无机材料学报 ›› 2017, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (10): 1009-1017.DOI: 10.15541/jim20160644 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20160644
• • 下一篇
魏永星1, 靳长清1, 曾一明2
收稿日期:2016-11-25
修回日期:2017-01-09
出版日期:2017-10-20
网络出版日期:2017-09-21
基金资助:WEI Yong-Xing1, JIN Chang-Qing1, ZENG Yi-Ming2
Received:2016-11-25
Revised:2017-01-09
Published:2017-10-20
Online:2017-09-21
Supported by:摘要:
多铁性材料同时具有多种铁性(铁电性、铁磁性或铁弹性)的有序, 可实现电磁信号的相互控制, 成为近年来研究热点。在具有成分无序的复杂体系中, 长程铁性有序有可能被打破, 材料将表现出弛豫特性。我们将至少存在一种铁性弛豫特性的多铁性材料称之为弛豫多铁性材料。这类多铁性材料的极化强度(或磁化强度)在外加电场(或外加磁场)作用下响应更加灵敏, 其磁电耦合机制与长程有序的多铁性材料不同。本文结合国内外最新研究成果, 首先介绍了和弛豫铁性有序相关的物理概念, 重点阐述了多铁性材料在铁电和铁磁双弛豫态下的磁电耦合机制; 然后, 详细介绍了钙钛矿结构(包括PbB1B2O3基和BiFeO3基材料)和非钙钛矿结构(包括层状Bi结构和非正常铁电体)弛豫多铁性材料的研究进展; 最后, 对该领域亟待解决的问题进行了展望。
中图分类号:
魏永星, 靳长清, 曾一明. 弛豫多铁性材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(10): 1009-1017.
WEI Yong-Xing, JIN Chang-Qing, ZENG Yi-Ming. Progress of Relaxor Multiferroic Materials[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(10): 1009-1017.
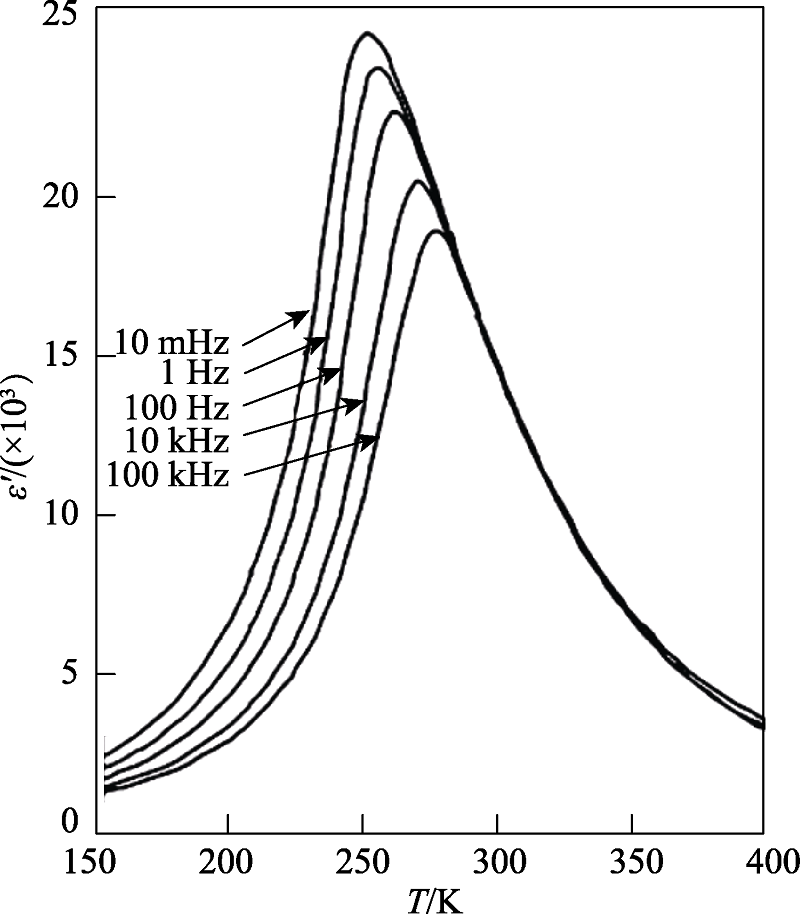
图1 典型弛豫铁电体Pb(Nb2/3Mg1/3)O3不同频率下介电常数与温度关系[13]
Fig. 1 Temperature dependence of dielectric constant for classical relaxor ferroelectrics Pb(Nb2/3Mg1/3)O3 at various frequencies[13]The classical relaxor ferroelectrics display the broad, frequency-dependent dielectric anomalies. The value of the maximum dielectric constant εm could reach above 10,000. The relation between the Tm and frequency could be described by V-F function
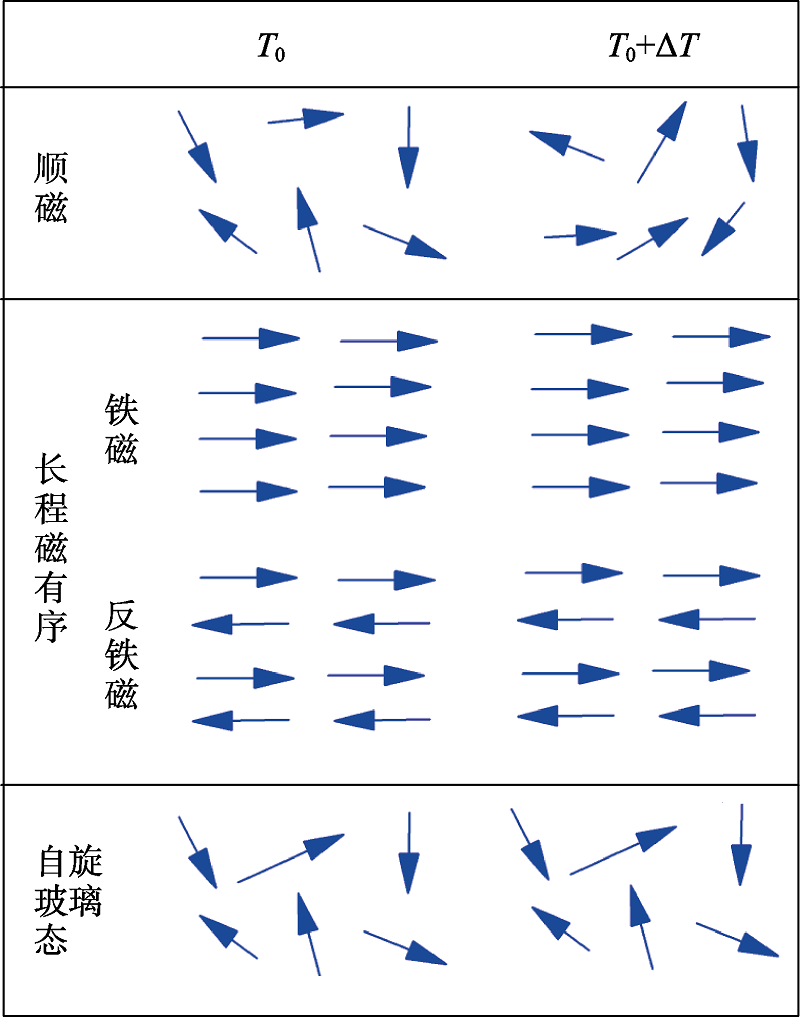
图2 顺磁态、长程磁有序态(铁磁、亚铁磁和反铁磁)及自旋玻璃态示意图
Fig. 2 Schematic representation of paramagnetic state, long- ranged magnetic state (ferromagnetic, ferrimagnetic, antiferromagnetic) and spin glass state
| Compositions | Polar ordering | Magnetic ordering |
|---|---|---|
| PbFe2/3W1/3O3 crystals[ | Ferroelectric relaxor Tm = 210 K @0.1 MHz Tf = 164 K | Anti-ferromagnetic TN = 350 K Magnetic glass state Tg = 10 K |
| PbFe0.5Nb0.5O3 ceramics[ | Ferroelectric Tm =373 K | Anti-ferromagnetic TN = 153 K Magnetic glass state Tg = 10.6 K |
| PbFe0.5Ta0.5O3 ceramics[ | Ferroelectric Tm = 259 K | Anti-ferromagnetic TN = 153 K Magnetic glass state Tg < 10 K |
| 0.8PbFe1/2Nb1/2O3-0.2PbMg1/2W1/2O3 ceramics[ | Ferroelectric relaxor Tm = 280 K @0.1 MHz Tf = 245 K | Magnetic glass state Tg = 25K |
| Pb(Fe0.66W0.33)0.8 Ti0.2O3 thin films[ | Ferroelectric relaxor Tm = 350 K @10 kHz Tf = 238 K | Ferrimagnetic |
| Pb(Fe0.66W0.33)0.2 (Zr0.53Ti0.47)0.8O3 thin film[ | Ferroelectric relaxor Tm < 600 K @1 MHz | Ferrimagnetic |
| Pb(Zr0.53Ti0.47)0.60 (Fe0.5Ta0.5)0.4O3 thin films[ | Ferroelectric relaxor Tm = 390 K @1 MHz Tf = 305 K | Ferrimagnetic |
表1 PbB1B2O3基弛豫多铁材料磁电特性
Table 1 Polar and magnetic orderings of the PbB1B2O3 based multiferroic materials
| Compositions | Polar ordering | Magnetic ordering |
|---|---|---|
| PbFe2/3W1/3O3 crystals[ | Ferroelectric relaxor Tm = 210 K @0.1 MHz Tf = 164 K | Anti-ferromagnetic TN = 350 K Magnetic glass state Tg = 10 K |
| PbFe0.5Nb0.5O3 ceramics[ | Ferroelectric Tm =373 K | Anti-ferromagnetic TN = 153 K Magnetic glass state Tg = 10.6 K |
| PbFe0.5Ta0.5O3 ceramics[ | Ferroelectric Tm = 259 K | Anti-ferromagnetic TN = 153 K Magnetic glass state Tg < 10 K |
| 0.8PbFe1/2Nb1/2O3-0.2PbMg1/2W1/2O3 ceramics[ | Ferroelectric relaxor Tm = 280 K @0.1 MHz Tf = 245 K | Magnetic glass state Tg = 25K |
| Pb(Fe0.66W0.33)0.8 Ti0.2O3 thin films[ | Ferroelectric relaxor Tm = 350 K @10 kHz Tf = 238 K | Ferrimagnetic |
| Pb(Fe0.66W0.33)0.2 (Zr0.53Ti0.47)0.8O3 thin film[ | Ferroelectric relaxor Tm < 600 K @1 MHz | Ferrimagnetic |
| Pb(Zr0.53Ti0.47)0.60 (Fe0.5Ta0.5)0.4O3 thin films[ | Ferroelectric relaxor Tm = 390 K @1 MHz Tf = 305 K | Ferrimagnetic |
| Compositions | Polar ordering | Magnetic ordering |
|---|---|---|
| Bi(Fe0.5Mn0.5)O3 thin films[ | Ferroelectric relaxor Tm = 440 K @1 MHz Tf = 314 K | Magnetic glass state Tf2 =122 K |
| 0.65BiFeO3- 0.35BaTiO3 ceramics[ | Ferroelectric relaxor Tm = 687 K @1 MHz | Ferrimagnetic |
| 0.67BiFeO3- 0.33BaTiO3 single crystal[ | Ferroelectric relaxor Tm = 650 K @0.1 MHz | Magnetic glass state |
| 0.5Bi(Fe0.5La0.5)O3- 0.5PbTiO3 ceramics[ | Ferroelectric relaxor Tm = 520 K @0.1 MHz | Ferrimagnetic |
| 0.6BiFeO3- 0.4Bi1/2K1/2TiO3 ceramics[ | Ferroelectric relaxor Tm = 703 K @0.1 MHz | Ferrimagnetic TN < 500 K |
| 0.4BiFe0.9Co0.1O3- 0.6Bi1/2K1/2TiO3 ceramics[ | Ferroelectric relaxor Tm = 693 K @0.1 MHz Tf < 573 K | Ferrimagnetic TN = 670 K |
表2 BiFeO3基弛豫多铁材料磁电特性
Table 2 Polar and magnetic orderings of the BiFeO3 based multiferroic materials
| Compositions | Polar ordering | Magnetic ordering |
|---|---|---|
| Bi(Fe0.5Mn0.5)O3 thin films[ | Ferroelectric relaxor Tm = 440 K @1 MHz Tf = 314 K | Magnetic glass state Tf2 =122 K |
| 0.65BiFeO3- 0.35BaTiO3 ceramics[ | Ferroelectric relaxor Tm = 687 K @1 MHz | Ferrimagnetic |
| 0.67BiFeO3- 0.33BaTiO3 single crystal[ | Ferroelectric relaxor Tm = 650 K @0.1 MHz | Magnetic glass state |
| 0.5Bi(Fe0.5La0.5)O3- 0.5PbTiO3 ceramics[ | Ferroelectric relaxor Tm = 520 K @0.1 MHz | Ferrimagnetic |
| 0.6BiFeO3- 0.4Bi1/2K1/2TiO3 ceramics[ | Ferroelectric relaxor Tm = 703 K @0.1 MHz | Ferrimagnetic TN < 500 K |
| 0.4BiFe0.9Co0.1O3- 0.6Bi1/2K1/2TiO3 ceramics[ | Ferroelectric relaxor Tm = 693 K @0.1 MHz Tf < 573 K | Ferrimagnetic TN = 670 K |
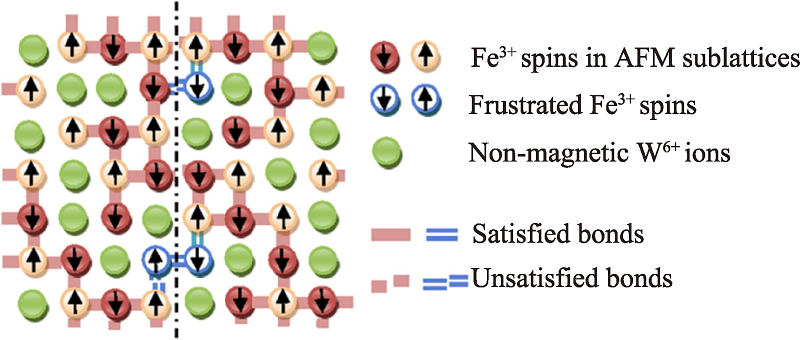
图3 PbFe2/3W1/3O3中Fe3+自旋排列示意图, 在反铁磁子晶格中存在挫败的Fe3+的自旋[31]
Fig. 3 Schematic representation of Fe3+ spins arrangement for PbFe2/3W1/3O3, The frustrated Fe3+ spins appear in AFM sublattices[31]
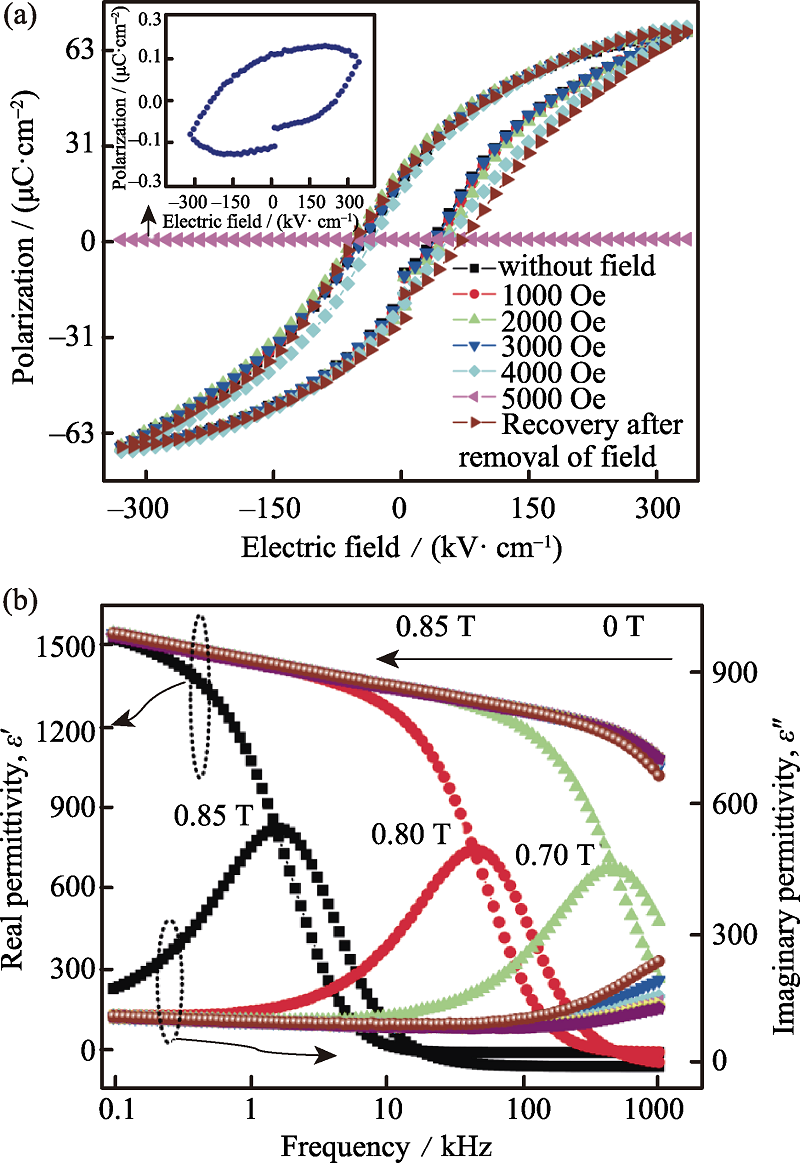
图4 Pb(Fe0.66 W0.33)0.2(Zr0.53Ti0.47)0.8O3在磁场作用下的(a)极化强度-电场曲线及(b)介电常数实部虚部与频率的关系[35]
Fig. 4 (a) The P-E loops and (b) the real and imaginary part of dielectric constant as a function of frequencies with various magnetic fields for Pb(Fe0.66 W0.33)0.2(Zr0.53Ti0.47)0.8O3[35]Increase of the magnetic field H leads to decrease in Pr. Pr is nearly zero when H reaches 0.5 T. This effect disappears after magnetic field being removed. Correspondingly, the anomaly peak of the imaginary part for dielectric constant shifts to the low frequency side with H increasing, which reveals the increase of the relaxation time
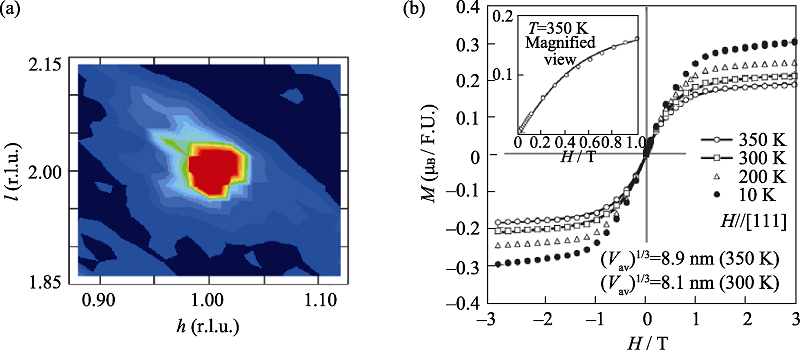
图6 0.67BiFeO3-0.33BaTiO3单晶(a)(112)衍射面在600 K时的漫反射强度等高线和(b)在不同温度下的M-H曲线[50]
Fig. 6 (a) Contour plots of the diffuse intensities at 600 K around the (112) reflection and (b) M-H loops at various temperatures for the single crystal of 0.67BiFeO3-0.33BaTiO3[50] The crystal shows the strong nuclear diffuse scattering, with a correlation length of 8 nm. It demonstrates the existence of the PNR. The M-H loops display the character of super-paramagnetism. The super-paramagnetism could be related to the short magnetic state. The fitting of Langevin function reveals the size of the short magnetic state is in the range of 8-9 nm
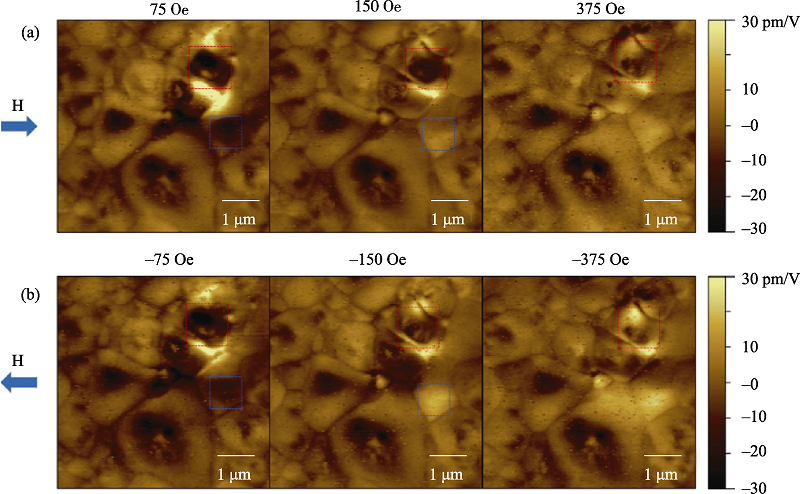
图7 磁场作用下的同步压力电显微镜实验[60]
Fig. 7 In situ PFM under magnetic field experiments[60]The polarization switches obviously in the regions marked by blue and red rectangles

图8 Bi5Ti3FeO15 (a)晶体结构(b)STEM图谱和(c)原子占位信息示意图[68-69]
Fig. 8 (a) Crystal structure, (b) STEM pattern and (c) schematic illustration of atom position information of Bi5Ti3FeO15[68-69]The crystal structure is obtained from ref [68]. Between the two [Bi2O2]2- layers, there are four Ti(Fe)O6 octahedra. The STEM measurement demonstrates Ti/Fe atoms shift from ideal position along [110]
| [1] | EERENSTEIN W, MATHUR N D, SCOTT J F.Multiferroic and magnetoelectric materials.Nature, 2006, 442(44): 759-765. |
| [2] | SCOTT J F.Data storage. Multiferroic memories.Nature, 2007, 6(4): 256-257. |
| [3] | SPALDIN N A, FIEBIG M.The renaissance of magnetoelectric multiferroics.Science, 2005, 309(5733): 391-392. |
| [4] | NAN C W.Research progress and future directions of multiferroic materials.Scientia Sinica Technologica, 2015, 45(4): 339-357. |
| [5] | WANG J, NEATON J B, ZHENG H, et al.Epitaxial BiFeO3 multiferroic thin film heterostructures.Science, 2003, 299(5673): 1719-1722. |
| [6] | KLMURA T, GOTO T, SHINTAL H, et al.Magnetic control of ferroelectric polarization.Nature, 2003, 426(6962): 55-58. |
| [7] | LIU J M, NAN C W.Decade of multiferroic researches.Physics, 2014, 43(02): 88-98. |
| [8] | WANG K F, LIU J M, WANG Y.Single phase multiferroic materials- coupling and adjusting between polar and magnetic order parameters.Chin. Sci. Bull, 2008, 53(10): 1098-1135. |
| [9] | CHI Z H, JIN C Q.Recent advances in single-phase magnetoelectric multiferroics.Prog. Phys., 2007, 27(2): 225-238. |
| [10] | DUAN C G.Progress in the study of magnetoelectric effect.Prog. Phys., 2009, 29(3): 215-238. |
| [11] | DONG S, LIU J M.Multiferroic materials: past, present and future.Physics, 2010, 39(10): 714-715. |
| [12] | PIRC R, BLINC R, SCOTT J F.Mesoscopic model of a system possessing both relaxor ferroelectric and relaxor ferromagnetic properties.Phys. Rev. B, 2009, 79(21): 214114. |
| [13] | BOKOV A A, YE Z G.Recent progress in relaxor ferroelectrics with perovskite structure.J. Mater. Sci., 2006, 41(1): 31-52. |
| [14] | YAO X, CHEN Z L, CROSS L E.Polarization and depolarization behavior of hot pressed lead lanthanum zirconate titanate ceramics,J. Appl. Phys., 1983, 54(6): 3399-3403. |
| [15] | CROSS L E.Relaxor ferroelectrics.Ferroelectrics, 1987, 76(1): 241-267. |
| [16] | SETTER N, CROSS L E.The contribution of structural disorder to diffuse phase transitions in ferroelectrics.J. Mater. Sci., 1980, 15(10): 2478-2482. |
| [17] | TAGANTSEV A K.Vogel-Fulcher relationship for the dielectric permittivity of relaxor ferroelectrics.Phys. Rev. Lett., 1994, 72(7): 1110-1113. |
| [18] | KIMURA T, TOMIOKA Y, KUMAI R, et al.Diffuse phase separation and phase transition in Cr-doped Nd1/2Ca1/2MnO3: A relaxor ferromagnet.Phys. Rev. Lett., 1999, 83(19): 3940-3943. |
| [19] | OKIMOTO Y, OGIMOTO Y, Matsubara M, et al.Direct observation of photoinduced magnetization in a relaxor ferromagnet.Appl. Phys. Lett., 2002, 80(6): 1031-1033. |
| [20] | KAMZIN A S, BOKOV V A.Mössbauer studies of PbFe2/3W1/3O3 multiferroics.Phys. Solid State, 2013, 55(6): 1191-1197. |
| [21] | MITOSERIU L, CARNASCIALI M M, PIAGGIO P, et al.Evidence of the relaxor-paraelectric phase transition in Pb(Fe2/3 W1/3)O3 ceramics.Appl. Phys. Lett., 2002, 81(26): 5006-5008. |
| [22] | YE Z, TODA K, SATO M, et al.Synthesis, structure and properties of the magnetic relaxor ferroelectric Pb(Fe2/3W1/3)O3 [PFW].J. Korean Phys. Soc., 1998, 32(3): S1028-S1031 . |
| [23] | PAVLENKO A V, TURIKA A V, Reznichenko L A, et al.Dielectric relaxation in the PbFe1/2Nb1/2O3 ceramics.Phys. Solid State, 2011, 53(9): 1872-1875. |
| [24] | CARPENTER M A, SCHIEMER J A, LASCU I, et al.Elastic and magnetoelastic relaxation behaviour of multiferroic (ferromagnetic + ferroelectric + ferroelastic) Pb(Fe0.5Nb0.5)O3 perovskite.J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, 2015, 27(28): 285901. |
| [25] | BOCHENEK D, GUZDEK P.Ferroelectric and magnetic properties of ferroelectromagnetic PbFe1/2Nb1/2O3 type ceramics.J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2011, 323(3): 369-374. |
| [26] | LAMPIS N, SCIAU P, LEHMANN A G.Rietveld refinements of the paraelectric and ferroelectric structures of PbFe0.5Ta0.5O3.J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, 2000, 12(17): 2367-2378. |
| [27] | DULKIN E, GRUSZKA I, KANIA A, et al.Electric field dependences of Curie and Néel phase transition temperatures in magnetoelectric relaxor multiferroic Pb(Fe0.5Ta0.5)O3 crystals seen via acoustic emission.Phys. Status Solidi B, 2016, 253(4): 738-743. |
| [28] | FALQUI A, LAMPIS N, GEDDOLEHMANN A, et al.Low- temperature magnetic behavior of perovskite compounds PbFe1/2Ta1/2O3 and PbFe1/2Nb1/2O3.J. Phys. Chem. B, 2005, 109(48): 22967-22970. |
| [29] | KLEEMANN W, SHVARTSMAN V V, BORISOV P, et al.Coexistence of antiferromagnetic and spin cluster glass order in the magnetoelectric relaxor multiferroic PbFe0.5Nb0.5O3.Phys. Rev. Lett., 2010, 105(25): 257202. |
| [30] | CHILLAL S, GVASALIYA S N, ZHELUDEV A, et al.Magnetic short-and long-range order in PbFe0.5Ta0.5O3.Phys. Rev. B, 2014, 89(17): 174418. |
| [31] | CHEN L, BOKOV A A, ZHU W M, et al.Magnetoelectric relaxor and reentrant behaviours in multiferroic Pb(Fe2/3W1/3)O3 crystal.Sci. Rep., 2016, 6: 22327. |
| [32] | LEVSTIK A, BOBNAR V, FILIPIČ C, et al.Magnetoelectric relaxor.Appl. Phys. Lett., 2007, 91(1): 012905. |
| [33] | KUMAR A, RIVERA I, KATIYAR R S, et al.Multiferroic Pb(Fe0.66W0.33)0.80Ti0.20O3 thin films: a room-temperature relaxor ferroelectric and weak ferromagnetic.Appl. Phys. Lett., 2008, 92(13): 132913. |
| [34] | CHENG Z X, WANG X L, ALVAREV G, et al. Magnetic glassy behavior in ferroelectric relaxor type solid solutions: magnetoelectric relaxor. J. Appl. Phys., 2009, 105(7): 07D902. |
| [35] | KUMAR A, SHARMA G L, KATIYAR R S, et al.Magnetic control of large room-temperature polarization.J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, 2009, 21(38): 382204. |
| [36] | KUMAR A, KATIYAR R S, SCOTT J F, et al.Fabrication and characterization of the multiferroic birelaxor lead-iron-tungstate/ lead-zirconate-titanate.J. Appl. Phys., 2010, 108(6): 064105. |
| [37] | SANCHEZ D A, KUMAR A, ORTEGA N, et al.Near-room temperature relaxor multiferroic. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2010, 97(20): 202910. |
| [38] | KEMPA M, KAMBA S, SAVINOV M, et al.Bulk dielectric and magnetic properties of PFW? PZT ceramics: absence of magnetically switched-off polarization.J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, 2010, 22(44): 445902. |
| [39] | CATALAN G, SCOTT J F.Physics and application of bismuth ferrite.Adv. Mater., 2009, 21: 2463-2485. |
| [40] | PALEWICZ A, PRZENIOSLO R, SOSNOWSKA I, et al.Atomic displacements in BiFeO3 as a function of temperature: neutron diffraction study. Acta Crystallogr. B, 2007, 63(4): 537-544. |
| [41] | NEATON J, EDERER C, WAGHMARE U, et al.First-principles study of spontaneous polarization in multiferroic BiFeO3.Phys. Rev. B, 2005, 71(1): 014113. |
| [42] | LEBEUGLE D, COLSON D, FORGET A, et al.Room-temperature coexistence of large electric polarization and magnetic order in BiFeO3 single crystals.Phys. Rev. B, 2007, 76(2): 024116. |
| [43] | ZHANG ST, LU M H, WU D, et al.Larger polarization and weak ferromagnetism in quenched BiFeO3 ceramics with a distorted rhombohedral crystal structure.Appl. Phys. Lett, 2005, 87(26): 262907. |
| [44] | ARNOLD D C, KNIGHT K S, CATALAN G, et al.The β-to-γ transition in BiFeO3: a powder neutron diffraction study.Adv. Fun. Mater., 2010, 20(13): 2116-2123. |
| [45] | MIAO J, ZHANG X, ZHAN Q, et al.Bi-relaxation behaviors in epitaxial multiferroic double-perovskite BiFe0.5Mn0.5O3/CaRuO3 heterostructures.Appl. Phys. Lett., 2011, 99(6): 062905. |
| [46] | WEI Y X, WANG X T, ZHU J T, et al.Dielectric, ferroelectric and piezoelectric properties of BiFeO3-BaTiO3 ceramics.J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2013, 96(10): 3163-3168. |
| [47] | WEI Y X, WANG X T, JIA J J, et al.Multiferroic and piezoelectric properties of 0.65BiFeO3-0.35BaTiO3 ceramic with pseudo-cubic symmetry.Ceram. Int., 2013, 38(4): 3499-3502. |
| [48] | VERMA K C, KOTNALA R K.Multiferroic magnetoelectric coupling and relaxor ferroelectric behavior in 0.7BiFeO3- 0.3BaTiO3 nanocrystals.Solid State Commun., 2011, 151(13): 920-923. |
| [49] | OZAKI T, KITAGAWA S, NISHIHARA S, et al.Ferroelectric properties and nano-scaled domain structures in (1-x)BiFeO3- xBaTiO3 (0.33 < x < 0.50).Ferroelectrics, 2009, 385: 155-161. |
| [50] | SODA M, MATSUURA M, WAKABAYASHI W, et al.Superparamagnetism induced by polar nanoregions in relaxor ferroelectric (1-x)BiFeO3-xBaTiO3. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn., 2011, 80(4): 043705. |
| [51] | BHATTACHAEJEE S, TRIPATHI S, PANDEY D.Morphotropic phase boundary in (1-x)BiFeO3-xPbTiO3: phase coexistence region and unusually large tetragonality.Appl. Phys. Lett., 2007, 91(4): 042903. |
| [52] | ZHU W M, GUO H Y, YE Z G.Structural and magnetic characterization of multiferroic (BiFeO3)(1-x)(PbTiO3)x solid solutions.Phys. Rev. B, 2008, 78(1): 014401. |
| [53] | AMORÍN H, CORREAS C, RAMOS P, et al. Very high remnant polarization and phase-change electromechanical response of BiFeO3-PbTiO3 at the multiferroic morphotropic phase boundary.Appl. Phys. Lett., 2012, 101(17): 172908. |
| [54] | SINGH A, GUPTA A, CHATTERJEE R.Enhanced magnetoelectric coefficient(α) in the modified BiFeO3-PbTiO3 system with large La substitution. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2008, 93(2): 022902. |
| [55] | MATSUO H, NOGUCHI Y, MIYAYAMA M, et al.Structural and piezoelectric properties of high-density (Bi0.5K0.5)TiO3-BiFeO3 ceramics.J. Appl. Phys., 2010, 108(10): 104103. |
| [56] | BENNETT J, BELL A J, STEVENSON T, et al.Multiferroic properties of BiFeO3-(K0.5Bi0.5)TiO3 ceramics.Mater. Lett., 2013, 94(3): 172-175. |
| [57] | MOROZOV M I, EINARSRUD M, GRANDE T.Polarization and strain response in Bi0.5K0.5TiO3-BiFeO3 ceramics.Appl. Phys. Lett., 2012, 101(25): 252904. |
| [58] | DORCET V, MARCHET P, TROLLIARD G, et al.Structural and dielectric studies of the Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3-BiFeO3 system.J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2007, 27(13/14/15): 4371-4374. |
| [59] | RAMANA E V, SURYANARAYANA S V, SANKARAM T B, et al.Synthesis and magnetoelectric studies on Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3-BiFeO3 solid solution ceramics.Solid State Sci., 2010, 12(5): 956-962. |
| [60] | HENRICHS L F, CESPEDES O, BENNETT J, et al.Multiferroic clusters: a new perspective for relaxor-type room-temperature multiferroics.Adv. Fun. Mater., 2016, 26(13): 2111-2121. |
| [61] | SHVARTSMAN V V, BEDANTA S, BORISOV P, et al.SrMnTiO3: a magnetoelectric multiglass.Phys. Rev. Lett., 2008, 101(16): 165704. |
| [62] | MULLER K A, BURKARD H.SrTiO3: an intrinsic quantum paraelectric below 4 K.Phys. Rev. B, 1979, 19(7): 3593-3602. |
| [63] | BEDNORZ J G, MULLER K A.Sr1-xCaxTiO3: an XY quantum ferroelectric with transitions to randomness. Phys. Rev. Lett., 1984, 52(25): 2289-2292. |
| [64] | TKACH A, VILARINHO P M, KHOLKIN A L.Polar behavior in Mn- doped SrTiO3 ceramics.Appl. Phys. Lett., 2005, 86(17): 172902. |
| [65] | TKACH A, VILARINHO P M, KHOLKIN A L, et al.Structure- microstructure-dielectric tunability relationship in Mn-doped strontium titanate ceramics.Acta Mater., 2005, 53(19): 5061-5069. |
| [66] | LI J B, HUANG Y P, RAO G H, et al.Ferroelectric transition of Aurivillius compounds Bi5Ti3FeO15 and Bi6Ti3Fe2O18.Appl. Phys. Lett., 2010, 96(22): 222903. |
| [67] | BAI W, YIN W B, YANG J, et al.Cryogenic temperature relaxor-like dielectric responses and magnetodielectric coupling in Aurivillius Bi5Ti3FeO15 multiferroic thin films.J. Appl. Phys., 2014, 116(8): 084103. |
| [68] | HERVOCHES C H, SNEDDEN A, RIGGS R, et al.Structural behavior of the four-layer Aurivillius-phase ferroelectrics SrBi4Ti4O15 and Bi5T i3FeO15. J. Solid State Chem., 2002, 164(2): 280-291. |
| [69] | ZHAO H Y, KIMURA H, CHENG Z X, et al.Large magnetoelectric coupling in magnetically short-range ordered Bi5Ti3FeO15 film.Sci. Rep., 2014, 4: 5255. |
| [70] | HEMBERGER J, LUNKENHEIMER P, FICHTL R, et al.Relaxor ferroelectricity and colossal magnetocapacitive coupling in ferromagnetic CdCr2S4.Nature, 2005, 434(7031): 364-367. |
| [71] | CATALAN G, SCOTT J F.Magnetoelectrics: is CdCr2S4 a multiferroic relaxor?Nature, 2007, 448(7156): E4-E5. |
| [72] | WALZ F.The Verwey transition—a topical review.J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, 2002, 14(12): R285-R340. |
| [73] | KATO K, IIDA S, YANAI K, et al. Ferrimagnetic ferroelectricity of Fe3O4. J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 1983, 31-34(6): 783-784. |
| [74] | ZIESE M, ESQUINAZI P D, PANTEL D, et al.Magnetite (Fe3O4): a new variant of relaxor multiferroic? J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, 2012, 24(8): 086007. |
| [75] | FIER I, WALMSLEY L, SOUZA J A.Relaxor behavior in multiferroic BiMn2O5 ceramics.J. Appl. Phys., 2011, 110(8): 084101. |
| [1] | 范桂芬, 徐 星, 王 凯, 吕文中, 梁 飞, 金善龙. 低温烧结CoFe2O4-(PZN-PZT)多铁复合材料磁电性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(6): 561-566. |
| [2] | 王 赛,侯育冬,郑木鹏,段成辉,朱满康,严 辉. FeTiNbO6金红石型陶瓷的结构和介电弛豫行为研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(1): 57-61. |
| [3] | 袁昌来, 轩敏杰, 许积文, 刘心宇, 周昌荣, 杨 云. Ba0.85Ca0.15Zr0.1Ti0.9O3/CoFe2O4叠层复合陶瓷的制备与磁电耦合效应研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2013, 28(3): 317-320. |
| [4] | 程花蕾, 杜红亮, 周万城, 罗 发, 朱冬梅. 铁酸镧掺杂对铌酸钾钠基陶瓷介电和铁电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2012, 27(11): 1228-1232. |
| [5] | 宋 伟, 王 暄, 张 冬, 孙 志, 韩 柏, 何丽娟, 雷清泉. 多铁材料BiFeO3的制备与表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2012, 27(10): 1053-1057. |
| [6] | 轩敏杰, 刘心宇, 袁昌来, 许积文, 马家峰. 铌酸钾钠/铁酸钴铜多铁性磁电复合材料的制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2012, 27(10): 1042-1046. |
| [7] | 姚春发, 李财富, 刘志权, 尚建库. (1-x)Pb(Fe2/3W1/3)O3-xPb(Mg1/2W1/2)O3多铁性材料的有序结构及磁性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2011, 26(6): 649-654. |
| [8] | 初宝进,李国荣,江向平,陈大任. Na1/2Bi1/2TiO3-BaTiO3系陶瓷压电性及弛豫相变研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2000, 15(5): 815-821. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||