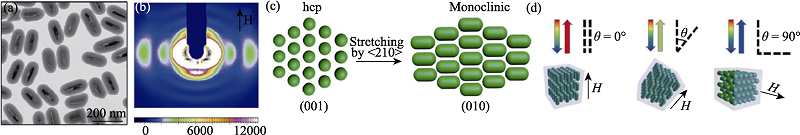
图9. 通过SAXS技术揭示的Fe3O4@SiO2纳米棒在磁场调控下的结构演化过程[
Fig. 9. Structural evolution of Fe3O4@SiO2 nanorods under magnetic field studied by SAXS[
(a) TEM image of the Fe3O4@SiO2 nanorods; (b) Small-angle X-ray diffraction pattern of an aqueous suspension of Fe3O4@SiO2 nanorods (volume fraction ϕ=21%) in the presence of a 200-Gauss external magnetic field, the color bar on the bottom shows the relative diffraction intensity; (c) Schematic illustration of the stretching of the hcp lattice along the <210> direction. The (001) facet of the original hcp lattice was transformed into the (010) facet of the new monoclinic structure. The main axis of nanorods is aligned along the <201> direction of the monoclinic lattice, which is parallel to external magnetic fields; (d) Schematic illustration of magnetically tuning the Bragg diffractions from crystalline colloidal array by changing the angle (θ) between the magnetic field and the incident light