |
| [14] | Pradhan N, Peng X. Efficient and color-tunable Mn-doped ZnSe nanocrystal emitters: control of optical performance via greener synthetic chemistry. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129(11): 3339-3347. |
| [15] | Chang W L, Wei L, Zhen S M, et al. Posterior rotating rod reduction strategy for irreducible atlantoaxial subluxations with congenital odontoid aplasia. Spine, 2010, 35(23): 2064-2070. |
| [16] | Li Dan, Liu Junye, Meng Jiwu, et al. The PL decay of Cu2+ doped ZnS nanoparticle. Chin. J. Lumin. 1998, 19(1): 85-88. |
| [17] | Srivastava B B, Jana S, Pradhan N. Doping Cu in semiconductor nanocrystals: some old and some new physical insights. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133(4): 1007-1015. |
| [18] | Quan Z W, Yang D M, Li C X, et al. Multicolor tuning of manganese- doped ZnS colloidal nanocrystals. Langmuir, 2009, 25(17): 1025-1026. |
| [19] | Cao L X, Zhang J H, Ren S L, et al. Luminescence enhancement of core-shell ZnS:Mn/ZnS nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2002, 80(23): 4300-4302. |
| [20] | Karar N, Chander H, Shivaprasad S M. Enhancement of luminescent properties of ZnS: Mn nanophosphors by controlled ZnO capping. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2004, 85(21): 5058-5060. |
| [21] | Yang H, Holloway P H. Efficient and photostable ZnS-passivated CdS:Mn luminescent nanocrystals. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2004, 14(2): 152-156. |
| [22] | Jana S, Srivastava B B, Acharya S, et al. Prevention of photooxidation in blue-green emitting Cu doped ZnSe nanocrystals. Chem. Comm., 2010, 46(16): 2853-2855. |
| [23] | Lippens P E, Lannoo M. Calculation of the band gap for small CdS and ZnS crystallites. Phys. Rev. B., 1989, 39(15): 10935-10942. |
| [24] | Suyver J, Beek, T, Wuister S.et al. Luminescence of nanocrystalline ZnSe:Cu. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2001, 79(25): 4222-4224. |
| [25] | Bruchez M, Moronne M, Gin, P, et al. Semiconductor nanocrystals as fluorescent biological labels. Science, 1998, 281(5385): 2013-2016. |
| [26] | Zheng J, Gao F, Wei G.et al. Enhanced photoluminescence of water- soluble Mn-doped ZnS quantum dots by thiol ligand exchange. Chem. Phys. Lett., 2012, 5(519/520): 73-77. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |